Summary
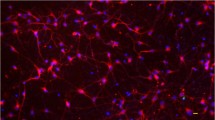
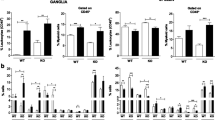
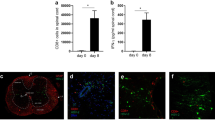
Clearance of herpes simplex virus (HSV) from sensory ganglia of infected mice is dependent on CD8+ cells but not on the death of infected neurons. The mechanism of action of CD8+ cells in HSV infected ganglia is therefore unknown. The determine which cytokines might be involved in the CD8+ cell dependent response to ganglionic HSV infection, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and IFN-γ mRNA levels were measured in infected ganglia from immunocompetent and anti-CD8 treated mice. Anti-CD8 treatment increased the abundance of mRNA encoding IL-4, and, to a lesser extent, IL-2, and IL-6. Significantly, IFN-γ mRNA was not affected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received May 17, 1999 Accepted June 29, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tscharke, D., Simmons, A. Anti-CD8 treatment alters interleukin-4 but not interferon-γ mRNA levels in murine sensory ganglia during herpes simplex virus infection. Arch. Virol. 144, 2229–2238 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050637
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050637