Summary
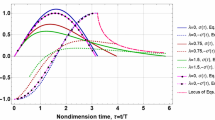
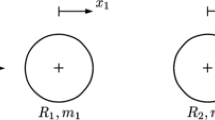
When an impact load is applied laterally to a plate, the deflection gradually spreads over time until the entire plate radius is affected. The determination of effects for a short-duration impact presents substantial mathematical difficulties. The normal-mode superposition is not only awkward but it does not lead to closed-form solutions. Some of the past works gave a possibility of such a solution by assuming a certain flexural wave spreading from the impact point. The complexity involved in that was simplified in this paper. This main part of this work is based on a shear wave approach, by relating the lateral stiffness to the propagation of a shear wave from impact point. This, along with some other simplifications, makes it possible to obtain the peak contact force by using compact expressions. The development is limited to impactor mass not exceeding one-half of the plate mass. The evaluation of rebound velocity or the coefficient of restitution was successfully resolved for only a limited range of parameters. The other subtopic is the quantification of the contact problem itself, which is nonlinear by nature. A transparent method of linearization is proposed, based either on experiment or on Hertzian formulation. The results presented in this paper are compared with the answers from finite-element simulations, physical experiments and with some cases available from literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldsmith W. (1960). Impact. Edward Arnold, London
Zener C. (1941). The intrinsic inelasticity of large plates. Phys. Rev. 59: 669
Sondergaard R. (1990). Measurements of solid spheres bouncing off flat plates. J. Appl. Mech. 57: 694
Johnson W. (1972). Impact Strength of Materials. Edward Arnold, London
Lambourg, C., et al.: Time-domain simulation of damped impacted plates. A numerical model and results. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 112 (2001)
Olsson, R.: Engineering Method for Prediction of Impact Response and Damage in Sandwich Panels. Swedish Defence Research Agency, FOI-R-0136-SE, June 2001
Nowacki W. (1961). Dynamics of Building Structures (in Polish). Arkady, Warsaw
Szuladzinski, G.: Transient response of circular, elastic plates to point loads (submitted)
Johnson K.L. (1985). Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, London
Blevins, R.D.: Formulas for Natural Frequency and Mode Shape. Van Nostrand Reinhold (1979)
ANSYS General-Purpose Structural Analysis Code, Version 10. Ansys Inc, Pittsburgh (2005)
Timoshenko S. (1951). Theory of Elasticity. McGraw-Hill, New York
Szuladzinski, G.: Parameters of impact of a heavy mass falling onto a concrete surface. In: Proc. 4th Asia-Pacific Conf. on Shock and Impact Loads on Structures. Singapore, November 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szuladzinski, G. Mass-plate impact parameters for the elastic range. Acta Mech 200, 111–125 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-008-0578-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-008-0578-5