Abstract
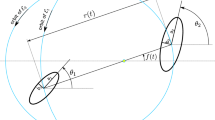
In this paper, the general analytical solution of the mechanical system consisting of an axisymmetric body spinning on a horizontal surface is analyzed. The motion equations are given by a three-dimensional system in which one of the equations is of second order. The invariance of the system under time translation is applied to reduce the order of the system by means of the classical Lie reduction method. As a result, a reduced autonomous first-order system is obtained. It is also explained how to recover the general analytical solution of the original system from the general solution of the reduced motion equations. Finally, some particular situations are considered with the goal of developing further the expression of the analytical solution found. The case of a spinning polar spheroid is also addressed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrose, D.M., Kelliher, J.P., Filho, M.C.L., Lopes, H.J.N.: Serfati solutions to the 2d Euler equations on exterior domains. J. Differ. Equ. 259(9), 4509–4560 (2015)
Ariska, M., Akhsan, H., Muslim, M.: Dynamic analysis of Tippe top on cylinder’s inner surface with and without friction based on Routh reduction. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1467, 012040 (2020)
Ariska, M., Akhsan, H., Zulherman, Z.: Utilization of maple-based physics computation in determining the dynamics of Tippe top. Jurnal Penelitian Fisika dan Aplikasinya (JPFA) 8(2), 123 (2018)
Bartsch, T., Ding, Y.: Periodic solutions of superlinear beam and membrane equations with perturbations from symmetry. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 44(6), 727–748 (2001)
Basquerotto, C.H.C.C., Righetto, E., da Silva, S.: As simetrias de Lie de um pião. Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Física, 40(2) (2017)
Basquerotto, C.H.C.C., Righetto, E., da Silva, S.: Applications of the Lie symmetries to complete solution of a bead on a rotating wire hoop. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 40(2) (2018)
Basquerotto, C.H.C.C., Ruiz, A.: On the reduction of nonlinear mechanical systems via moving frames: a bead on a rotating wire hoop and a spinning top. Acta Mech. 231(12), 4867–4879 (2020)
Bluman, G.: Symmetries and Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1989)
Bluman, G., Anco, S.: Symmetry and Integration Methods for Differential Equations. Springer, New York (2002)
Bocko, J., Nohajová, V., Harčarik, T.: Symmetries of differential equations describing beams and plates on elastic foundations. Procedia Eng. 48, 40–45 (2012)
Borisov, A.V., Ivanov, A.P.: Dynamics of the tippe top on a vibrating base. Regular Chaotic Dyn. 25(6), 707–715 (2020)
Braams, C.: On the influence of friction on the motion of a top. Physica 18(8–9), 503–514 (1952)
Branicki, M., Moffatt, H., Shimomura, Y.: Dynamics of an axisymmetric body spinning on a horizontal surface. III. geometry of steady state structures for convex bodies. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 462(2066), 371–390 (2005)
Branicki, M., Shimomura, Y.: Dynamics of an axisymmetric body spinning on a horizontal surface. IV. stability of steady spin states and the ‘rising egg’ phenomenon for convex axisymmetric bodies. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 462(2075), 3253–3275 (2006)
Campo, A.R.D.: Tippe top (topsy-turnee top) continued. Am. J. Phys. 23(8), 544–545 (1955)
Clarksonz, P.A., Mansfield, E.L.: Symmetry reductions and exact solutions of a class of nonlinear heat equations. Physica D 70(3), 250–288 (1994)
Cohen, R.J.: The tippe top revisited. Am. J. Phys. 45(1), 12–17 (1977)
Craddock, M.: Symmetry groups of linear partial differential equations and representation theory: The Laplace and axially symmetric wave equations. J. Differ. Equ. 166(1), 107–131 (2000)
Ebenfeld, S., Scheck, F.: A new analysis of the Tippe top: Asymptotic states and Liapunov stability. Ann. Phys. 243(2), 195–217 (1995)
Fang, Y., Fu, W., An, C., Yuan, Z., Fei, J.: Modelling, simulation and dynamic sliding mode control of a MEMS gyroscope. Micromachines 12(2), 190 (2021)
Featherstone, R.: Rigid Body Dynamics Algorithms. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Fokker, A.: The tracks of tops pegs on the floor. Physica 18(8–9), 497–502 (1952)
Friswell, M.I., Penny, J.E.T., Garvey, S.D.: Dynamics of Rotating Machines. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Genta, G.: Dynamics of Rotating Systems. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Goldstein, H.: Classical Mechanics. Addison Wesley, San Francisco (2002)
Gray, C.G., Nickel, B.G.: Constants of the motion for nonslipping tippe tops and other tops with round pegs. Am. J. Phys. 68(9), 821–828 (2000)
Hydon, P.E.: Symmetry Methods for Differential Equations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2005)
Ibragimov, N.H.: A Practical Course in Differential Equations and Mathematical Modelling: Classical and New Methods, Nonlinear Mathematical Models. Symmetry and Invari, World Scientific Pub Co Inc (2010)
Lane, M.T.: On analytic modeling of lunar perturbations of artificial satellites of the earth. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 46(4), 287–305 (1989)
Li, Q., Xiao, D., Zhou, X., Hou, Z., Zhuo, M., Xu, Y., Wu, X.: Dynamic modeling of the multiring disk resonator gyroscope. Micromachines 10(3), 181 (2019)
Liu, C.S.: Elastoplastic models and oscillators solved by a Lie-group differential algebraic equations method. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 69, 93–108 (2015)
Luo, S., Hu, W., Yu, J., Zhu, R., He, L., Li, X., Ma, P., Wang, C., Liu, F., Roeterdink, W.G., Stolte, S., Ding, D.: Rotational dynamics of quantum state-selected symmetric-top molecules in nonresonant femtosecond laser fields. J. Phys. Chem. A 121(4), 777–783 (2017)
Mankala, K.K., Agrawal, S.K.: Dynamic modeling and simulation of satellite tethered systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 127(2), 144–156 (2004)
Moffatt, H.K., Shimomura, Y.: Spinning eggs: a paradox resolved. Nature 416(6879), 385–386 (2002)
Moffatt, H.K., Shimomura, Y., Branicki, M.: Dynamics of an axisymmetric body spinning on a horizontal surface. I. Stability and the gyroscopic approximation. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 460(2052), 3643–3672 (2004)
Montenbruck, O., Gill, E., Lutze, F.: Satellite orbits: models, methods, and applications. Appl. Mech. Rev. 55(2), B27 (2002)
Mustafa, M., Al-Dweik, A.Y.: Noether symmetries and conservation laws of wave equation on static spherically symmetric spacetimes with higher symmetries. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 23(1–3), 141–152 (2015)
Olver, P.: Applications of Lie Groups to Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1986)
Olver, P.: Equivalence, Invariants and Symmetry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2008)
Paliathanasis, A., Tsamparlis, M.: Lie point symmetries of a general class of PDEs: the heat equation. J. Geom. Phys. 62(12), 2443–2456 (2012)
Perry, J.: Spinning Tops and Gyroscopic Motions. Dover Publications, New York (1957)
Ruiz, A., Muriel, C., Ramírez, J.: Exact general solution and first integrals of a remarkable static Euler–Bernoulli beam equation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 69, 261–269 (2019)
Sasaki, K.: Spinning eggs—Which end will rise? Am. J. Phys. 72(6), 775–781 (2004)
Shimomura, Y., Branicki, M., Moffatt, H.: Dynamics of an axisymmetric body spinning on a horizontal surface. II. Self-induced jumping. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 461(2058), 1753–1774 (2005)
Stepanova, I.V.: Symmetry analysis of nonlinear heat and mass transfer equations under Soret effect. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 20(3), 684–691 (2015)
Thomson, W.T.: Introduction to Space Dynamics. Guilford Publications, New York (2012)
Trentin, J.F.S., Cenale, T.P., da Silva, S., de Souza Ribeiro, J.M.: Attitude control of inverted pendulums using reaction wheels: comparison between using one and two actuators. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 234(3), 420–429 (2019)
Trentin, J.F.S., da Silva, S., de S. Ribeiro, J.M., Schaub, H.: An experimental study to swing up and control a pendulum with two reaction wheels. Meccanica (2021)
Trentin, J.F.S., Silva, S.D., Ribeiro, J.M.D.S., Schaub, H.: Inverted pendulum nonlinear controllers using two reaction wheels: design and implementation. IEEE Access 8, 74922–74932 (2020)
Vaidya, K.S., Parker, R.G.: Space-fixed formulation for the vibration of rotating, prestressed, axisymmetric bodies and shells. J. Sound Vib. 495, 115907 (2021)
Wang, C.C., Yau, H.T.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis and sliding mode control for a gyroscope system. Nonlinear Dyn. 66(1–2), 53–65 (2010)
Wittenburg, J.: Dynamics of Systems of Rigid Bodies. Vieweg+Teubner Verlag, Wiesbaden (1977)
Zub, S.I., Zub, S.S., Lyashko, V.S., Lyashko, N.I., Lyashko, S.I.: Mathematical model of interaction of a symmetric top with an axially symmetric external field. Cybern. Syst. Anal. 53(3), 333–345 (2017)
Zub, S.S.: Hamiltonian dynamics of the symmetric top in external axially-symmetric fields. magnetic retention of a rigid body. J. Autom. Inf. Sci. 50(7), 48–69 (2018)
Acknowledgements
A. Ruiz thanks the financial support from FEDER–Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades–Agencia Estatal de Investigación, via the project PGC2018-101514-B-I00 and from Junta de Andalucía to the research group FQM–377. C.H.C.C. Basquerotto is grateful for the financial support provided by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq - Brazil) in grant number 426050/2018-5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz, A., Basquerotto, C.H.C.C. Reduced motion equations of an axisymmetric body spinning on a horizontal surface via Lie symmetries. Acta Mech 233, 3853–3865 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03306-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03306-3