Abstract
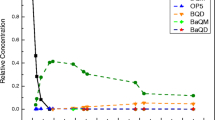
The objective of the presented paper is to characterize the effectiveness of the removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater during ozonation in laboratory-scale conditions. Almost 100 pharmaceuticals and their metabolites from different therapeutic classes were studied in effluent from the wastewater treatment plant, Devínska Nová Ves, used for ozonation. Telmisartan, diclofenac, and fexofenadine were found at the highest concentrations (1800 ng/dm3, 680 ng/dm3, and 620 ng/dm3, respectively). The concentrations of another 13 pharmaceuticals and metabolites exceeded 100 ng/dm3, and the rest of the compounds were below 100 ng/dm3. These water samples underwent ozonation in intervals of 0–10 min. The flow of ozone during the test was 50 mg O3/min. The results show that the removal of pharmaceuticals is significant after the first minute of ozonation, when most of the studied compounds were below the limit of quantification. The total concentration of the studied compounds after the first minute decreased to 190 ng/dm3 (97.2% removal efficiency). More than 99% removal efficiency was achieved after 10 min of ozonation.
Graphic abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tran NH, Gin KYH (2017) Sci Total Environ 1503:599–600
Couto CF, Lange LC, Amaral MCS (2019) J Water Process Eng 32:100927
Rizzo L, Malato S, Antakyali D, Bertsou VG, Dolic MB, Gernjak W, Heath E, Ivancev-Tumbas I, Karaolia P, Lado Ribeiro AR, Mascolo G, McArdell ChS, Schaar H, Silva AMT, Fatta-Kassinos D (2019) Sci Total Environ 655:986
Peña A, Delgado-Moreno L, Rodríguez-Liébana JA (2019) Sci Total Environ 134:468
Altmann J, Ruhl AS, Zietzschmann F, Jekel M (2014) Water Res 55:185
Czölderová M, Behúl M, Filip J, Zajíček P, Grabic R, Vojs-Staňová A, Gál M, Kerekeš K, Híveš J, Ryba J, Rybanská M, Brandeburová P, Mackuľak T (2018) Chem Eng J 349:269
Guillossou R, Le Roux J, Mailler R, Pereira-Derome CS, Varrault G, Bressy A, Vulliet E, Morlay C, Nauleau F, Rocher V, Gasperi J (2020) Water Res 172:115487
Hansen KMS, Spiliotopoulou A, Chhetri RK, Casas ME, Bester K, Andersen HR (2016) Chem Eng J 290:507
Marcelino RBP, Leão MMD, Lago RM, Amorim CC (2017) J Environ Manag 195:110
Wang J, Chen H (2020) Sci Total Environ 704:135249
Hoigné J, Bader H (1976) Water Res 10:377
Keysers C, Grunebaum T, Thöle, Pinnekamp J (2013) Micropol and Ecohazard 2013. The 8th IWA Specialist Conference on Assessment and Control of Micropollutants/Hazardous Substances in Water
Knopp G, Prasse C, Ternes TA, Cornel P (2016) Water Res 100:580
Margot J, Kienle C, Magnet A, Weil M, Rossi L, Felippe Alencastro L, Abegglen C, Thonney D, Chevre N, Scharer M, Barrz DA (2013) Sci Total Environ 480:461–462
Lee Y, von Gunten U (2012) Water Res 46:6177
Borowska E, Bourgin M, Hollender J, Kienle C, McArdell ChS, von Gunten U (2016) Water Res 94:350
Derco J, Valičková M, Šilhárová K, Dudáš J, Luptáková A (2013) Chem Pap 67:1585
Fedorova G, Randak T, Lindberg RH, Grabic R (2013) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 27:1751
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency under the contracts No. APVV 0122-12 and APVV 0119-17, by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic via project “CENAKVA” (No. LM2018099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szabová, P., Hencelová, K., Sameliaková, Z. et al. Ozonation: effective way for removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater. Monatsh Chem 151, 685–691 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-020-02600-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-020-02600-x