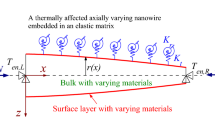
Abstract
Axial buckling analysis of magnetically affected double-nanowire systems carrying electric current is of high interest. Using Lorentz and Biot–Savart laws, the magnetic forces on each nanowire are appropriately evaluated. By employing Timoshenko and higher-order beam theories, the governing equations of the nanosystem are extracted in the context of the surface elasticity theory of Gurtin–Murdoch. By applying a meshless technique, the critical buckling load of the nanosystem is calculated. In a particular case, the predicted results by the suggested numerical methodology are also verified with those of the assumed mode method, and a reasonably good agreement is achieved. The influences of the electric current, magnetic field strength, interwire distance, and surface energy effect on the buckling behavior of the nanosystem are examined. The capability of the Timoshenko beam theory in capturing the predicted results by the higher-order beam theory is also explained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z.L., Song, J.: Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312, 242–246 (2006)
Wang, X., Song, J., Liu, J., Wang, Z.L.: Direct-current nanogenerator driven by ultrasonic waves. Science 316, 102–105 (2007)
Gurtin, M.E., Murdoch, A.I.: A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 57, 291–323 (1975)
Gurtin, M.E., Murdoch, A.I.: Effect of surface stress on wave propagation in solids. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 4414–4421 (1976)
Gurtin, M.E., Murdoch, A.I.: Surface stress in solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 14, 431–440 (1978)
He, J., Lilley, C.M.: Surface effect on the elastic behavior of static bending nanowires. Nano Lett. 8, 1798–1802 (2008)
Liu, C., Rajapakse, R.K.N.D.: Continuum models incorporating surface energy for static and dynamic response of nanoscale beams. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 9, 422–431 (2010)
Jiang, L.Y., Yan, Z.: Timoshenko beam model for static bending of nanowires with surface effects. Phys. E 42, 2274–2279 (2010)
Ansari, R., Sahmani, S.: Bending behavior and buckling of nanobeams including surface stress effects corresponding to different beam theories. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 49, 1244–1255 (2011)
Zhang, G.Y., Gao, X.L., Wang, J.Z.: A non-classical model for circular Kirchhoff plates incorporating microstructure and surface energy effects. Acta Mech. 226, 4073–4085 (2015)
Wang, G.F., Feng, X.Q., Yu, S.W.: Surface buckling of a bending microbeam due to surface elasticity. Europhys. Lett. 77, 44002 (2007)
Wang, G.F., Feng, X.Q.: Surface effects on buckling of nanowires under uniaxial compression. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 141913 (2009)
Wang, G.F., Feng, X.Q.: Effect of surface stresses on the vibration and buckling of piezoelectric nanowires. Europhys. Lett. 91, 56007 (2010)
Yan, Z., Jiang, L.Y.: The vibrational and buckling behaviors of piezoelectric nanobeams with surface effects. Nanotechnology 22, 245703 (2011)
Li, Y., Song, J., Fang, B., Zhang, J.: Surface effects on the postbuckling of nanowires. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 44, 425304 (2011)
Wang, K.F., Wang, B.L.: Combining effects of surface energy and non-local elasticity on the buckling of nanoplates. Micro Nano Lett. 6, 941–943 (2011)
Park, H.S.: Surface stress effects on the critical buckling strains of silicon nanowires. Comput. Mater. Sci. 51, 396–401 (2012)
Zhang, J., Wang, C., Adhikari, S.: Surface effect on the buckling of piezoelectric nanofilms. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 45, 285301 (2012)
Yan, Z., Jiang, L.Y.: Vibration and buckling analysis of a piezoelectric nanoplate considering surface effects and in-plane constraints. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. 468, 3458–3475 (2012)
Youcef, D.O., Kaci, A., Houari, M.S.A., Tounsi, A., Benzair, A., Heireche, H.: On the bending and stability of nanowire using various HSDTs. Adv. Nano Res. 3, 177–191 (2015)
Huang, D.W.: Size-dependent response of ultra-thin films with surface effects. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45, 568–579 (2008)
Gheshlaghi, B., Hasheminejad, S.M.: Surface effects on nonlinear free vibration of nanobeams. Compos. Part B Eng. 42, 934–937 (2011)
Ansari, R., Sahmani, S.: Surface stress effects on the free vibration behavior of nanoplates. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 49, 1204–1215 (2011)
Eltaher, M.A., Emam, S.A., Mahmoud, F.F.: Free vibration analysis of functionally graded size-dependent nanobeams. Appl. Math. Comput. 218, 7406–7420 (2012)
Malekzadeh, P., Shojaee, M.: Surface and nonlocal effects on the nonlinear free vibration of non-uniform nanobeams. Compos. Part B Eng. 52, 84–92 (2013)
Hosseini-Hashemi, S., Nazemnezhad, R.: An analytical study on the nonlinear free vibration of functionally graded nanobeams incorporating surface effects. Compos. Part B Eng. 52, 199–206 (2013)
Ansari, R., Mohammadi, V., Shojaei, M.F., Gholami, R., Sahmani, S.: On the forced vibration analysis of Timoshenko nanobeams based on the surface stress elasticity theory. Compos. Part B Eng. 60, 158–166 (2014)
Song, F., Huang, G.L., Varadan, V.K.: Study of wave propagation in nanowires with surface effects by using a high-order continuum theory. Acta Mech. 209, 129–139 (2010)
Liu, W.K., Jun, S., Zhang, Y.F.: Reproducing kernel particle methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 20, 1081–1106 (1995)
Liu, W.K., Jun, S., Li, S., Adee, J., Belytschko, T.: Reproducing kernel particle methods for structural dynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 38, 1655–1679 (1995)
Jun, S., Liu, W.K., Belytschko, T.: Explicit reproducing kernel particle methods for large deformation problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 41, 137–166 (1998)
Liu, W.K., Jun, S., Sihling, D.T., Chen, Y., Hao, W.: Multiresolution reproducing kernel particle method for computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 24, 1391–1415 (1997)
Chen, J.S., Yoon, S., Wang, H.P., Liu, W.K.: An improved reproducing kernel particle method for nearly incompressible finite elasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. 181, 117–145 (2000)
Zhang, L.T., Wagner, G.J., Liu, W.K.: Modelling and simulation of fluid structure interaction by meshfree and FEM. Commun. Numer. Methods Eng. 19, 615–621 (2003)
Kiani, K., Ghaffari, H., Mehri, B.: Application of elastically supported single-walled carbon nanotubes for sensing arbitrarily attached nano-objects. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 107–120 (2013)
Kiani, K.: Longitudinally varying magnetic field influenced transverse vibration of embedded double-walled carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 87, 179–199 (2014)
Kiani, K.: Axial buckling analysis of a slender current-carrying nanowire acted upon by a magnetic field using the surface energy approach. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 48, 245302 (2015)
Kiani, K.: Column buckling of magnetically affected stocky nanowires carrying electric current. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 83, 140–151 (2015)
Kiani, K.: Surface effect on free transverse vibrations and dynamic instability of current-carrying nanowires in the presence of a longitudinal magnetic field. Phys. Lett. A 378, 1834–1840 (2014)
Kiani, K.: Forced vibrations of a current-carrying nanowire in a longitudinal magnetic field accounting for both surface energy and size effects. Phys. E 63, 27–35 (2014)
Kiani, K.: Vibrations and instability of pretensioned current-carrying nanowires acted upon by a suddenly applied three-dimensional magnetic field. Mater. Chem. Phys. 162, 531–541 (2015)
Kiani, K.: Stability and vibrations of doubly parallel current-carrying nanowires immersed in a longitudinal magnetic field. Phys. Lett. A 379, 348–360 (2015)
Timoshenko, S.P.: On the correction for shear of the differential equation for transverse vibrations of prismatic bars. Philos. Mag. 41, 744–746 (1921)
Timoshenko, S.P.: On the transverse vibrations of bars of uniform cross-section. Philos. Mag. 43, 12531 (1922)
Wagner, G.J., Liu, W.K.: Application of essential boundary conditions in mesh-free methods: a corrected collocation method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 47, 1367–1379 (2000)
Bickford, W.B.: A consistent higher order beam theory. Dev. Theor. Appl. Mech. 11, 137–150 (1982)
Reddy, J.N.: A simple higher-order theory for laminated composite plates. J. Appl. Mech. 51, 745–752 (1984)
Hebali, H., Tounsi, A., Houari, M.S.A., Bessaim, A., Bedia, E.A.A.: New quasi-3D hyperbolic shear deformation theory for the static and free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates. J. Eng. Mech. 140, 374–383 (2014)
Belabed, Z., Houari, M.S.A., Tounsi, A., Mahmoud, S.R., Bég, O.A.: An efficient and simple higher order shear and normal deformation theory for functionally graded material (FGM) plates. Compos. Part B Eng. 60, 274–283 (2014)
Tounsi, A., Bourada, M., Kaci, A., Houari, M.S.A.: A new simple shear and normal deformations theory for functionally graded beams. Steel Compos. Struct. 18, 409 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiani, K. Elastic buckling of current-carrying double-nanowire systems immersed in a magnetic field. Acta Mech 227, 3549–3570 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-016-1679-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-016-1679-1