Abstract
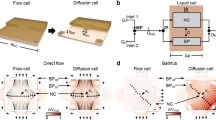
In the frame of this contribution, two electrochemical flow cells developed for scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) are presented. Forced convection was generated by a flow of the mediator solution through the flow cells. A description of the mandatory design aspects of the experimental flow cell setups is included. Using a macroscopic working electrode as a substrate electrode, forced convection leads to the formation of a stable diffusion layer during amperometric experiments in contrast to a growing diffusion layer in quiescent solution. To characterize the effects of forced convection, the diffusion layer around a platinum substrate electrode integrated into the cells was investigated utilizing chronoamperometric measurements and hydrodynamic SECM imaging in amperometric substrate generation-tip collection (SG/TC) mode. Both methods proved the stability and the time-independency of the diffusion layer. Mathematical simulations using COMSOL Multiphysics were computed to investigate the flow profile generated by the flowing mediator solution in the relevant region close to the substrate electrode. In summary, two different electrochemical flow cells for SECM were developed and characterized. Both cell designs enabled steady-state diffusion layer characteristics at a macroscopic substrate electrode offering interesting possibilities such as time-independent measurements in the context of the SG/TC mode.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kwak J, Bard AJ (1989) Anal Chem 61:1794
Bard AJ, Fan FF, Kwak J, Lev O (1989) Anal Chem 61:132
Liu HY, Fan FRF, Lin CW, Bard AJ (1986) J Am Chem Soc 108:3838
Bergner S, Vatsyayan P, Matysik FM (2013) Anal Chim Acta 775:1
Polcari D, Dauphin-Ducharme P, Mauzeroll J (2016) Chem Rev 116:13234
Bard AJ, Mirkin MV (2012) Scanning electrochemical microscopy, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wiesendanger R (1994) Scanning probe microscopy and spectroscopy: methods and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wittstock G, Burchardt M, Pust SE, Shen Y, Zhao C (2007) Angew Chem 119:1604
Iffelsberger C, Vatsyayan P, Matysik FM (2017) Anal Chem 89:1658
Combellas C, Fermigier M, Fuchs A, Kanoufi F (2005) Anal Chem 77:7966
Kottke PA, Fedorov AG (2005) J Electroanal Chem 583:221
Nkuku CA, LeSuer RJ (2007) J Phys Chem B 111:13271
Cornut R, Poirier S, Mauzeroll J (2012) Anal Chem 84:3531
Kuss S, Kuss C, Trinh D, Schougaard SB, Mauzeroll J (2013) Electrochim Acta 110:42
Kuss S, Trinh D, Danis L, Mauzeroll J (2015) Anal Chem 87:8096
Edwards MA, Whitworth AL, Unwin PR (2011) Anal Chem 83:1977
Cooper JA, Compton RG (1998) Electroanalysis 10:141
Fisher AC, Compton RG (1991) J Phys Chem 95:7538
Lee C, Miller CJ, Bard AJ (1991) Anal Chem 63:78
Acknowledgements
Timo Raith gratefully acknowledges the financial support from the Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raith, T., Wert, S., Iffelsberger, C. et al. Development and characterization of electrochemical flow cells for hydrodynamic scanning electrochemical microscopy. Monatsh Chem 149, 1671–1677 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-018-2201-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-018-2201-3