Abstract
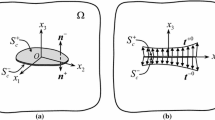
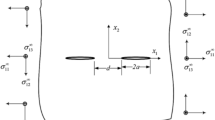
This paper presents a semi-analytic solution for multiple cracks beneath a half-space surface under elastohydrodynamic lubrication (EHL) contact. The solution not only takes into account the fluid–structure interactions in the EHL contact but also the interactions among all the cracks. In developing the governing equation, each crack of mixed modes I and II is modeled as a continuous distribution of climb and glide dislocations with unknown densities. With such a treatment, the original problem for materials with multiple cracks is converted into two subproblems: a homogeneous EHL contact problem with the fluid pressure distribution and the lubricant film thickness to be determined, and a half-space problem with unknown dislocation densities, which are iteratively obtained by a modified conjugate gradient method. A numerical algorithm is developed to integrate the two problems. The computational process is performed until the convergence of the displacements, which are the sum of the displacements due to the fluid pressure and the subsurface cracks. Sample cases are presented to analyze the pressure and lubricant film thickness profiles of EHL contact and the subsurface stresses for cracked materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Habchi W.: A Full-System Finite Element Approach to Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems: Application to Ultra-Low-Viscosity Fluids. University of Lyon, France (2008)
Ai, X.: Numerical Analyses of Elastohydrodynamically Lubricated Line and Point Contacts with Rough Surfaces by Using Semi-system and Multigrid Methods. Northwestern University, USA (1993)
Dowson D., Higginson G.R.: A numerical solution to the elastohydrodynamic problem. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1, 6–15 (1959)
Dowson, D., Higginson, G.R.:Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication, the Fundamentals of Roller and Gear Lubrication. Pergamon, Oxford (1966)
Zhu D., Cheng H.S.: An analysis and computational procedure for EHL film thickness, friction and flash temperature in line and point contacts. Tribol. T. 32, 364–370 (1989)
Zhu, D., Hu, Y.Z.: The study of transition from full film elastohydrodynamic to mixed and boundary lubrication. In: Proceedings of the STLE/ASME, 1999, pp. 150–156 (1999)
Zhu D., Hu Y.Z.: A computer program package for the prediction of EHL and mixed lubrication characteristics, friction, subsurface stresses and flash temperatures based on measured 3-D surface roughness. Tribol. T. 44, 383–390 (2001)
Zhu D., Wang Q.J.: Elastohydrodynamic lubrication: a gateway to interfacial mechanics—review and prospect. J. Tribol. 133, 041001-1–041001-14 (2011)
Habchi W., Eyheramendy D., Vergne P., Morales-Espejel G.: A full-system approach of the elastohydrodynamic line/point contact problem. J. Tribol. 130, 021501-1–021501-10 (2008)
Weng G.J.: Some elastic properties of reinforced solids, with special reference to isotropic ones containing spherical inclusions. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 22, 845–856 (1984)
Qiu Y.P., Weng G.J.: The influence of inclusion shape on the overall elastoplastic behavior of a two-phase isotropic composite. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 27, 1537–1550 (1991)
Liu Y.W., Fang Q.H.: Analysis of a screw dislocation inside an inhomogeneity with interface stress. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 464, 117–123 (2007)
Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W., Wen P.H.: A piezoelectric screw dislocation interacting with an elliptical inclusion containing electrically conductive interfacial rigid lines. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 50, 683–693 (2008)
Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W., Wen P.H.: Screw dislocations in a three-phase composite cylinder model with interface stress. J. Appl. Mech. 75, 041019-1–041019-8 (2008)
Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W., Jin B., Wen P.H.: Effect of interface stresses on the image force and stability of an edge dislocation inside a nanoscale cylindrical inclusion. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 46, 1413–1422 (2009)
Li Z., Li Y., Sun J., Feng X.Q.: An approximate continuum theory for interaction between dislocation and inhomogeneity of any shape and properties. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 113529-1–113529-7 (2011)
Feng H., Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W., Jin B.: Image force and stability of a screw dislocation inside a coated cylindrical inhomogeneity with interface stresses. Acta Mech. 220, 315–329 (2011)
Zhao Y.X., Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W.: Edge misfit dislocation formation at theinterface of a nanopore and infinite substrate with surface/interface effects. Philos. Mag. 92, 4230–4249 (2012)
Fang Q.H., Zhang L.C.: Prediction of the threshold load of dislocation emission in silicon during nanoscratching. Acta Mater. 61, 5469–5476 (2013)
Chen J.B., Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W.: Interaction between dislocation and subsurface crack under condition of slip caused by half-plane contact surface normal force. Eng. Fract. Mech. 114, 115–126 (2013)
Zhao Y.X., Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W.: Edge misfit dislocations in core-shell nanowire with surface/interface effects and different elastic constants. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 74, 173–184 (2013)
Zhao Y.H., Weng G.J.: Plasticity of a two-phase composite with partially debonded inclusions. Int. J. Plast. 12, 781–804 (1996)
Li C., Weng G.J.: Antiplane crack problem in functionally graded piezoelectric materials. J. Appl. Mech. 69, 481–488 (2002)
Liu Y.W., Fang Q.H., Jiang C.P.: Interaction between an edge dislocation and a circular inclusion with interfacial rigid lines. Acta Mech. 180, 157–174 (2005)
Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W.: Size-dependent interaction between an edge dislocation and a nanoscale inhomogeneity with interface effects. Acta Mater. 54, 4213–4220 (2006)
Wang G.F., Feng X.Q., Yu S.W.: Interface effects on the diffraction of plane compressional waves by a nanosized spherical inclusion. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 043533-1–043533-6 (2007)
Fang Q.H., Jin B., Liu Y., Liu Y.W.: Interaction between screw dislocations and inclusions with imperfect interfaces in fiber-reinforced composites. Acta Mech. 203, 113–125 (2009)
Pan Y., Weng G.J., Meguid S.A., Bao W.S., Zhu Z.-H., Hamouda A.M.S.: Percolation threshold and electrical conductivity of a two-phase composite containing randomly oriented ellipsoidal inclusions. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 123715-1– 123715-5 (2011)
Markenscoff X.: Evolution equation of moving defects: dislocations and inclusions. Int. J. Fract. 166, 35–40 (2010)
Hoh H.J., Xiao Z.M., Luo J.: On the fracture behavior of a Zener–Stroh crack with plastic zone correction in three-phase cylindrical composite material. Mech. Mater. 45, 1–9 (2012)
Hoh H.J., Xiao Z.M., Luo J.: Plastic zone size and crack tip opening displacement of a Dugdale crack interacting with a coated circular inclusion. Philos. Mag. 90, 3511–3530 (2010)
Luo J., Zhou K., Xiao Z.M.: Stress investigation on a Griffith crack initiated from an eccentric disclination in a cylinder. Acta Mech. 202, 65–77 (2009)
Markenscoff X.: The expanding spherical inhomogeneity with transformation strain. Int. J. Fract. 174, 41–48 (2012)
Zhou, K., Wei, R.: Multiple cracks in a half-space under contact loading. Acta Mech. 225, 1487–1502 (2014)
Miller G.R., Keer L.M.: Interaction between a rigid indenter and a near-surface void or inclusion. J. Appl. Mech. 50, 615–620 (1983)
Kuo C.H.: Stress disturbances caused by the inhomogeneity in an elastic half-space subjected to contact loading. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 44, 860–873 (2007)
Kuo C.H.: Contact stress analysis of an elastic half-plane containing multiple inclusions. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 45, 4562–4573 (2008)
Leroux J., Fulleringer B., Nelias D.: Contact analysis in presence of spherical inhomogeneities within a half-space. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 47, 3034–3049 (2010)
Zhou K., Keer L.M., Wang Q.J.: Semi-analytic solution for multiple interacting three-dimensional inhomogeneous inclusions of arbitrary shape in an infinite space. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 87, 617–638 (2011)
Zhou K., Keer L.M., Wang Q.J., Ai X., Sawamiphakdi K., Glaws P., Paire M., Che F.: Interaction of multiple inhomogeneous inclusions beneath a surface. Comput. Method. Appl. M 217, 25–33 (2012)
Zhou K., Chen W.W., Keer L.M., Ai X., Sawamiphakdi K., Glaws P., Wang Q.J.: Multiple 3D inhomogeneous inclusions in a half space under contact loading. Mech. Mater. 43, 444–457 (2011)
Zhou K., Chen W.W., Keer L.M., Wang Q.J.: A fast method for solving three-dimensional arbitrarily shaped inclusions in a half space. Comput. Method. Appl. M 198, 885–892 (2009)
Liu S., Wang Q.J., Liu G.: A versatile method of discrete convolution and FFT (DC-FFT) for contact analyses. Wear 243, 101–111 (2000)
Dowson D.: A generalized Reynolds equation for fluid-film lubrication. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 4, 159–170 (1962)
Barus C.: Isothermals, isopiestics and isometrics relative to viscosity. Am. J. Sci. 45, 87–96 (1893)
Venner C.H., ten Napel W.E.: Multilevel solution of the elastohydrodynamically lubricated circular contact problem part 2: smooth surface results. Wear 152, 369–381 (1992)
Venner C.H., ten Napel W.E.: Multilevel solution of the elastohydrodynamically lubricated circular contact problem part I: theory and numerical algorithm. Wear 152, 351–367 (1992)
Venner C.H., Lubrecht A.A.: Multi-Level Methods in Lubrication. Materials & Mechanical. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Q., Zhou, K. Elastohydrodynamic lubrication modeling for materials with multiple cracks. Acta Mech 225, 3395–3408 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-014-1145-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-014-1145-x