Summary
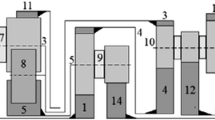
The non-oriented and oriented graph techniques are used for kinematic analysis of bevel-gear trains. In both techniques, the kinematic structure of the gear trains is represented by a graph. Although the non-oriented graphs are simple to draw, they are used only to determine the carrier nodes of the fundamental circuits. On the other hand, the oriented graphs carry more information than the non-oriented graphs since each line in an oriented graph represents a pair of complementary variables. In this paper, these two techniques are compared and the advantages of the oriented graph technique are demonstrated by the kinematic analysis of an articulated robotic mechanism used by the Cincinnati Milacron T3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freudenstein, F.: An application of boolean algebra to the motion of epicyclic drives. ASME J. Eng. Ind. 93, 176–182 (1971).
Freudenstein, F., Yang, A. T.: Kinematics and statics of coupled epicyclic spur-gear trains. Mechanism Machine Design 7, 263–275 (1972).
Tsai, L.W.: The kinematics of spatial robotic bevel-gear trains. IEEE J. Robotics Automation 4, 150–155 (1988).
Koenig, H. E., Blackwell, W. A.: Electromechanical system theory. New York: McGraw-Hill 1961.
Koenig, H. E., Tokad, Y., Kesevan, H. K.: Analysis of discrete physical systems. New York: McGraw-Hill 1967.
Koenig, H. E., Reed, M. B.: Linear-graph representation of multi-terminal elements. In: Proc. Natl. Electr. Conf., pp. 661–674, 1958.
Roe, P. H. O’N.: Networks and systems. Reading, Mass.: Addison Wesley 1966.
Chou, J. C. K., Kesevan, H. K., Singhal, K.: A systems approach to three-dimensional multibody systems using graph-theoretical model. IEEE Trans. Sys. Man. Cyber. SMC-12, 219–230 (1986).
Tokad, Y.: A network model for rigid-body motion. Dynamics Control 2, 59–82 (1992).
Uyguroglu, M., Tokad, Y.: Kinematic analysis of robotic bevel-gear trains: An application of network model approach. Meccanica 33, 177–194 (1998).
Uyguroglu, M., Tokad, Y.: A dynamic model for the bendix wrist. Acta Mech. 133, 199–218 (1999).
Stackhouse, T.: A new concept in wrist flexibility. In: Proc. 9th. Int. Symp. on Industrial Robots, pp. 589–599, Washington, D.C., 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uyguroğlu, M., Demirel, H. Kinematic analysis of bevel-gear trains using graphs. Acta Mechanica 177, 19–27 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-005-0212-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-005-0212-8