Abstract
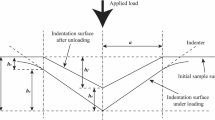
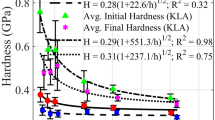
This paper presents the results of an experimental study for nano-indentation size effects for different face centered cubic metals with different purities. The selected materials are: Silver, Copper, Aluminum, Lead, and Nickel. Nano-indentation tests are run using a Berkovich indenter with continuous stiffness measurement procedure where hardness is measured continuously with indentation depth. The results show three distinctive regions for the indentation size effects for the material, where hardness could increase or decrease with increasing indentation. This behavior is modeled through a proposed simple power law model, which includes the effect of grain boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stelmashenko N.A., Walls M.G., Brown L.M., Milman Y.V.: Microindentations on W and Mo oriented single crystals: an STM study. Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 2855–2865 (1993)
Ma Q., Clarke D.R.: Size dependent hardness of silver single crystals. J. Mater. Res. 10, 853–863 (1995)
Voyiadjis, G.Z., Almasri, A.H.: Variable material length scale associated with nano indentation experiments. J. Eng. Mech. (in press) (2009)
Ascheron C., Huse C., Kuhn G., Neumann H.: Microhardness of Sn-doped in P. Cryst. Res. Technol. 24, 33–35 (1989)
Vengatesan B., Kanniah H., Ramasvamy P.: Microhardness and crack patterns of CVT grown CdGa2S4 single crystals. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 5, 987–988 (1986)
Tickoo R., Tandon R.P., Bamzai K.K., Kotru P.N.: Microindentation studies on samarium-modified lead titanate ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 80, 446–451 (2003)
Guille J., Sieskind M.: Microindentation studies on BaFCl single crystals. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 899–903 (1991)
Sayan P., Ulrich J.: Effect of various impurities on the hardness of NaCl Crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. 36, 1253–1262 (2001)
Delince M., Jacques P.J., Pardoen T.: Separation of size-dependent strengthening contributions in fine-grained Dual Phase steels by nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 54, 3395–3404 (2006)
Klepaczko, J.R.: Constitutive modelling in dynamic plasticity based on physical state variables: a review. In: International Proceedings on Mechanical and Physical Behaviour of Materials under Dynamic Loading, Les Editions de Physique, Les Ulis, C3/49, 553–560 (1988)
Abed F.H., Voyiadjis G.Z.: A consistent modified Zerilli—Armstrong flow stress model for BCC and FCC metals for elevated temperatures. Acta Mech. 175, 1–18 (2005)
Voyiadjis G.Z., Almasri A.H.: A physically based constitutive model for fcc metals with applications to dynamic hardness. Mech. Mater. 40, 549–563 (2008)
Oliver W.C., Pharr G.M.: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564–1583 (1992)
Joslin D.L., Oliver W.C.: A new method for analyzing data from continuous depth-sensing microindentation tests. J. Mater. Res. 5(1), 123–126 (1990)
Hendrix B.C.: The use of shape correction factors for elastic indentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 10, 255–257 (1995)
Hay, J.L., Pharr, G.M.: Instrumented indentation testing. In: Kuhn, H., Medlin, D. (eds.) ASM Handbook: Mechanical Testing and Evaluation, vol. 8, pp. 232–243. Materials Park, Ohio (2000)
Sneddon I.N.: The relation between load and penetration in the axisymmetric Boussinesq problem for a punch of arbitrary profile. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47–57 (1965)
McElhaney K.W., Valssak J.J., Nix W.D.: Determination of indenter tip geometry and indentation contact area for depth sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1300–1306 (1998)
Tabor D.: The Hardness of Metals. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1951)
Voyiadjis, G.Z., Abu Al-Rub, R.K.: Length scales in gradient plasticity. In: Ahzi, S., Cherkaoui, M., Khaleel, M.A., Zbib, H.M., Zikry, M.A., LaMatina, B. (eds.) Proceedings of the IUTAM symposium on multiscale modeling and characterization of elastic–inelastic behavior of engineering materials. Kluwer, Morocco, pp. 167–174 (2002)
Abu Al-Rub R.K., Voyiadjis G.Z.: Analytical and experimental determination of the material intrinsic length scale of strain gradient plasticity theory from micro- and nano-indentation experiments. Int. J. Plast. 20, 1139–1182 (2004)
Milman Y.V.: Plasticity characteristic obtained by indentation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 074013 (2008)
Yang B., Vehoff H.: Dependence of nanohardness upon indentation size and grain size—a local examination of the interaction between dislocations and grain boundaries. Acta Mater. 55, 849–856 (2007)
Petryk H., Stupkiewicz S.: A quantitative model of grain refinement and strain hardening during severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 444, 214–219 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almasri, A.H., Voyiadjis, G.Z. Nano-indentation in FCC metals: experimental study. Acta Mech 209, 1–9 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-009-0151-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-009-0151-x