Summary
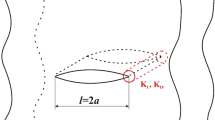
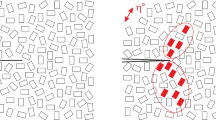
A crack with growth in ferroelectric ceramics under purely electric loading is analyzed. The crack tip stress intensity factor for the growing crack under small scale conditions is evaluated by employing the model of nonlinear domain switching. The electrical fracture toughness is obtained from the result of the stress intensity factor. It is shown that the ferroelectric material can be either toughened or weakened as the crack grows. Fatigue crack growth in a ferroelectric material under cyclic electric loading is also examined. The incremental fatigue crack growth under cyclic electric loading is obtained numerically. The fatigue crack growth rate is affected strongly by the electrical nonlinear behavior. It is found that the curve of fatigue crack growth rate versus electric field intensity factor is linear on the log-log plot at intermediate values of the electric field intensity factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, T.-Y., Zhao, M. H., Tong, P.: Fracture of piezoelectric ceramics. Adv. Appl. Mech. 38, 147–289 (2002).
McMeeking, R. M., Evans, A. G.: Mechanics of transformation-toughening in brittle materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 65, 242–246 (1982).
Budiansky, B., Hutchinson, J. W., Lambropoulos, J. C.: Continuum theory of dilatant transformation toughening ceramics. Int. J. Solids Struct. 19, 337–355 (1983).
Zhu, T., Yang, W.: Toughness variation of ferroelectrics by polarization switch under nonuniform electric field. Acta Mater. 45, 4695–4702 (1997).
Yang, W., Zhu, T.: Switch-toughening of ferroelectrics subjected to electric fields. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 291–311 (1998).
Zeng, X., Rajapakse, R. K. N. D.: Domain switching induced fracture toughness variation in ferroelectrics. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 203–211(2001).
Meschke, F., Kolleck, A., Schneider, G. A.: R-curve behavior of BaTiO3 due to stress-induced ferroelastic domain switching. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 17, 1143–1149 (1997).
Kolleck, A., Schneider, G. A., Meschke, F. A.: R-curve behavior of BaTiO3- and PZT-ceramics under the influence of an electric field applied parallel to the crack front. Acta Mater. 48, 4099–4113 (2000).
Fett, T., Glazounov, A., Hoffmann, M. J., Munz, D., Thun, G.: On the interpretation of different R-curves for soft PZT. Engng. Fract. Mech. 68, 1207–1218 (2001).
Förderreuther, A., Thurn, G., Zimmermann, A., Aldinger, F.: R-curve effect, influence of electric field and process zone in BaTiO3- ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 2023–2031 (2002).
Cao, H., Evans, A. G.: Electric-field-induced fatigue crack growth in piezoelectrics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77, 1783–1786 (1994).
Weitzing, H., Schneider, G. A., Steffens, J., Hammer, M., Hoffmann, M. J.: Cyclic fatigue due to electric loading in ferroelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 1333–1337 (1999).
Liu, B., Fang, D., Hwang, K. C.: Electric-field-induced fatigue crack growth in ferroelectric ceramics. Mater. Lett. 54, 442–446 (2002).
Zhu, T., Yang, W.: Fatigue crack growth in ferroelectrics driven by cyclic electric loading. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 47, 81–97 (1999).
Gao, H., Barnett, D. M.: An invariance property of local energy release rates in a strip saturation model of piezoelectric fracture. Int. J. Fract. 79, R25–R29 (1996).
Gao, H., Zhang, T. Y., Tong, P.: Local and global energy release rates for an electrically yielded crack in a piezoelectric ceramic. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 45, 491–510 (1997).
Beom, H. G., Atluri, S. N.: Effect of electric fields on fracture behavior of ferroelectric ceramics. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 51, 1107–1125 (2003).
Beom, H. K., Youn, S. K.: Electrical fracture toughness for a conducting crack in ferroelectric ceramics. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 145–157 (2004).
Jeong, K. M., Beom, H. G.: Conducting crack growth in ferroelectric ceramics subjected to electric fields. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 275–282 (2004).
Jeong, K. M., Kim, I. O., Beom, H. G.: Effect of electric displacement saturation on the stress intensity factor for a crack in a ferroelectric ceramic. Mech. Res. Comm. 31, 373–382 (2004).
Beom, H. G.: Small scale nonlinear analysis of electrostrictive crack problems. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 47, 1379–1395 (1999).
Hwang, S. C., Lynch, C. S., McMeeking, R. M.: Ferroelectric/ferroelastic interactions and a polarization switching model. Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 2073–2084 (1995).
Rice, J. R.: Three-dimensional elastic crack tip interactions with transformation strains and dislocations. Int. J. Solids Struct. 21, 781–791 (1985).
Gao, H.: Application of 3-D weight functions – I. Formulations of crack interfaces with transformation strains and dislocations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 37, 133–153 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beom, H., Jeong, K. Crack growth in ferroelectric ceramics under electric loading. Acta Mechanica 177, 43–60 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-004-0198-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-004-0198-7