Summary.
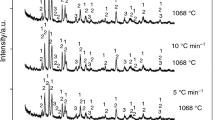
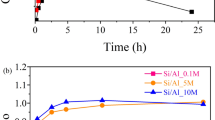
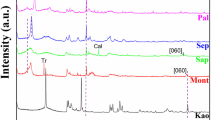
Solid crystalline calcium silicate hydrate (I) synthesized from equimolar amounts of Ca and Si under hydrothermal conditions at 120°C shows cation exchange properties towards divalent metal cations such as Ni, Cu, Cd, or Hg. It also exhibits caesium selectivity in the presence of Na+. The exchange capacity and selectivity of the solid can be increased by 10 and 28%, respectively, upon substitution of 0.01 mol of the Ca2+ in its structure by Na+. The ability of metal cation uptake by the solid was found to obey the order Ni2+ > Hg2+ > Cu2+ > Cd2+. The different affinities of calcium silicate hydrate (I) towards these ions can be used for their separation from solutions and also in nuclear waste treatment. The mechanism of the exchange reaction is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received June 11, 2001. Accepted September 10, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Korashy, S. Synthetic Crystalline Calcium Silicate Hydrate (I): Cation Exchange and Caesium Selectivity. Monatshefte fuer Chemie 133, 333–343 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007060200012
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007060200012