Summary.
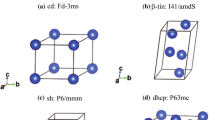
The main reason of the degradation of silicon monocrystals at heating is a structural transformation connected with a partial transition of the diamond-like structure into the structure of white tin. The reason for this transformation being observed under high pressures is the appearance of stress zones at the boundaries of variously oriented crystal microvolumes due to heat expansion anisotropy. The high stress concentration in the microvolumes provides sufficient pressure for the indicated phase transformation which results in the observed degradation of the electrophysical properties of silicon. The prevention of the structural transformation is considered to be possible by doping of Si by transition or rare-earth metals which increases the interatomic energy and decreases the thermal expansion coefficient. The choice of the doping additions is based on the bonding energy and the charge density calculated for a system of non-polarised ionic radii. The technology to increase the thermal stability of silicon has been patented#.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
VM Glazov VS Zemskov (1967) Physical–Chemistry Foundation of Semiconductors Alloying. Science Moscow 503
VM Glazov VB Koltsov VZ Cutsova AR Regel YN Taran GG Timoshina KI Uzlov ES Falkevitch (1991) Fiz Tekn Poluprov 25 588 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksF2nt78%3D
YY Tonkov (1979) Phase Diagram of Elements at High Pressure. Science Moscow 286
P Pirous R Chaim U Dahmen KH Westmacott (1990) Acta Metall Mater 38 IssueID2 313
P Pirous R Chaim U Dahmen KH Westmacott (1990) Acta Metall Mater 38 IssueID2 323
U Dahmen KH Westmacott P Pirous R Chaim (1990) Acta Metall Mater 38 IssueID2 329
YN Taran VZ Cutcova KI Uzlov (1987) Dokl Akad Nauk USSR Phys-Mat and Tech Sci 6 74
EV Prihod’ko (1995) Metallochemistry of Multicomponent Systems. Metallurgiya Moscow 320
AG Milnes (1974) Deep Impurities in Semiconductors. Carnegie-Mellon University Wiley New York London Sydney Toronto 562
Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (1989–1990). CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, p F197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Patent of Russia, No 2094904, 13/10/1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potemkin, A., Koltsov, V. & Vahrameeva, M. Thermodynamic Aspects of the Increased Thermal Stability of Silicon by Doping with Transition or Rare-earth Metals. Monatsh. Chem. 136, 1877–1883 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-005-0381-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-005-0381-0