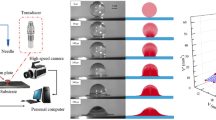
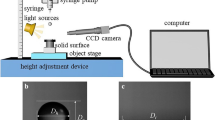
Abstract
The process of a submillimeter sphere eccentric impacting a single droplet under electric field is experimentally investigated by using high-speed micrographic techniques in this paper. The spheres are released at a fixed height to impact different positions of droplets. With the increase in electric field intensity, the impact behavior evolves from oscillation mode to submergence mode. The trajectory of the sphere deviates from the impact direction affected by the eccentric impact. Each mode can be divided into three stages: slamming, cavity developing, and reverting. In the slamming stage, the sphere is decelerated by hydrodynamic forces where the kinetic energy loss increases with the increase in Weber number We. Surface tension becomes the dominant force in the cavity developing stage due to the expanding cavity. The impact angle \(\alpha \) and We show little influence on the expanding speed; thereinto We has a significant effect on the limit diameter of the cavity. The cavity with different \(\alpha \) and We reaches a peak value near the critical state of the impact angle of 90 degrees. A scaling law is constructed to obtain the transitional boundary between the impact modes based on dimensional analysis and data rearrangement. The electric force is mainly used to accelerate the sphere in the gas phase and has little influence on the solid–liquid interaction behavior after contacting the droplet.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, C., Liu, C., Chen, R., Meng, X., Wang, W., Ji, J., Kang, L., Liang, J., Li, X., Liu, Y., et al.: Fine particulate matter air pollution and under-5 children mortality in china: a national time-stratified case-crossover study. Environ. Int. 159, 107022 (2022)
Tessum, M.W., Raynor, P.C.: Effects of spray surfactant and particle charge on respirable coal dust capture. Saf. Health Work 8(3), 296–305 (2017)
Teng, C., Li, J.: Performance of reduction on particle emission by combining the charged water drop atomization and electric field in wet electrostatic precipitator. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 155, 543–554 (2021)
Di Natale, F., Carotenuto, C., Parisi, A., Flagiello, D., Lancia, A.: Wet electrostatic scrubbing for flue gas treatment. Fuel 325, 124888 (2022)
Wang, A., Song, Q., Ji, B., Yao, Q.: Thermophoretic motion behavior of submicron particles in boundary-layer-separation flow around a droplet. Phys. Rev. E 92(6), 063031 (2015)
Ji, B., Song, Q., Yao, Q.: Numerical study of hydrophobic micron particle’s impaction on liquid surface. Phys. Fluids 29(7), 077102 (2017)
Lee, D.-G., Kim, H.-Y.: Impact of a superhydrophobic sphere onto water. Langmuir 24(1), 142–145 (2008)
Lee, D.-G., Kim, H.-Y.: Sinking of small sphere at low Reynolds number through interface. Phys. Fluids 23(7), 072104 (2011)
Truscott, T.T., Epps, B.P., Belden, J.: Water entry of projectiles. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 46, 355–378 (2014)
Jiang, Y., Bai, T., Gao, Y., Guan, L.: Water entry of a constraint posture body under different entry angles and ventilation rates. Ocean Eng. 153, 53–59 (2018)
Louf, J.-F., Chang, B., Eshraghi, J., Mituniewicz, A., Vlachos, P.P., Jung, S.: Cavity ripple dynamics after pinch-off. J. Fluid Mech. 850, 611–623 (2018)
Aristoff, J.M., Bush, J.W.: Water entry of small hydrophobic spheres. J. Fluid Mech. 619, 45–78 (2009)
Aristoff, J.M., Truscott, T.T., Techet, A.H., Bush, J.W.: The water entry of decelerating spheres. Phys. Fluids 22(3), 032102 (2010)
Watson, D.A., Bom, J.M., Weinberg, M.P., Souchik, C.J., Dickerson, A.K.: Water entry dynamics of spheres with heterogeneous wetting properties. Phys. Rev. Fluids 6(4), 044003 (2021)
Watson, D.A., Stephen, J.L., Dickerson, A.K.: Jet amplification and cavity formation induced by penetrable fabrics in hydrophilic sphere entry. Phys. Fluids 30(8), 082109 (2018)
Guleria, S.D., Dhar, A., Patil, D.V.: Experimental insights on the water entry of hydrophobic sphere. Phys. Fluids 33(10), 102109 (2021)
Liu, D., He, Q., Evans, G.: Penetration behaviour of individual hydrophilic particle at a gas-liquid interface. Adv. Powder Technol. 21(4), 401–411 (2010)
Wang, A., Song, Q., Ji, B., Yao, Q.: In-situ observation of hydrophobic micron particle impaction on liquid surface. Powder Technol. 311, 408–415 (2017)
Wang, A., Song, Q., Yao, Q.: Study on inertial capture of particles by a droplet in a wide Reynolds number range. J. Aerosol. Sci. 93, 1–15 (2016)
Verezub, O., Kaptay, G., Matsushita, T., Mukai, K.: Penetration dynamics of solid particles into liquids high-speed experimental results and modelling. In: Materials Science Forum, vol. 473, pp. 429–434. Trans Tech Publ (2005)
Chen, H., Liu, H.-R., Lu, X.-Y., Ding, H.: Entrapping an impacting particle at a liquid-gas interface. J. Fluid Mech. 841, 1073–1084 (2018)
Ji, B., Song, Q., Wang, A., Yao, Q.: Critical sinking of hydrophobic micron particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 207, 17–29 (2019)
Ji, B., Tang, Z., Song, Q.: Oblique impact dynamics of micron particles onto a liquid surface. Phys. Rev. Fluids 5(11), 114006 (2020)
Ji, B., Song, Q., Yao, Q.: Impact of hydrophobic micron ellipsoids on liquid surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 532, 711–717 (2018)
Zhu, S., Zhao, C., Haifeng, L., Chen, X.: Influence of surfactant on the penetration time of hydrophilic microparticles impacting into the gas–liquid interface at low impact velocities. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 160, 383–394 (2020)
Zhu, S.-J., Liu, R.-Z., Wang, T., Niu, Y.-J., Lu, H.-F., Chen, X.-L.: Penetration time of hydrophilic micron particles impacting into an unconfined planar gas–liquid interface. Chem. Eng. Sci. 193, 282–297 (2019)
Ji, B., Song, Q., Shi, K., Liu, J., Yao, Q.: Oblique impact of microspheres on the surface of quiescent liquid. J. Fluid Mech. 900, A17 (2020)
Dubrovsky, V., Podvysotsky, A., Shraiber, A.: Particle interaction in three-phase polydisperse flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 18(3), 337–352 (1992)
Sechenyh, V., Amirfazli, A.: An experimental study for impact of a drop onto a particle in mid-air: the influence of particle wettability. J. Fluids Struct. 66, 282–292 (2016)
Mitra, S., Doroodchi, E., Pareek, V., Joshi, J.B., Evans, G.M.: Collision behaviour of a smaller particle into a larger stationary droplet. Adv. Powder Technol. 26(1), 280–295 (2015)
Zuo, Z., Wang, J., Huo, Y., Liu, H., Xu, R.: Particle motion induced by electrostatic force of a charged droplet. Environ. Eng. Sci. 33(9), 650–658 (2016)
Bernardin, J.D., Mudawar, I., Walsh, C.B., Franses, E.I.: Contact angle temperature dependence for water droplets on practical aluminum surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 40(5), 1017–1033 (1997)
Levedev, N.: Force acting on conducting sphere in the field of a parallel plate condenser. Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 7, 268 (1962)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [51806087].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, Z., Jiang, P., Wang, L. et al. Eccentric impact of a submillimeter sphere on droplet surface under electric field. Acta Mech 234, 3547–3556 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03574-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03574-7