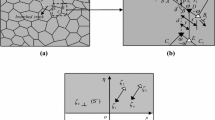
Abstract
A theoretical model is established to investigate the interaction between the cooperative grain boundary (GB) sliding and migration and a semi-elliptical blunt crack in deformed nanocrystalline materials. By using the complex variable method, the effect of two disclination dipoles produced by the cooperative GB sliding and migration process on the emission of lattice dislocations from a semi-elliptical blunt crack tip is explored. Closed-form solutions for the stress field and the force acting on the dislocation are obtained in complex form, and the critical stress intensity factors for the first dislocation emission from a blunt crack under mode I and mode II loadings are calculated. Then, the influence of disclination strength, curvature radius of blunt crack tip, crack length, locations and geometry of disclination dipoles, and grain size on the critical stress intensity factors is presented detailedly. It is shown that the cooperative GB sliding and migration and the grain size have significant influence on the dislocation emission from a blunt crack tip.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyers M.A., Mishra A., Benson D.J.: Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 427–556 (2006)
Dao M., Lu L., Asaro R.J., De Hosson J.T.M., Ma E.: Toward a quantitative understanding of mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals. Acta Mater. 55, 4041–4065 (2007)
Zhu L.L., Zheng X.J.: Influence of interface energy and grain boundary on the elastic modulus of nanocrystalline materials. Acta Mech. 213, 223–234 (2010)
Alizada A.N., Sofiyev A.H., Kuruoglu N.: Stress analysis of a substrate coated by nanomaterials with vacancies subjected to uniform extension load. Acta Mech. 223, 1371–1383 (2012)
Wu M.S., Zhou K., Nazarov A.A.: Crack nucleation at disclinated triple junctions. Phys. Rev. B. 76, 134105-1–134105-6 (2007)
Zhou K., Wu M.S., Nazarov A.A.: Relaxation of a disclinated tricrystalline nanowire. Acta Mater. 56, 5828–5836 (2008)
Voyiadjis G.Z., Deliktas B.: Modeling of strengthening and softening in inelastic nanocrystalline materials with reference to the triple junction and grain boundaries using strain gradient plasticity. Acta Mech. 213, 3–26 (2010)
Khan A.S., Farrok B., Takacs L.: Effect of grain refinement on mechanical properties of ball-milled bulk aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 489, 77–84 (2008)
Farrok B., Khan A.S.: Grain size, strain rate, and temperature dependence of flow stress in ultra-fine grained and nanocrystalline Cu and Al: synthesis, experiment, and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plast. 25, 715–732 (2009)
Zhou K., Nazarov A.A., Wu M.S.: Continuum and atomistic studies of a disclinated crack in a bicrystalline nanowire. Phys. Rev. B 73, 045410-1–045410-11 (2006)
Barai P., Weng G.J.: Mechanics of very fine-grained nanocrystalline materials with contribution from grain interior, GB zone, and grain boundary sliding. Int. J. Plast. 25, 2410–2434 (2009)
Bobylev S.V., Mukherjee A.K., Ovid’ko I.A.: Emission of partial dislocations from amorphous intergranular boundaries in deformed nanocrystalline ceramics. Scr. Mater. 60, 36–39 (2009)
Xia S.H., Wang J.T.: A micromechanical model of toughening behavior in the dual-phase composite. Int. J. Plast. 26, 1442–1460 (2010)
Barai P., Weng G.J.: Mechanics of a nanocrystalline coating and grain-size dependence of its plastic strength. Mech. Mater. 43, 496–504 (2011)
Liu Y.G., Zhou J.Q., Shen T.D., Hui D.: Effects of ultrafine nanograins on the fracture toughness of nanocrystalline materials. J. Mater. Res. 26, 1734–1741 (2011)
Rupert T.J., Trelewicz J.R., Schuh C.A.: Grain boundary relaxation strengthening of nanocrystalline Ni–W alloys. J. Mater. Res. 27, 1285 (2012)
Liu Y.G., Zhou J.Q., Shen T.D.: A combined dislocation–cohesive zone model for fracture in nanocrystalline materials. J. Mater. Res. 27, 694–700 (2012)
Ovid’ko I.A.: Deformation and diffusion modes in nanocrystalline materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 50, 65–82 (2005)
Koch C.C.: Structural nanocrystalline materials: an overview. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 1403–141 (2007)
Ovid’ko I.A., Sheinerman A.G.: Special strain hardening mechanism and nanocrack generation in nanocrystalline materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 171927 (2007)
Ovid’ko I.A., Sheinerman A.G.: Enhanced ductility of nanomaterials through optimization of grain boundary sliding and diffusion processes. Acta Mater. 57, 2217–2228 (2009)
Sergueeva A.V., Mara N.A., Krasilnikov N.A., Valiev R.Z., Mukherjee A.K.: Cooperative grain boundary sliding in nanocrystalline materials. Philos. Mag. 86, 5797–5804 (2006)
Ovid’ko I.A., Sheinerman A.G., Aifantis E.C.: Stress-driven migration of grain boundaries and fracture processes in nanocrystalline ceramics and metals. Acta Mater. 56, 2718–1727 (2008)
Zhou K., Nazarov A.A., Wu M.S.: Competing relaxation mechanisms in a disclinated nanowire: temperature and size effects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 035501-1–1035504-4 (2007)
Zhou K., Hoh H.J., Wang X., Keer L.M., Pang H.J.L., Song B., Wang Q.J.: A review of recent works on inclusions. Mech. Mater. 60, 144–158 (2013)
Youssef K.M., Scattergood R.O., Murty K.L., Koch C.C.: Nanocrystalline Al-Mg alloy with ultrahigh strength and good ductility. Scr. Mater. 54, 251–256 (2006)
Sergueeva A.V., Mara N.A., Mukherjee A.K.: Grain boundary sliding in nanomaterials at elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 4, 1433–1438 (2007)
Bhaduri S., Bhaduri S.B.: Enhanced low temperature toughness of Al 2 O 3−ZnO 2 nano/nano composites. Nanostruct. Mater. 8, 755–763 (1997)
Mirshams R.A., Xiao C.H., Whang S.H., Yin W.M.: R-Curve characterization of the fracture toughness of nanocrystalline nickel thin sheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 315, 21–27 (2001)
Zhao Y., Qian J., Daemen L.L., Pantea C., Zhang J., Voroninm G.A. et al.: Enhancement of fracture toughness in nanostructured diamond-SiC composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1356–1358 (2004)
Kaminskii A.A., Akchurin M.S., Gainutdinov R.V. et al.: Microhardness and fracture toughness of Y 2 O 3- and Y 3 Al 5 O 12- based nanocrystalline laser ceramics. Crystallogr. Rep. 50, 569–573 (2005)
Gutkin M.Yu, Ovid’ko I.A.: Grain boundary migration and rotational deformation mode in nanocrystalline materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 251916 (2005)
Bobylev S.V, Morozov N.F., Ovid’ko I.A.: Cooperative grain boundary sliding and migration process in nanocrystalline solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 055504 (2010)
Ovid’ko I.A., Sheinerman A.G., Aifantis E.C.: Effect of cooperative grain boundary sliding and migration on crack growth in nanocrystalline solids. Acta Mater. 59, 5023–5031 (2011)
Fang Q.H., Feng H., Liu Y.W., Lin S., Zhang N.: Special rotational deformation effect on the emission of dislocations from a crack tip in deformed nanocrystalline solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 11, 1406–1412 (2012)
Huang M.X., Li Z.H.: Dislocation emission criterion from a blunt crack tip. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52, 1991–2003 (2004)
Fischer L.L., Beltz G.E.: The effect of crack blunting on the competition between dislocation nucleation and cleavage. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 49, 635–654 (2001)
Huang M.X., Rivera Dı’az del Castillo P.E.J., Li Z.H.: Edge dislocation dipole emission from a blunt crack tip and its morphological effects. Scr. Mater. 54, 649–653 (2006)
Luo J., Xiao Z.M.: Analysis of a screw dislocation interacting with an elliptical nano inhomogeneity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 47, 883–893 (2009)
Chen B.J., Xiao Z.M., Liew K.M.: Electro-elastic stress analysis for a wedge-shaped crack interacting with a screw dislocation in piezoelectric solid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 40, 621–635 (2002)
Muskhelishvili N.L.: Some Basic Problems of Mathematical Theory of Elasticity. Noordhoff, Leyden (1975)
Zhang T.Y., Li J.C.M.: Interaction of an edge dislocation with an interfacial crack. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 2215–2226 (1992)
Xiao Z.M., Chen B.J.: A screw dislocation interacting with a coated fiber. Mech. Mater. 32, 485–494 (2000)
Xiao Z.M., Bai J.: On piezoelectric inhomogeneity related problem-part I: a close-form solution for the stress field outside a circular piezoelectric inhomogeneity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 37, 945–959 (1999)
Zhou K.M.S., Wu M.S.: Elastic fields due to an edge dislocation in an isotropic film-substrate by the image method. Acta Mech. 211, 271–292 (2010)
Zhou K.: Elastic field and effective moduli of periodic composites with arbitrary inhomogeneity distribution. Acta Mech. 223, 293–308 (2012)
Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W., Jiang C.P., Li B.: Interaction of a wedge disclination dipole with interfacial cracks. Eng. Fract. Mech. 73, 1235–1248 (2006)
Liu Y.W., Fang Q.H.: Interaction of a wedge disclination dipole with circular inclusion. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 203, 443–458 (2006)
Song H.P., Fang Q.H., Liu Y.W.: Elastic behavior of a wedge disclination dipole near a sharp crack emanating from a semi-elliptical blunt crack. Chin. Phys. B 19, 056101 (2010)
Hirth J.P., Lothe J.: Theory of Dislocations, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1964)
Fang Q.H., Song H.P., Liu Y.W.: Elastic behaviour of an edge dislocation near a sharp crack emanating from a semi-elliptical blunt crack. Chin. Phy. B 19, 016102 (2010)
Creager M., Paris P.C.: Elastic field equations for blunt cracks with reference to stress corrosion cracking. Int. J. Fract. 3, 247–252 (1967)
Rice J.R., Thomson R.: Ductile versus brittle behavior of crystals. Philos. Mag. 29, 73–80 (1974)
Feng H., Fang Q.H., Zhang L.C, Liu Y.W.: Effect of cooperative grain boundary sliding and migration on emission of dislocations from a crack tip in nanocrystalline materials. Mech. Mater. 61, 39–48 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Fang, Q., Feng, H. et al. Effect of cooperative grain boundary sliding and migration on dislocation emitting from a semi-elliptical blunt crack tip in nanocrystalline solids. Acta Mech 225, 2005–2019 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-1039-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-1039-3