Summary
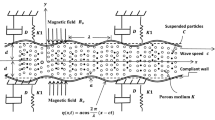
In real systems there is always a certain amount of slip, which, however, is hard to detect experimentally because of the required space resolution. In this paper, we analyze the effect of slip boundary conditions on the dynamics of fluids in porous media by studying the flow of a Newtonian and non-Newtonian Maxwellian fluid in an axisymmetric cylindrical tube (pore), in which the flow is induced by traveling transversal waves on the tube wall. Like in peristaltic pumping, the traveling transversal waves induce a net flow of the liquid inside the pore. The viscosity as well as the compressibility of the liquid is taken into account. This problem has numerous applications in various branches of science, including stimulation of fluid flow in porous media under the effect of elastic waves and studies of blood flow dynamics in living creatures. The Navier-Stokes equations for an axisymmetric cylindrical pore are solved by means of a perturbation analysis, in which the ratio of the wave amplitude to the radius of the pore is small parameter. In the second order approximation, a net flow induced by the traveling wave is calculated for various values of the compressibility of the liquid, relaxation time and Knudsen number. The calculations disclose that the compressibility of the liquid, Knudsen number of slip flow and non-Newtonian effects in presence of peristaltic transport have a strong influence of the net flow rate. The effects of all parameters of the problem are numerically discussed and graphically explained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. T. Aarts G. Ooms (1998) ArticleTitleNet flow of compressible viscous liquids induced by traveling waves in porous media J. Engng. Math. 34 435–450 Occurrence Handle0989.76079 Occurrence Handle1657896 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004314014329
L. K. Antanovskii H. Ramkisson (1997) ArticleTitleLong wave peristaltic transport of a compressible viscous liquid in a finite pipe subject to a time-dependent pressure drop Fluid Dyn. Res. 19 115–123 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-5983(96)00030-5
A. Jabbarzadeh J. D. Atkinson R. I. Tanner (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of the wall roughness on slip and rheological properties of hexadecane in molecular dynamics simulation of Couette shear flow between two sinusoidal walls Phys. Rev. E 61 IssueID1 690–699 Occurrence Handle10.1103/PhysRevE.61.690
W. Kwang H. Chu J. Fang (2000) ArticleTitlePeristaltic transport in a slip flow Euro. Phys. J. B 16 543–547 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s100510070215
G. C. Georgiou M. J. Crochet (1994) ArticleTitleCompressible viscous flow in slits with slip at the wall J. Rheol. 38 IssueID3 639–654 Occurrence Handle10.1122/1.550479
F. Lu H. P. Lee S. P. Lim (2003) ArticleTitleMechanical description of interfacial slips for quartz crystal micro balances with viscoelastic liquid loading Smart Mater. Struct. 12 881–898 Occurrence Handle10.1088/0964-1726/12/6/004
J. R. Castrejon-Pita J. A. Rio Particledel A. A. Castrejon-Pita G. Huelsz (2003) ArticleTitleExperimental observation of dramatic differences in the dynamic response of Newtonian and Maxwellian fluids Phys. Rev. E 68 046301 Occurrence Handle10.1103/PhysRevE.68.046301
M. Torralba A. A. Castrejon-Pita J. R. Castrejon-Pita G. Huelsz J. A. Rio Particledel J. Ortin (2005) ArticleTitleMeasurements of the bulk and interfacial velocity profiles in oscillating Newtonian and Maxwellian fluids Phys. Rev. E 72 016308 Occurrence Handle10.1103/PhysRevE.72.016308
I. J. Roa K. R. Rajagapol (1999) ArticleTitleThe effect of slip boundary conditions on the flow of fluids in a channel Acta Mech. 135 113–126 Occurrence Handle1690164 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01305747
F. E. Larrode C. Housiadas Y. Drossinos (2000) ArticleTitleSlip-flow heat transfer in circular tubes Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 43 2669–2680 Occurrence Handle0983.76079 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0017-9310(99)00324-5
W. Chu (1996) ArticleTitleStokes slip flow between corrugated walls ZAMP 47 591–598 Occurrence Handle0864.76025 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00914873
K.-H. W. Chu (1999) ArticleTitleSmall-Knudsen-number flow in a corrugated tube Meccanica 34 133–137 Occurrence Handle0945.76563 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004570107716
M. N. Kogan (1969) Rarefied gas dynamics Plenum Press New York
A. Vasudeviah K. Balamurugan (1999) ArticleTitleStokes slip flow in a corrugated pipe Int. J. Engng. Sci. 37 1629–1641 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0020-7225(98)00138-4
Y. Zhu S. Granick (2002) ArticleTitleLimits of the hydrodynamic no-slip boundary condition Phys. Rev. Lett 88 IssueID10 106102 Occurrence Handle10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.106102
F. Yin Y. C. Fung (1969) ArticleTitlePeristaltic waves in circular cylindrical tubes J. App. Mech. 36 579–587
D. Tsiklauri I. Beresnev (2001) ArticleTitleNon-Newtonian effects in the peristaltic flow of a Maxwell fluid Phys. Rev. E 64 036303 Occurrence Handle10.1103/PhysRevE.64.036303
J. A. Rio ParticleDel M. L. Haro ParticleDe S. Whitaker (1998) ArticleTitleEnhancement in the dynamic response of a viscoelastic fluid flowing in a tube Phys. Rev. E 58 6323–6327 Occurrence Handle10.1103/PhysRevE.58.6323
Anderson, J. D.: Modern compressible flow with historical perspective. McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. 1990.
C. Y. Wang (2003) ArticleTitleStagnation flows with slip: exact solutions of the Navier-Stokes Equations ZAMP 54 184–189 Occurrence Handle1036.76005 Occurrence Handle10.1007/PL00012632
G. S. Beavers D. D. Joseph (1967) ArticleTitleBoundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall J. Fluid Mech. 30 197–207 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112067001375
Nayfeh, A. H.: Perturbation methods. John Wiley & Sons 1973.
S. Takabatake K. Ayukawa A. Mori (1988) ArticleTitlePeristaltic pumping in circular cylindrical tubes: a numerical study of fluid transport and its efficiency J. Fluid Mech. 193 267–283 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112088002149
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Shehawy, E.F., El-Dabe, N.T. & El-Desoky, I.M. Slip effects on the peristaltic flow of a non-Newtonian Maxwellian fluid. Acta Mechanica 186, 141–159 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-006-0343-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-006-0343-6