Abstract
Fluid flow in the ureter is sometimes accompanied by solid particles that are produced in the kidneys or result from the breakup of larger kidney stones; ureteral peristalsis is affected by the presence of these solids. Peristaltic flow is analyzed for a solitary traveling wave in an axisymmetric tube with an incompressible, Newtonian fluid in which identical, solid spherical particles are distributed. A two-phase flow model is used in conjunction with a perturbation method based on a small radius to length ratio of the wave to obtain a closed-form solution of the flow and particle velocities. The phenomenon of trapping in which closed fluid recirculation streamlines in a moving coordinate frame occurs is discussed. Peristaltic pumping is affected as particle volume fraction is increased. The pressure drop diminishes as the amplitude ratio (wave amplitude/wave radius) decreases. The pressure in the contracted part of the ureter increases as the particle volume fraction is increased. It is suggested that certain pathological and physiological manifestations on the ureter can be related to these findings. The results may also be relevant to the transport of other physiological fluids and industrial applications in which peristaltic pumping is used.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
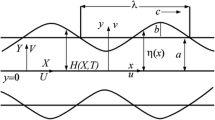
- a :
-
Particle radius
- a b :
-
Wave amplitude
- b :
-
Characteristic length
- c :
-
Wave velocity
- C :
-
Volume fraction
- H :
-
Equation of wall in fixed frame
- M :
-
Drag force per unit volume
- p :
-
Pressure
- P :
-
Pressure rise over characteristic length
- q :
-
Flow rate in moving frame
- q c :
-
Critical flow rate for bifurcation in moving frame
- q λ :
-
Flow rate characteristic value in moving frame
- Q :
-
Time-averaged flow rate in fixed frame
- \({\widehat Q}\) :
-
Instantaneous flow rate in fixed frame
- (r, z):
-
Spatial coordinates in moving frame
- (R, Z):
-
Spatial coordinates in fixed frame
- R b :
-
Wave radius
- Re 0 :
-
Liquid Reynolds number
- \({\overline {Re}}\) :
-
Modified Reynolds number
- S :
-
Stokes drag coefficient
- t :
-
Time
- (u, v):
-
Axial and radial velocity in moving frame
- (U, V):
-
Axial and radial velocity in fixed frame
- α :
-
= ρ p /ρ f , Density ratio between phases
- \({\epsilon}\) :
-
= R b /b, Nondimensional wave slope
- η :
-
Equation of wall in moving frame
- λ:
-
Axial length
- μ :
-
Viscosity
- μ 0 :
-
Fluid viscosity
- ρ :
-
Density
- τ :
-
Viscous stress tensor
- \({\phi}\) :
-
= a b /R b , Amplitude ratio
- ψ :
-
Stream-function
- f :
-
Fluid phase
- p :
-
Particle phase
- r :
-
Relative
- s :
-
Suspension
- * :
-
Dimensional quantities
References
Shapiro A.H., Jaffrin M.Y., Weinberg S.L.: Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 37, 799–825 (1969)
Yin F., Fung Y.C.: Peristaltic transport. J. Appl. Mech. 35, 669–675 (1969)
Zien T.F., Ostrach S.: A long wave approximation of peristaltic motion. J. Biomech. 3, 63–75 (1970)
Manton M.J.: Long-wavelength peristaltic pumping at low Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 68, 681–693 (1975)
Lykoudis P., Roos R.: The fluid mechanics of the ureter from a lubrication theory point of view. J. Fluid Mech. 43, 661–674 (1970)
Griffiths D.J.: Flow of urine through the ureter: a collapsible, muscular tube undergoing peristalsis. J. Biomech. Eng. 111, 206–211 (1989)
Takabatake S., Ayukawa K., Mori A.: Peristaltic flow in circular cylindrical tubes under finite wavelengths and finite Re. J. Fluid Mech. 193, 267–283 (1988)
Xiao Q., Damodaran M.: A numerical investigation of peristaltic waves in circular tubes. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 16(3), 201–216 (2002)
Yin F., Fung Y.: Comparison of theory and experiment in peristaltic transport. J. Fluid Mech. 47, 93–112 (1971)
Ramachandra Rao A., Mishra M.: Nonlinear and curvature effects on peristaltic flow of a viscous fluid in an asymmetric channel. Acta Mech. 168, 35–59 (2001)
Srinivasacharya W., Mishra M., Rao A.R.: Peristaltic pumping of a micropolar fluid in a tube. Acta Mech. 161, 165–178 (2003)
Hayat T., Ali N., Ashgar A.: An analysis of peristaltic transport for flow of a Jeffrey fluid. Acta Mech. 193, 101–112 (1998)
Pozrikidis C.: A study of peristaltic flow. J. Fluid Mech. 180, 515–527 (1987)
Graw M., Engelhardt H.: Simulation of physiological ureteral peristalsis. Urol. Int. 41, 1–8 (1986)
Misra J.C.: Biomathematics: Modelling and Simulation. World Scientific, Singapore (2006)
Misra J.C., Pandey K.: A mathematical model for oesophageal swallowing of a food-bolus. Math. Comput. Model. 33, 997–1009 (2001)
Widmaier E.P., Raff H., Strang K.T.: Vander’s Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function. McGraw-Hill, New York (2001)
Mernone A.V., Mazumdar J.N., Lucas S.K.: A mathematical study of peristaltic transport of a Casson fluid. Math. Comput. Model. 35, 895–912 (2002)
Misra J., Pandey K.: Peristaltic transport of blood in small vessels: study of a mathematical model. Comput. Math. Appl. 43, 1183–1193 (2002)
Gupta B.B., Seshadri V.: Peristaltic transport in non-uniform tubes. J. Biomech. 9, 105–109 (1976)
Fauci L.J., Dillon R.: Biofluidmechanics of reproduction. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 38, 371–394 (2006)
Eytan O., Elad D.: Analysis of intra-uterine fluid motion induced by uterine contractions. Bull. Math. Biol. 61, 221–238 (1999)
Ishii M., Hibiki T.: Thermo-Fluid Dynamics of Two-Phase Flow. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Drew D.: Stability of a Stokes layer of a dusty gas. Phys. Fluids 22(11), 2081–2086 (1979)
Drew D.: Mathematical modeling of two-phase flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 15, 261–291 (1983)
Drew D.A., Passman S.L.: Theory of Multicomponent Fluids. Springer, Berlin (1999)
Kleinstreuer C.: Two-Phase Flow: Theory and Applications. Taylor and Francis, London (2003)
Enwald H., Peirano E., Almstedt A.E.: Eulerian two-phase flow theory applied to fluidization. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 22, 21–66 (1996)
Patankar N.A., Joseph D.D.: Modeling and numerical simulation of particulate flows by the Eulerian–Lagrangian approach. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 27, 1659–1684 (2001)
Jiménez-Lozano J., Sen M., Dunn P.F.: Particle motion in unsteady two-dimensional peristaltic flow with application to the ureter. Phys. Rev. E 79(4), 041901 (2009)
Jiménez-Lozano J., Sen M.: Particle dispersion in two-dimensional peristaltic flow. Phys. Fluids 22, 043303 (2010)
Stewart H.B.: Two-phase flow: models and methods. J. Comput. Phys. 56, 363–409 (1984)
Srivastava L.M., Srivastava V.P.: Peristaltic transport of a particle-fluid suspension. J. Biomech. Eng. 111, 157–165 (1989)
Mekheimer K.S., El Shehawey E.F., Elaw A.M.: Peristaltic motion of a particle-fluid suspension in a planar channel. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 37(11), 2895–2920 (1998)
Misra J., Pandey K.: Peristaltic transport of particle-fluid suspension in a cylindrical tube. Comput. Math. Appl. 28(4), 131–145 (1994)
Sha W.T., Soo S.L.: On the effect of \({P\nabla\alpha}\) term in multiphase dynamics. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 5, 153–158 (1979)
Felderhof B.U.: Virtual mass and drag in two-phase flow. J. Fluid Mech. 225, 177–196 (1991)
Drew D.A.: Two-phase flows: constitutive equations for lift and Brownian motion and some basic flows. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 62(2), 149–163 (1976)
Charm S., Kurland G.: Blood Flow and Microcirculation. Wiley, New York (1974)
Siddiqui A.M., Schwarz W.H.: Peristaltic flow of a second-order fluid in tubes. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 53, 257–284 (1994)
Boyarski S., Gottschalk C., Tanagho E., Zimskind P.: Urodynamics: Hydrodynamics of the Ureter and Renal Pelvis. Academic Press, San Diego (1971)
Guerra A., Allegri F., Meschi T., Adorni G., Prati B., Nouvenne A., Novarini A., Maggiore U., Fiaccadori E., Borghi L.: Effects of urine dilution on quantity, size and aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals induced in vitro by an oxalate load. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 43(6), 585–589 (2005)
Jiménez-Lozano J., Sen M.: Streamline topologies of two-dimensional peristaltic flow and their bifurcations. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Identif. 49(7), 704–715 (2010)
Shigeta M., Kasaoka Y., Yasumoto H., Inoue K., Usui T., Hayashi M., Tazuma S.: Fate of residual fragments after successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Int. J. Urol. 6, 169–172 (1999)
Kiil F.: The Function of the Ureter and Renal Pelvis. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia (1957)
Boyarski S., Labay P.: Ureteral Dynamics. The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore (1972)
Weinberg S.L.: Ureteral function: II. The ureteral catheter and the uremetrogram. Investig. Urol. 12(4), 255–261 (1975)
Shafik A.: Electroureterogram: human study of the electromechanical activity of the ureter. Urology 48(5), 696–699 (1996)
Shafik A.: Ureteric profilometry: a study of the ureteric pressure profile in the normal and pathologic ureter. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 32, 14–19 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiménez-Lozano, J., Sen, M. & Corona, E. Analysis of peristaltic two-phase flow with application to ureteral biomechanics. Acta Mech 219, 91–109 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-010-0438-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-010-0438-y