Abstract
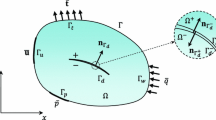
A new element is proposed for describing a discontinuous medium, such as holes and cracks, inside the region of the element. The underlying idea is to construct numerically the base functions of the discontinuous region by capturing the results calculated by fine finite elements in small-scale and then to construct the element in macro-scale with the crack and hole based on the theories of the multi-scale finite element method and the extended finite element method. Some numerical analysis is performed. The results show that the proposed element can well describe the field of displacement, strain, and stress intensity of the discontinuous region inside the element and can significantly decrease the number of elements and nodes of the calculated porous structure. The precision of the proposed element is also acceptable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang H.W., Wu J.K., Fu Z.D.: Extended multiscale finite element method for elasto-plastic analysis of 2D periodic lattice truss materials. Comput. Mech. 45, 623–635 (2010)
Zhang H.W., Wu J.K., Lv J., Fu Z.D.: Extended multiscale finite element method for mechanical analysis of heterogeneous materials. Acta Mech. Sin. 26, 899–920 (2010)
Zhang H.W., Fu Z.D., Wu J.K.: Coupling multiscale finite element method for consolidation analysis of heterogeneous saturated porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 32, 268–279 (2009)
Zhang H.W., Zhang S., Bi J.Y., Schrefler B.A.: Thermo-mechanical analysis of periodic multiphase materials by a multiscale asymptotic homogenization approach. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 69, 87–113 (2007)
Zhang H.W., Wang H., Wang J.B.: Parametric variational principle based elastic-plastic analysis of heterogeneous materials with Voronoi finite element method. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 43, 206–217 (2007)
Li X.K., Liu Q.P., Zhang J.B.: A micro–macro computational homogenization procedure for modeling the mechanical response of granular material modeled as heterogeneous Cosserat continuum modeling of granular materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47, 291–303 (2010)
Wu J.C., Shi X.Q., Ye S.J., Xue Y.Q., Zhang Y., Yu J.: Numerical simulation of land subsidence induced by groundwater overexploitation in Su-Xi-Chang area, China. Environ. Geol. 57, 1409–1421 (2009)
Yuan Z., Fish J.: Toward realization of computational homogenization in practice. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 73, 361–380 (2008)
Miehe C., Bayreuther C.G.: On multiscale FE analyses of heterogeneous structures, from homogenization to multigrid solvers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 71, 1135–1180 (2007)
Xia Z.H., Zhou C.W., Yong Q.L., Wang X.W.: On selection of repeated unit cell model and application of unified periodic boundary conditions in micro-mechanical analysis of composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 266–278 (2006)
Yan J., Cheng G.D., Liu S.T., Liu L.: Comparison of prediction on effective elastic property and shape optimization of truss material with periodic microstructure. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 48, 400–413 (2006)
Thomas Y.H.: Multiscale modelling and computation of fluid flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 47, 707–719 (2005)
He X.G., Ren L.: Finite volume multiscale finite element method for solving the groundwater flow problems in heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 41, W10417 (2005)
Efendiev Y., Hou T., Ginting V.: Multiscale finite element methods for nonlinear problems and their applications. Commun. Math. Sci. 2, 553–589 (2004)
Jenny P., Lee S.H., Tchelepi H.A.: Multi-scale finite-volume method for elliptic problems in subsurface flow simulation. J. Comput. Phys. 187, 47–67 (2003)
Terada K., Kikuchi N.: A class of general algorithms for multiscale analyses of heterogeneous media. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 5427–5464 (2001)
Fries T.P.: A corrected XFEM approximation without problems in blending elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 75, 503–532 (2008)
Zi G., Belytschko T.: New crack-tip elements for XFEM and applications to cohesive cracks. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 57, 2221–2240 (2003)
Chessa J., Smolinski P., Belytschko T.: The extended finite element method (XFEM) for solidification problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 53, 1959–1977 (2002)
Dauxz C., Moes N., Dolbow J., Sukumark N., Belytschko T.: Arbitrary branched and intersecting cracks with the extended finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 48, 1741–1760 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Chen, Jy., Li, J. et al. Study on the element with the hole and crack. Acta Mech 225, 1915–1930 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-1029-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-013-1029-5