Abstract
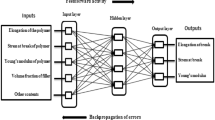
This study is aimed to develop an artificial neural network (ANN)-based method for predicting the elastic modulus of Continuous SiC fiber-reinforced SiC ceramic matrix (SiC/SiC) mini-composites. The mesomechanical model with pores is established based on the microstructure of ceramic matrix mini-composites. The main factors affecting the tensile elastic modulus of mini-composites were obtained using a fidelity mesomechanical model combined with finite element analysis (FEA). Secondly, based on the main factors and the finite element simulation data, the backpropagation (BP) neural network is established to map the complex relationship between the elastic modulus and the structural parameters of the mini composite material. Finally, FEA is used to verify the rationality of the neural network. The results show that the ANN algorithm is robust in the prediction of tensile modulus of mini composite materials, and the prediction error of the neural network model using only one hidden layer and 2300 groups of data samples is less than 0.7% in the input of fiber elastic modulus, fiber volume ratio, and porosity. Therefore, the ANN model proposed in this study helps to evaluate the performance of SiC/SiC mini-composites during the design phase, shortening the design and manufacturing time.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvin, M.A., Anderson, I., Heidloff, A., White, E., Bhatt, R., Grady, J., McMordie, B., Warnes, B.: Development of advanced material systems for future gas turbine applications. In: ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition (2015). https://doi.org/10.1115/gt2015-43456
DiCarlo, J.A., Mark, V.R.: Ceramic composite development for gas turbine engine hot section components. In: ASME Turbo Expo 2006: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1115/gt2006-90151
Bansal, N.P., Lamon, J.: Ceramic matrix composites: materials. Model. Technol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118832998
Wen, H., Xu, N., Yuanming, X.: An experimental study on the in situ strength of SiC fibre in unidirectional SiC/Al composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 34(12), 1161–1166 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2003.08.005
Yuanxin, Z., Yuanming, X.: In situ strength distribution of carbon fibers in unidirectional metal-matrix composites-wires. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61(14), 2017–2023 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(01)00100-2
Henning, R., Piet, W.M.P.: Tensile strength distribution of all-oxide ceramic matrix mini-composites with porous alumina matrix phase. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36(13), 3185–3191 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.05.012
Choi, J., Tamma, K.K.: Woven fabric composites—part I: Predictions of homogenized elastic properties and micromechanical damage analysis. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 50(10), 2285–2298 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.112
Choi, A.H., Heness, G., Ben-Nissan, B.: Using finite element analysis (FEA) to understand the mechanical properties of ceramic matrix composites, In: Advances in Ceramic Matrix Composites. Elsevier. 286–311(2014). https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857098825.2.286
Jiang, H., Ren, Y., Liu, Z., Zhang, S.: Microscale finite element analysis for predicting effects of air voids on mechanical properties of single fiber bundle in composites. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 1363–1381 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2928-6
Rayhan, S.B., Rahman, M.M.: Modeling elastic properties of unidirectional composite materials using Ansys Material Designer. Procedia Struct. Integr. 28, 1892–1900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostr.2020.11.012
Bishop, C.M., Nasrabadi, N.M.: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, vol. 4. Springer, New York (2006)
Raudys, S.J., Jain, A.K.: Small size effects in statistical pattern recognition: recommendations for practicioners. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (1991). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.75512
Jin, L., Li, S., Yu, J., He, J.: Robot manipulator control using neural networks: a survey. Neurocomputing 285, 23–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.01.002
Yang, H.-J., Tan, M.: Sliding mode control for flexible-link manipulators based on adaptive neural networks. Int. J. Autom. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-018-1122-2
Witten, I.H.: Chapter 6 – Implementations: Real Machine Learning Schemes. (2011). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374856-0.00006-7
Mair, C., Kadoda, G., Lefley, M., Phalp, K., Schofield, C., Shepperd, M., Webster, S.: An investigation of machine learning based prediction systems. J. Syst. Softw. 53(1), 23–29 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0164-1212(00)00005-4
Chen, F., Hao, L., Xu, Z., Hou, S., Yang, D.: User-friendly optimization approach of fed-batch fermentation conditions for the production of iturin A using artificial neural networks and support vector machine. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 18(4), 273–280 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2015.05.001
Sommer, C., Gerlich, D.W.: Machine learning in cell biology—teaching computers to recognize phenotypes. J. Cell Sci. 126(24), 5529–5539 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.123604
Tarca, A.L., Carey, V.J., Chen, X., Romero, R., Drăghici, S.: Machine learning and its applications to biology. PLoS Comput. Biol. 3(6), e116 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030116
Pidaparti, R.M.V., Palakal, M.J.: Material model for composites using neural networks. AIAA J. 31(8), 1533–1535 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.11810
Charles, Y., Youngsoo, K., Seunghwa, R., Grace, X.G.: Prediction of composite microstructure stress-strain curves using convolutional neural networks. Mater. Des. 189, 108509 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108509
Rao, H.S., Mukherjee, A.: Artificial neural networks for predicting the macromechanical behaviour of ceramic-matrix composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 5(4), 307–322 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-0256(95)00002-X
Bezerra, E.M., Ancelotti, A.C., Pardini, L.C., Rocco, J.A.F.F., Iha, K., Ribeiro, C.H.C.: Artificial neural networks applied to epoxy composites reinforced with carbon and E-glass fibers: analysis of the shear mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 464(1–2), 177–185 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.01.131
Khan, S.M., Malik, S.A., Gull, N., Saleemi, S., Islam, A., Butt, M.T.Z.: Fabrication and modelling of the macro-mechanical properties of cross-ply laminated fibre-reinforced polymer composites using artificial neural network. Adv. Compos. Mater 28(4), 409–423 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/09243046.2019.1573448
António, C.A.C., Hoffbauer, L.N.: Uncertainty assessment approach for composite structures based on global sensitivity indices. Compos. Struct. 99, 202–212 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.12.001
Robin, M.G., Louise, G., Stephen, H., Ian, E., Adam, L.C., Thomas, J.M., David, E.J.A.: Micromechanical properties of vapour-exposed SiCf/BN/SiC ceramic-matrix composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42(7), 3148–3155 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2022.02.022
Zhang, S., Gao, X.G., Song, Y.D.: In situ strength model for continuous fibers and multi-scale modeling the fracture of C/SiC composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 26(1), 357–370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-018-9696-y
Zhang, Y., Ping, X., Wang, C., Xiao, Z., Yang, J., Chen, M.: A new computational approach for three-dimensional singular stress analysis of interface voids. Acta Mech. 232(2), 639–660 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02842-0
Fang, G., Xiguang, G., Song, Y.: XFEM analysis of crack propagation in fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites with different interphase thicknesses. Compos. Interfaces 27, 1–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/09276440.2019.1637195
Yang, C., James, M.: Effect of irradiation swelling on the mechanical properties of unidirectional SiC/SiC composites: a numerical investigation at microstructural level. J. Nucl. Mater. 569, 153918 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2022.153918
Fang, G., Gao, X., Song, Y.: XFEM analysis of the effect of fiber volume fraction on crack propagation in fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composites. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing (2019) https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/678/1/012027
Zhou, L.-C., Chen, M., Liu, C., Wu, H.-A.: A multi-scale stochastic fracture model for characterizing the tensile behavior of 2D woven composites. Compos. Struct. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPSTRUCT.2018.07.128
Ha, S.K., Huang, Y., Han, H.H., Jin, K.K.: Micromechanics of failure for ultimate strength predictions of composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 44(20), 2347–2361 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998310372464
Omairey, S.L., Dunning, P.D., Sriramula, S.: Development of an ABAQUS plugin tool for periodic RVE homogenisation. Eng. Comput. 35, 567–577 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-0256(95)00002-X
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project, (Y2019-I-0018-0017), State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control for Aerospace (Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics) (Grant No. MCMS-E-0521G01).
Funding
This work was funded by the National Science and Technology Major Project (Y2019-I-0018–0017), State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control for Aerospace (Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics) (Grant No. MCMS-E-0521G01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Mu, F. & Chuwei, Z. Prediction of tensile elastic modulus of SiC/SiC mini-composites with the artificial neural network. Acta Mech 234, 4733–4748 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03640-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03640-0