Abstract
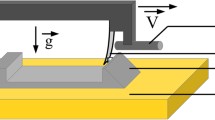
We report results of 3D discrete element method simulations aiming at investigating the role of the boundary vibration in inducing frictional weakening in sheared granular layers. We study the role of different vibration amplitudes applied at various shear stress levels, for a granular layer in the stick-slip regime and in the steady-sliding regime. Results are reported in terms of friction drops and kinetic energy release associated with frictional weakening events. We find that a larger vibration amplitude induces larger frictional weakening events. The results show evidence of a threshold below which no induced frictional weakening takes place. Friction drop size is found to be dependent on the shear stress at the time of vibration. A significant increase in the ratio between the number of slipping contacts to the number of sticking contacts in the granular layer is observed for large vibration amplitudes. These vibration-induced contact rearrangements enhance particle mobilization and induce a friction drop and kinetic energy release. This observation provides some insight into the grain-scale mechanisms of frictional weakening by boundary vibration in a dense sheared granular layer. In addition to characterizing the basic physics of vibration-induced shear weakening, we are attempting to understand how a fault fails in the earth under seismic wave forcing. This is the well-known phenomenon of dynamic earthquake triggering. We believe that the granular physics are key to this understanding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brace W.F., Byerlee J.D.: Stick-slip as a mechanism for earthquakes. Science 153(3739), 990–992 (1966)
Brace, W.F., Byerlee, J.D.: California earthquakes: why only shallow focus? Science 168(3939), 1573–1575 (1970)
Johnson T., Wu F.T., Scholz C.H., Url S.: Source parameters for stick-slip and for earthquakes. Science 179(4070), 278–280 (1973)
Daniels K.E., Hayman N.W.: Force chains in seismogenic faults visualized with photoelastic granular shear experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 113(B11), 1–13 (2008)
Hayman, N.W., Ducloué, L., Foco, K.L., Daniels, K.E.: Granular controls on periodicity of stick-slip events: kinematics and force-chains in an experimental fault. Pure Appl. Geophys. 168(12), 2239–2257 (2011)
Luding S., Clément E., Blumen A., Rajchenbach J., Duran J.: Studies of columns of beads under external vibrations. Phys. Rev. E 49, 1634 (1994)
Savage H.M., Marone C.: Potential for earthquake triggering from transient deformations. J. Geophys. Res. 113, 1–15 (2008)
Janda A., Maza D., Garcimartín A., Lanuza J., Clément E.: Unjamming a granular hopper by vibration. Europhys. Lett. 87, 24002 (2009)
Capozza R., Vanossi A., Vezzani A., Zapperi S.: Suppression of friction by mechanical vibrations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 085502 (2009)
Melhus M.F., Aranson I., Volfson D., Tsimring L.S.: Effect of noise on solid-to-liquid transition in small granular systems under shear. Phys. Rev. B 80, 041305 (2009)
Jia X., Brunet T., Laurent J.: Elastic weakening of a dense granular pack by acoustic fluidization: slipping, compaction, and aging. Phys. Rev. E 84(84), 020301(R) (2011)
van der Elst N., Brodsky E.E., Le Bas P.-Y., Johnson P. A.: Auto-acoustic compaction in steady shear flows: experimental evidence for suppression of shear dilatancy by internal acoustic vibration. J. Geophys. Res. 117, B09314 (2012)
Pollitz F., Stein R., Sevilgen V., Bürgmann R.: The 11 April 2012 east indian ocean earthquake triggered large aftershocks worldwide. Nature 490, 250–253 (2012)
Shelly D.R., Peng Z., Hill D.P., Aiken C.: Triggered creep as a possible mechanism for delayed dynamic triggering of tremor and earthquakes. Nat. Geosci. 4(6), 384–388 (2011)
Velasco A. A., Hernandez S., Parsons T., Pankow K.: Global ubiquity of dynamic earthquake triggering. Nat. Geosci. 1, 375–379 (2009)
Marsan D., Lengline O.: Extending earthquakes’ reach through cascading. Science 319, 1076–1079 (2008)
Gomberg J., Bodin P., Larson K., Dragert H.: Earthquake nucleation by transient deformations caused by the m = 7.9 Denali, Alaska, earthquake. Nature 427, 621–624 (2004)
Gomberg J., Reasenberg P., Bodin P., Harris R.: Earthquake triggering by seismic waves following the landers and hector mine earthquakes. Nature 411(6836), 462–466 (2001)
Freed A.M.: Earthquake triggering by static, dynamic, and postseismic stress transfer. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 33, 335–367 (2005)
Falk M., Langer J.: Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. E 57(6), 7192–7205 (1998)
DiDonna B.A., Lubensky T.C.: Nonaffine correlations in random elastic media. Phys. Rev. E 72, 066619 (2005)
Griffa M., Daub E.G., Guyer R.A., Johnson P.A., Marone C., Carmeliet J.: Vibration-induced slip in sheared granular layers and the micromechanics of dynamic earthquake triggering. Europhys. Lett. 96, 14001 (2011)
Griffa M., Ferdowsi B., Daub E., Guyer R., Johnson P., Marone C., Carmeliet J.: Meso-mechanical analysis of deformation characteristics for dynamically triggered slip in a granular medium. Philos. Mag. 92, 3520–3539 (2012)
Griffa M., Ferdowsi B., Daub E., Guyer R., Johnson P., Marone C., Carmeliet J.: Influence of vibration amplitude on dynamic triggering of slip in sheared granular layers. Phys. Rev. E 87, 012205 (2013)
Schoepfer M.P.J., Abe S., Childs C., Walsh J.: The impact of porosity and crack density on the elasticity, strength and friction of cohesive granular materials: insights from dem modelling. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 46, 250–261 (2009)
Johnson P.A., Savage H., Knuth M., Gomberg J., Marone C.: Effects of acoustic waves on stick-slip in granular media and implications for earthquakes. Nature 451(7174), 57–60 (2008)
Place D., Mora P.: The lattice solid model to simulate the physics of rocks and earthquakes: incorporation of friction. Comput. Phys. 150, 332–372 (1999)
Wang Y., Abe S., Latham S., Mora P.: Implementation of particle-scale rotation in the 3-D lattice solid model. Pure Appl. Geophys. 163, 1769–1785 (2006)
Mair K., Abe S.: 3d numerical simulations of fault gouge evolution during shear: grain size reduction and strain localization. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 274, 72–81 (2008)
Cundall P.A., Strack O.D.L.: A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Geotechnique 29, 47–65 (1979)
Aharonov E., Sparks D.: Rigidity phase transition in granular packings. Phys. Rev. E 60, 6890–6896 (1999)
Wang Y.: A new algorithm to model the dynamics of 3-D bonded rigid bodies with rotations. Acta Geotech. 4, 117–127 (2009)
Ruina A.: Slip instability and state variable friction laws. J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth 88, 10359–10370 (1983)
Palmer A.C., Rice J.R.: The growth of slip surfaces in the progressive failure of over-consolidated clay. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 332, 527–548 (1973)
Ida Y.: Cohesive force across the tip of a longitudinal-shear crack and griffith’s specific surface energy. J. Geophys. Res. 77, 3796–3805 (1972)
Johnson P., Carpenter B., Knuth M., Kaproth B., Le Bas P.-Y., Daub E., Marone C.: Nonlinear dynamical triggering of slow slip on simulated earthquake faults with implications to earth. J. Geophys. Res. 117, 1–9 (2012)
Gomberg J., Johnson P.A.: Dynamic triggering of earthquakes. Nature 437, 830 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferdowsi, B., Griffa, M., Guyer, R.A. et al. Effect of boundary vibration on the frictional behavior of a dense sheared granular layer. Acta Mech 225, 2227–2237 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-014-1136-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-014-1136-y