Abstract
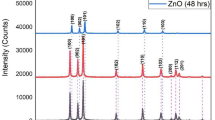
ZnO photoelectrodes were successfully treated using hydrochloric vapor. The vapor was generated from hydrochloric acid solution with sonication assistance. The morphology showed a formation of plate-like structures after the vapor treatment, resulting in light scattering which was observed in terms of increased reflectance compared with the non-treated photoelectrodes. A dye-sensitized solar cell fabricated with the treated photoelectrodes exhibited an enhanced power conversion efficiency of 3.00% in comparison to the non-treated photoelectrodes base of 2.35%. The enhanced power conversion efficiency was observed in direct relation to the increased short-circuit current density. The increased short-circuit current density is due to the achieved light scattering in the photoelectrodes. Moreover, an extended open-circuit voltage was observed due to reduced electron recombination in the device. Therefore, a chemical vapor treatment of ZnO photoelectrodes via hydrochloric acid resulted in a successful scattering layer formation and a reduced recombination process for power conversion efficiency enhancement of ZnO dye-sensitized solar cells.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang H, Wang B, Yu J, Hu Y, Xia C, Zhang J, Liu R (2015) Sci Rep 5:9305
Xue X, Tian J, Liao W, Shan Z (2014) Electrochim Acta 123:463
Sutthana S, Wongratanaphisan D, Gardchareon A, Phadungdhitidhada S, Ruankham P, Choopun S (2016) Surf Coat Tech 306:30
Deepak TG, Anjusree GS, Thomas S, Arun TA, Nair SV, Sreekumaran Nair A (2014) RSC Adv 4:7615
Que M, Que W, Yin X, Shao J (2016) Mater Res Bull 83:19
Musavi Gharavi PS, Mohammadi MR (2015) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 137:113
Arachchi NDH, Peiris GS, Shimomura M, Jayaweera PM (2016) Hydrometallurgy 166:73
Wan K, Wu F, Dou Y, Fang L, Mao C (2016) J Alloy Compd 680:373
Chu L, Qin Z, Liu W, Ma XG (2016) Appl Surf Sci 389:802
Zhao P, Yao S, Wang M, Wang B, Sun P, Liu F, Liang X, Sun Y, Lu G (2015) Electrochim Acta 170:276
Peng JD, Shih PC, Lin HH, Tseng CM, Vittal R, Suryanarayanan V, Ho KC (2014) Nano Energy 10:212
Wu MT, Chow TJ (2014) Microporous Mesoporous Mater 196:354
Fei C, Tian J, Wang Y, Liu X, Lv L, Zhao Z, Cao G (2014) Nano Energy 10:353
Yang S, Kim H, Ahn SH, Lee CS (2015) Electrochim Acta 166:117
Towannang M, Pimanpang S, Thiangkaew A, Rutphonsan P, Maiaugree W, Harnchana V, Jarernboon W, Amornkitbamrung V (2012) Synth Met 162:1954
Hua Y, Chang S, He J, Zhang C, Zhao J, Chen T, Wong WY, Wong WK, Zhu X (2014) Chem Eur J 6300
Park KH, Mondal S, Ghosh S, Das S, Bhaumik A (2016) Microporous Mesoporous Mater 225:255
Choi J, Kang G, Park T (2015) Chem Mater 27:1359
Vibha S, Aswal DK (2015) Semicond Sci Technol 30:064005
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI), Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moungsrijun, S., Sujinnapram, S., Choopun, S. et al. Chemical vapor treatment of zinc oxide photoelectrodes for efficiency enhancement of dye-sensitized solar cells. Monatsh Chem 148, 1191–1196 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-017-1952-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-017-1952-6