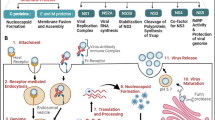
Abstract
Previous studies have demonstrated the relevance of several soluble molecules in the pathogenesis of dengue. In this regard, a possible role for angiotensin II (Ang II) in the pathophysiology of dengue has been suggested by the observation of a blockade of Ang II in patients with dengue, increased expression of molecules related to Ang II production in the plasma of dengue patients, increased expression of circulating cytokines and soluble molecules related to the action of Ang II, and an apparent relationship between DENV, Ang II effects, and miRNAs. In addition, in ex vivo experiments, the blockade of Ang II AT1 receptor and ACE-1 (angiotensin converting enzyme 1), both of which are involved in Ang II production and its function, inhibits infection of macrophages by DENV, suggesting a role of Ang II in viral entry or in intracellular viral replication of the virus. Here, we discuss the possible mechanisms of Ang II in the entry and replication of DENV. Ang II has the functions of increasing the expression of DENV entry receptors, creation of clathrin-coated vesicles, and increasing phagocytosis, all of which are involved in DENV entry. This hormone also modulates the expression of the Rab5 and Rab7 proteins, which are important in the endosomal processing of DENV during viral replication. This review summarizes the data related to the possible involvement of Ang II in the entry of DENV into cells and its replication.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brady OJ, Gething PW, Bhatt S, Messina JP, Brownstein JS, Hoen AG, Moyes CL, Farlow AW, Scott TW, Hay SI (2012) Refining the global spatial limits of dengue virus transmission by evidence-based consensus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1760. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001760
Messina JP, Brady OJ, Scott TW, Zou C, Pigott DM, Duda KA, Bhatt S, Katzelnick L, Howes RE, Battle KE, Simmons CP, Hay SI (2014) Global spread of dengue virus types: mapping the 70 year history. Trends Microbiol 22:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2013.12.011
Recker M, Vannice K, Hombach J, Jit M, Simmons CP (2016) Assessing dengue vaccination impact: Model challenges and future directions. Vaccine 34:4461–4465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.06.082
Screaton G, Mongkolsapaya J, Yacoub S, Roberts C (2015) New insights into the immunopathology and control of dengue virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol 15:745–759. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3916
Halstead SB, Nimmannitya S, Cohen SN (1970) Observations related to pathogenesis of dengue hemorrhagic fever. IV. Relation of disease severity to antibody response and virus recovered. Yale J Biol Med 42:311–328
Littaua R, Kurane I, Ennis FA (1990) Human IgG Fc receptor II mediates antibody-dependent enhancement of dengue virus infection. J Immunol 144:3183–3186
Kontny U, Kurane I, Ennis FA (1988) Gamma interferon augments Fc gamma receptor-mediated dengue virus infection of human monocytic cells. J Virol 62:3928–3933. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.62.11.3928-3933.1988
Nanaware N, Banerjee A, Mullick Bagchi S, BagchiP, Mukherjee A (2021) Dengue Virus Infection: A Tale of Viral Exploitations and Host Responses. Viruses 13: 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101967
Dalrymple N, Mackow ER (2011) Productive dengue virus infection of human endothelial cells is directed by heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycan receptors. J Virol 85:9478–9485. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.05008-11
Cruz-Oliveira C, Freire JM, Conceição TM, Higa LM, Castanho M, Da Poian AT (2015) Receptors and routes of dengue virus entry into the host cells. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:155–170. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuu004
Mukhopadhyay S, Kuhn RJ, Rossmann MG (2005) A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1067
Martina BE, Koraka P, Osterhaus AD (2009) Dengue virus pathogenesis: an integrated view. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:564–581. https://doi.org/10.11128/CMR.00035-09
Mosquera-Sulbaran JA, Pedreañez A, Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Hernandez-Fonseca H (2023) Angiotensin II and dengue. Arch Virol 168:191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-023-05814-6
Hunyady L, Catt KJ (2006) Pleiotropic AT1 receptor signaling pathways mediating physiological and pathogenic actions of angiotensin II. Mol Endocrinol 20:953–970. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2004-0536
Dandona P, Dhindsa S, Ghanim H, Chaudhuri A (2007) Angiotensin II and Inflammation: The Effect of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade. J Hum Hypertens 21:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002101
Hernández-Fonseca JP, Durán A, Valero N, Mosquera J (2015) Losartan and enalapril decrease viral absorption and interleukin 1 beta production by macrophages in an experimental dengue virus infection. Arch Virol 160:2861–2865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2581-1
Timmermans PB, Wong PC, Chiu AT, Herblin WF, Benfield P, Carini DJ, Lee RJ, Wexler RR, Saye JA, Smith RD (1993) Angiotensin II receptors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Pharmacol Rev 45:205–251
Van Kats JP, Danser AH, van Meegen JR, Sassen LM, Verdouw PD, Schalekamp MA (1998) Angiotensin production by the heart: a quantitative study in pigs with the use of radiolabeled angiotensin infusion. Circulation 98:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1161/01. cir.98.1.73
Kobori H, Pieto-Carrasquero MC, Ozawa Y, Navar LG (2004) AT1 receptor mediated augmentation of intrarenal angiotensinogen in angiotensin II dependent hypertension. Hypertension 43:1126–1132. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000122875.91100.28
Moulik S, Speth RC, Turner BB, Rowe BP (2002) Angiotensin II receptor subtype distribution in the rabbit brain. Exp Brain Res 142:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-001-0940-5
Ghiani BU, Masini MA (1995) Angiotensin II bindings sites in the rat pancreas and their modulation after sodium loading and depletion. Comp Biochem Physiol Physiol 111:439–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9629(95)00030-b
Karlsson C, Lindell K, Ottosson M, Sjostrom L, Carlsson B, Carlsso L (1998) Human Adipose Tissue Expresses Angiotensinogen and Enzymes Required for Its Conversion to Angiotensin II. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 83:3925–3929. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.83.11.5276
de Mello W (2003) Effect of extracellular and intracellular angiotensin on heart cell function; on the cardiac renin-angiotensin system. Regul Pept 114:87–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-0115(03)00121-6
Re RN, Cook JL (2006) The intracrine hypothesis: an update. Regul Pept 133:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regpep.2005.09.012
Rüster C, Wolf G (2013) The role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in obesity-related renal diseases. Semin Nephrol 33:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.12.002
Ruster C, Wolf G (2006) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2985–2991. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006040356
Porrello ER, Delbridge LM, Thomas WG (2009) The angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor: an enigmatic seven transmembrane receptor. Front BioSci 14:958–972. https://doi.org/10.2741/3289
Schulman IH, Raij L (2008) The angiotensin II type 2 receptor: what is its clinical significance? Curr Hypertens Rep 10:188–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-008-0036-8
Marchesi C, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL (2008) Role of the renin-angiotensin system in vascular inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2008.05.003
Chua CC, Hamdy RC, Chua BH (1998) Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by angiotensin II in rat heart endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1401:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-4889(97)00129-8
Kitayama H, Maeshima Y, Takazawa Y, Yamamoto Y, Wu Y, Ichinose K, Hirokoshi K, Sugiyama H, Yamasaki Y, Makino H (2006) Regulation of angiogenic factors in angiotensin II infusion model in association with tubulointerstitial injuries. Am J Hypertens 19:718–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.09.022
Suzuki Y, Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O, Ruperez M, Esteban V, Egido J (2003) Inflammation and angiotensin II. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:881–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00271-6
Alvarez A, Cerda-Nicolas M, Abu N, Nabah Y, Mata M, Issekutz AC, Panés J, Lobb RR, Sanz MJ (2004) Direct evidence of leukocyte adhesion in arterioles by angiotensin II. Blood 104:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-08-2974
Piqueras L, Kubes P, Alvarez A, O’Connor E, Issekutz AC, Esplugues JV, Sanz MJ (2000) Angiotensin II induces leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions in vivo via AT(1) and AT(2) receptor-mediated P-selectin upregulation. Circulation 102:2118–2123. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.102.17.2118
Pueyo ME, Gonzalez W, Nicoletti A, Savoie F, Arnal JF, Michel JB (2000) Angiotensin stimulates endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 via nuclear factor-kappaB activation inducedby intracellular oxidative stress. Artherocler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:645–651. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.20.3.645
Crowley SD, Frey CW, Gould SK, Griffiths R, Ruiz P, Burchette JL, Howell DN, Makhanova N, Yan M, Kim HS, Tharaux PL, Coffman TM (2008) Stimulation of lymphocyte responses by angiotensin II promotes kidney injury in hypertension. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 295:F515–F524. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00527.2007
Jurewicz M, McDermott DH, Sechler JM, Tinckam K, Takakura A, Carpenter CB, Milford E, Abdi R (2007) Human T and natural killer cells possess a functional renin-angiotensin system: further mechanisms of angiotensin II induced inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1093–10102. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006070707
Kvakan H, Kleinewietfeld M, Qadri F, Park JK, Fischer R, Schwarz I, Rahn HP, Plehm R, Wellner M, Elitok S, Gratze P, Luft R, Muller FCDN (2009) Regulatory T cells ameliorate angiotensin II-induced cardiac damage. Circulation 119:2904–2912. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.832782
Welch WJ (2008) Angiotensin II-dependent superoxide: effects on hypertension and vascular dysfunction. Hypertension 52:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.090472
Wu R, Laplante MA, de Champlain J (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors attenuate angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress, hypertension, and cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Hypertension 45:1139–1144. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000164572.92049.29
Wen Y, Liu Y, Tang T, Lv L, Liu H, Ma K, Liu B (2016) NLRP3 inflammasome activation is involved in Ang II-induced kidney damage via mitochondrial dysfunction. Oncotarget 7:54290–54302. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11091
Thakur S, Li L, Gupta S (2014) NF-κB-mediated integrin-linked kinase regulation in angiotensin II-induced pro-fibrotic process in cardiac fibroblasts. Life Sci 107:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. lfs.2014.04.030
Weber KT, Swamynathan SK, Guntaka RV, Sun Y (1999) Angiotensin II and Extracellular Matrix Homeostasis. J Biochem Cell Biol 31:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1357-2725(98)00125-3
Than A, Leow MK, Chen P (2013) Control of adipogenesis by the autocrine interplays between angiotensin 1–7/Mas receptor and angiotensin II/AT1 receptor signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 288:15520–15531. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.459792
Chalmers L, Kaskel FJ, Bamgbola O (2006) The role of obesity and its bioclinical correlates in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 13:352–364. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2006.07.010
Gao N, Wang H, Zhang X, Yang Z (2015) The inhibitory effect of angiotensin II on BKCa channels in podocytes via oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem 398:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2221-1
Hongo M, Ishizaka N, Furuta K, Yahagi N, Saito K, Sakurai R, Matsuzaki G, Koike K, Nagai R (2009) Administration of angiotensin II, but not catecholamines, induces accumulation of lipids in the rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol 604:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.12.006
Glenn DJ, Cardema MC, Ni W, Zhang Y, Yeghiazarians Y, Grapov D, Fiehn O, Gardner DG (2015) Cardiac steatosis potentiates angiotensin II effects in the heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 308:H339–350. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00742.2014
Mayor F Jr, Cruces-Sande M, Arcones AC, Vila-Bedmar R, Briones AM, Salaices M, Murga C (2018) G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) as an integrative signalling node in the regulation of cardiovascular function and metabolic homeostasis. Cell Signal 41:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.04.002
Kintscher U, Lyon CJ, Law RE (2004) Angiotensin II, PPAR-gamma and atherosclerosis. Front Biosci 9:359–369. https://doi.org/10.2741/1225
Kochueva M, Sukhonos V, Shalimova A, Psareva V, Kirichenko N (2014) State of integral remodeling parameters of target organs in patients with essential hypertension and obesity. Georgian Med News 231:26–30
Frohlich ED (2002) Clinical management of the obese hypertensive patient. Cardiol Rev 10:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1097/00045415-200205000-00001
Rajagopalan S, Laursen JB, Borthayre A, Kurz S, Keiser J, Haleen S, Giaid A, Harrison DG (1997) Role for endothelin-1 in angiotensin II-mediated hypertension. Hypertension 30:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.30.1.29
Lin YJ, Kwok CF, Juan CC, Hsu YP, Shih KC, Chen CC, Ho LT (2014) Angiotensin II enhances endothelin-1-induced vasoconstriction through upregulating endothelin type A receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.119
Xue B, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Guo F, Beltz TG, Thunhorst RL, Felder RB, Johnson AK (2016) Leptin Mediates High-Fat Diet Sensitization of Angiotensin II-Elicited Hypertension by Upregulating the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System and Inflammation. Hypertension 67:970–976. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06736
Deji N, Kume S, Araki S, Isshiki K, Araki H, Chin-Kanasaki M, Tanaka Y, Nishiyama A, Koya D, Haneda M, Kashiwagi A, Maegawa H, Uzu T (2012) Role of angiotensin II-mediated AMPK inactivation on obesity-related salt-sensitive hypertension. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 418:559–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.070
Mutch NJ, Wilson HM, Booth NA (2001) Plasminogen Activator inhibitor-1 and Haemostasis in Obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 6:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1079/pns200199
Skurk T, Lee YM, Hauner H (2001) Angiotensin II and its metabolites stimulate PAI-1 protein release from human adipocytes in primary culture. Hypertension 37:1336–1340. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.37.5.1336
Mikolajczyk TP, Guzik TJ (2019) Adaptive Immunity in Hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 21:68. https://
Bernstein KE, Khan Z, Giani JF, Cao DY, Bernstein EA, Shen XZ (2018) Angiotensin-converting enzyme in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Nephrol 14:325–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2018.15
Pan XX, Wu F, Chen XH, Chen DR, Chen HJ, Kong LR, Ruan CC, Gao PJ (2021) T-cell senescence accelerates angiotensin II-induced target organ damage. Cardiovasc Res 17:271–283. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaa032
Ferguson JF, Aden LA, Barbaro NR, Van Beusecum JP, Xiao L, Simmons AJ, Warden C, Pasic L, Himmel LE, Washington MK, Revetta FL, Zhao S, Kumaresan S, Scholz MB, Tang Z, Chen G, Reilly MP, Kirabo A (2019) High dietary salt-induced dendritic cell activation underlies microbial dysbiosis-associated hypertension. JCI Insight 13:e126241. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.126241
Medzhitov R (2009) Approaching the Asymptote: 20 Years Later. Immunity 30:766–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.004
Chu L-W, Yang C-J, Peng K-J, Chen P-L, Wang S-J, Ping Y-H (2019) TIM-1 As a Signal Receptor Triggers Dengue Virus-Induced Autophagy. Int J Mol Sci 20:4893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194893
Urcuqui-Inchima S, Patiño C, Torres S, Haenni A-L, Díaz FJ (2010) Recent Developments in Understanding Dengue Virus Replication. Adv Virus Res 77:1–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385034-8.00001-6
66, Begum F, Das S, Mukherjee D, Ray U (2019) Hijacking the Host Immune Cells by Dengue Virus: Molecular Interplay of Receptors and Dengue Virus Envelope. Microorganisms 7:323. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090323
Dejarnac O, Hafirassou ML, Chazal M, Versapuech M, Gaillard J, Perera-Lecoin M, Umana-Diaz C, Bonnet-Madin L, Carnec X, Tinevez JY, Delaugerre C, Schwartz O, Roingeard P, Jouvenet N, Berlioz-Torrent C, Meertens L, Amara A (2018) TIM-1 Ubiquitination Mediates Dengue Virus Entry. Cell Rep 23:1779–1793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.013
Kossmann S, Hu H, Steven S, Schonfelder T, Fraccarollo D, Mikhed Y, Brahler M, Knorr M, Brandt M, Karbach SH, Becker C, Oelze M, Bauersachs J, Widder J, Munzel T, Daiber A, Wenzel P (2014) Inflammatory monocytes determine endothelial nitric-oxide synthase uncoupling and nitro-oxidative stress induced by angiotensin II. J Biol Chem 289:27540–27550. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.604231
Rucker AJ, Crowley SD (2017) The role of macrophages in hypertension and its complications. Pflugers Arch 469:419–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-1950-x
Hermansson C, Lundqvist A, Magnusson LU, Ullström C, Bergström G, Hultén LM (2014) Macrophage CD14 expression in human carotid plaques is associated with complicated lesions, correlates with thrombosis, and is reduced by angiotensin receptor blocker treatment. Int Immunopharmacol 22:318–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2014.07.009
Gelinas L, Falkenham A, Oxner A, Sopel M, Légaré J-F (2011) Highly purified human peripheral blood monocytes produce IL-6 but not TNFalpha in response to angiotensin II. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 12:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470320310391332
Sun P, Zhang W, Zhu W, Yan H, Zhu J (2009) Expression of renin-angiotensin system on dendritic cells of patients with coronary artery disease. Inflammation 32:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-009-9141-3
Pokidysheva E, Zhang Y, Battisti AJ, Bator-Kelly CM, Chipman PR, Xiao C, Gregorio GG, Hendrickson WA, Kuhn RJ, Rossmann MG (2006) Cryo-EM reconstruction of dengue virus in complex with the carbohydrate recognition domain of DC-SIGN. Cell 124:485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.042
Beirag N, Kumar C, Madan T, Shamji MH, Bulla R, Mitchell D, Murugaiah V, Neto MM, Temperton N, Idicula-Thomas S, Varghese PM, Kishore U (2022) Human surfactant protein D facilitates SARS-CoV-2 pseudotype binding and entry in DC-SIGN expressing cells, and downregulates spike protein induced inflammation. Front Immunol 13:960733. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.960733
Kwon DS, Gregorio G, Bitton N, Hendrickson WA, Littman DR (2002) DC-SIGN-mediated internalization of HIV is required for trans-enhancement of T cell infection. Immunity 16:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00259-5
Bi X, Niu J, Ding W, Zhang M, Yang M, Gu Y (2016) Angiopoietin-1 attenuates angiotensin II-induced ER stress in glomerular endothelial cells via a Tie2 receptor/ERK1/2-p38 MAPK-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Endocrinol 428:118–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.03.027
Menikdiwela KR, Ramalingam L, Allen L, Scoggin S, Kalupahana NS, Moustaid-Moussa N (2019) Angiotensin II Increases Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Adipose Tissue and Adipocytes. Sci RepJun 9:8481. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44834-8
Young CN, Davisson RL (2015) Angiotensin-II, the brain, and hypertension: an update. Hypertension 66:920–926. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.03624
Gerolde Cardoso V, Lopes Gonçalves G, Costa-Pessoa JM, Thieme K, Bezerra Lins B, Malavazzi Casare FA, Charleaux de Ponte M, Saraiva Camara NO, Oliveira-Souza M (2018) Angiotensin II-induced podocyte apoptosis is mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress/PKC-δ/p38 MAPK pathway activation and trough increased Na+/H + exchanger isoform 1 activity. BMC Nephrol 19:179. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-0968-4
Berk BC, Corson MA (1997) Angiotensin II signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: role of tyrosine kinases. Circ Res 80:607–616. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.80.5.607
Fiebeler A, Park J-K, Muller DN, Lindschau C, Mengel M, Merkel S, Banas B, Luft FC, Haller H (2004) Growth arrest specific protein 6/Axl signaling in human inflammatory renal diseases. Am J Kidney Dis 43:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2003.10.016
Melaragno MG, Wuthrich DA, Poppa V, Gill D, Lindner V, Berk BC, Corson MA (1998) Increased expression of Axl tyrosine kinase after vascular injury and regulation by G protein-coupled receptor agonists in rats. Circ Res 83:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.83.7.697
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Lesauskaite V, Ivanoviene L, Valanciūte A (2003) [Programmed cellular death and atherogenesis: from molecular mechanisms to clinical aspects]. Med (Kaunas) 39:529–534
Huang C, Gao J, Wei T, Shen W (2022) Angiotensin II-Induced Erythrocyte Senescence Contributes to Oxidative Stress. Rejuvenation Res 25:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2021.0054
Patel JM, Sekharam KM, Block ER (1990) Oxidant injury increases cell surface receptor binding of angiotensin II to pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Biochem Toxicol 5:253–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.2570050408
Meertens L, Carnec X, Lecoin MP, Ramdasi R, Guivel-Benhassine F, Lew E, Lemke G, Schwartz O, Amara A (2012) The TIM and TAM families of phosphatidylserine receptors mediate dengue virus entry. Cell Host Microbe 12:544–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.009
Earp HS, Huckle WR, Dawson TL, Li X, Graves LM, Dy R (1995) Angiotensin II activates at least two tyrosine kinases in rat liver epithelial cells. Separation of the major calcium-regulated tyrosine kinase from p125FAK. J Biol Chem 270:28440–28447. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.47.28440
Berk BC, Corson MA (1997) Angiotensin II Signal Transduction in Vascular Smooth Muscle. Role of Tyrosine Kinases. Circul Res 80:607–616. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.80.5.607
Medeiros GF, Mendes A, Castro RA, Baú EC, Nader HB, Dietrich CP (2000) Distribution of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the animal kingdom: widespread occurrence of heparin-like compounds in invertebrates. Biochim Biophy Acta 1475:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4165(00)00079-9
Gallagher JT, Lyon M (2000) Molecular structure of Heparan Sulfate and interactions with growth factors and morphogens. In: Iozzo MV (ed) Proteoglycans: structure, biology and molecular interactions. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, New York, pp 27–59
Iozzo RV (1998) Matrix proteoglycans: from molecular design to cellular function. Ann Rev Biochem 67:609–652. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.609
Buzza MS, Zamurs L, Sun J, Bird CH, Smith AI, Trapani JA, Froelich CJ, Nice EC, Bird PI (2005) Extracellular matrix remodeling by human granzyme B via cleavage of vitronectin, fibronectin, and laminin. J Biol Chem 280:23549–23558. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M412001200
Hallak LK, Spillmann D, Collins PL, Peeples ME (2000) Glycosaminoglycan sulfation requirements for respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Virol 74:10508–10513. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.74.22.10508-10513.2000
Kaplan M, Aviram M (2000) Macrophage plasma membrane chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan binds oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Atherosclerosis 149:5–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9150(99)00287-7
Anderson R (2003) Manipulation of cell surface macromolecules by flaviviruses». Adv Virus Res 59:229–274. https://
Foris G, Dezso B, Medgyesi GA, Fust G (1983) Effect of angiotensin II on macrophage functions. Immunology 48:529
Dezso B, Foris G (1981) Effect of angiotensin II on the Fc receptor activity of rat macrophages. Immunology 42:277
Suzuki Y, Shirato I, Okumura K, Ravetch JV, Takai T, Tomino Y, Ra C (1998) Distinct contribution of Fc receptors and angiotensin II-dependent pathways in anti-GBM glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 54:1166–1174. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00108.x
Piccini Luana E, Castilla V, Damonte EB (2015) Dengue-3 Virus Entry into Vero Cells: Role of Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis in the Outcome of Infection. PLoS ONE 10:e0140824. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140824
Ho M-R, Tsai T-T, Chen C-L, Jhan M-K, Tsai C-C, Lee Y-C, Chen C-H, Lin C-F (2017) Blockade of dengue virus infection and viral cytotoxicity in neuronal cells in vitro and in vivo by targeting endocytic pathways. Sci Rep 7:6910. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07023-z
Inoue Y, Tanaka N, Tanaka Y, Inoue S, Morita K, Zhuang M, Hattori T, Sugamura K (2007) Clathrin-Dependent Entry of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus into Target Cells Expressing ACE2 with the Cytoplasmic Tail Deleted. J Virol 81:8722–8729. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00253-07
Hennig R, Pollinger K, Tessmar J, Goepferich A (2015) Multivalent targeting of AT1 receptors with angiotensin II-functionalized nanoparticles. J Drug Target 23:681–689. https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2015.1035276
Thomas WG, Thekkumkara TJ, Baker KM (1996) Molecular mechanisms of angiotensin II (AT1a) receptor endocytosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 3. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.1996.tb02817.x. :S74-80
Takizawa T, Matsukawa S, Higuchi Y, Nakamura S, Nakanishi Y, Fukuda R (1993) Induction of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by infuenza virus infection in tissue culture cells. J Gen Virol 74:2347–2355. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-74-11-2347
Banki K, Hutter E, Gonchorof NJ, Perl A (1998) Molecular ordering in HIVinduced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273:11944–11953. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.19.11944
Gautier I, Coppey J, Durieux C (2003) Early apoptosis-related changes triggered by HSV-1 in individual neuronlike cells. Exp Cell Res 289:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00258-1
Moller-Tank S, Kondratowicz AS, Davey RA, Rennert PD, Maury W (2013) Role of the phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-1 in enveloped-virus entry. J Virol 87:8327–8341. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01025-13
Mosquera JA, Hernandez JP, Valero N, Espina LM, Añez GJ (2005) Ultrastructural studies on dengue virus type 2 infection of cultured human monocytes. Virol J 2:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-2-26
Carnec X, Meertens L, Dejarnac O, Perera-Lecoin M, Lamine Hafirassou M, Kitaura J, Ramdasi R, Schwartz O, Amara A (2015) The Phosphatidylserine and Phosphatidylethanolamine Receptor CD300a Binds Dengue Virus and Enhances Infection. J Virol 90:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01849-15
Pelkmans L (2005) Secrets of caveolae- and lipid raft-mediated endocytosis revealed by mammalian viruses. Biochem Biophys Acta 1746:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.06.009
Ishizaka N, Griendling KK, Lassègue B, Alexander RW (1998) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor: relationship with caveolae and caveolin after initial agonist stimulation. Hypertension 32:459–466. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.32.3.459
Oh Y-B, Gao S, Lim JM, Kim HT, Park B-H, Kim SH (2011) Caveolae are essential for angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated ANP secretion. Peptides 32:1422–1430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2011.06.002
Csaba B, Nagy JP, Végh B, Németh A, Jenei A, MirzaHosseini S, Sebe A, Rosivall L (2012) Angiotensin II increases the permeability and PV-1 expression of endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302:C267–C276. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00138.2011
Chanthick C, Kanlaya R, Kiatbumrung R, Pattanakitsakul S-N, Thongboonkerd V (2016) Caveolae-mediated albumin transcytosis is enhanced in dengue-infected human endothelial cells: A model of vascular leakage in dengue hemorrhagic fever. Sci Rep 6:31855. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31855
Acosta EG, Castilla V, Damonte EB (2009) Alternative infectious entry pathways for dengue virus serotypes into mammalian cells. Cell Microbiol 11:1533–1549. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01345.x
Peng T, Wang J-L, Chen W, Zhang J-L, Gao N, Chen Z-T, Xu X-F, Fan D-Y, An J (2009) Entry of dengue virus serotype 2 into ECV304 cells depends on clathrin-dependent endocytosis, but not on caveolae-dependent endocytosis. Can J Microbiol 55:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1139/w08-107
Rosales C, Uribe-Querol E (2017) Phagocytosis: A Fundamental Process in Immunity. Biomed Res Int 2017:9042851. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9042851
Sobhy H (2017) A comparative review of viral entry and attachment during large and giant dsDNA virus infections. Arch Virol 162:3567–3585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3497-8
Chaturvedi UC, Nagar R, Shrivastava R (2006) Macrophage and dengue virus: friend or foe? Indian J Med Res 124:23–40
Barhoumi T, Mansour FA, Jalouli M, Alamri HS, Ali R, Harrath AH, Aljumaa M, Boudjelal M (2023) Angiotensin II modulates THP-1-like macrophage phenotype and inflammatory signatures via angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Front Cardiovasc Med 10:1129704. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2023.1129704
Weinstock JV, Kassab JT (1984) Angiotensin II stimulation of granuloma macrophage phagocytosis and actin polymerization in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. Cell Immunol 89:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8749(84)90196-5
Rodgers K, Xiong S, Espinoza T, Roda N, Maldonado S, diZerega GS (2000) Angiotensin II increases host resistance to peritonitis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 7:635–640. https://doi.org/10.1128/CDLI.7.4.635-640.2000
Belline P, Silva da Melo P, Haun M, Boucault Palhares F, Boer PA, Rocha Gontijo JA, Figueiredo JF (2004) Effect of angiotensin II and losartan on the phagocytic activity of peritoneal macrophages from Balb/C mice. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 99:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0074-02762004000200009
Daughaday CC, Brandt WE, McCown JM, Russell PK (1981) Evidence for two mechanisms of dengue virus infection of adherent human monocytes: trypsin-sensitive virus receptors and trypsin-resistant immune complex receptors. Infect Immun 32:469–473. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.32.2.469-473.1981
Mukherjee S, Sirohi D, Dowd K, Chen Z, Diamond MS, Kuhn RJ, Pierson TC (2016) Enhancing dengue virus maturation using a stable furin over-expressing cell line. Virology 497:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2016.06.022
Rodenhuis-Zybert IA, van der Schaar HM, da Silva Voorham JM, van der Ende-Metselaar H, Lei H-Y, Wilschut J, Smit JM (2010) Immature dengue virus: a veiled pathogen? PLoS Pathog 6:e1000718. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000718
Seachrist JL, Laporte SA, Dale LB, Babwah AV, Caron MG, Anborgh PH, Ferguson SSG (2002) Rab5 association with the angiotensin II type 1A receptor promotes Rab5 GTP binding and vesicular fusion. J Biol Chem 277:679–685. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109022200
Dale LB, Seachrist JL, Babwah AV, Ferguson SSG (2004) Regulation of angiotensin II type 1A receptor intracellular retention, degradation, and recycling by Rab5, Rab7, and Rab11 GTPases. J Biol Chem 279:13110–13118. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M313333200
Hunyady L, Baukal AJ, Gaborik Z, Olivares-Reyes JA, Bor M, Szaszak M, Lodge R, Catt KJ, Balla T (2002) Differential PI 3-kinase dependence of early and late phases of recycling of the internalized AT1 angiotensin receptor. J Cell Biol 157:1211–1222. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200111013
Kouretova J, Hammamy MZ, Epp A, Hardes K, Kallis S, Zhang L, Hilgenfeld R, Bartenschlager R, Steinmetzer T (2017) Effects of NS2B-NS3 protease and furin inhibition on West Nile and Dengue virus replication. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 32:712–721. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2017.1306521
Cilhoroz BT, Schifano ED, Panza GA, Ash GI, Corso L, Chen MH, Deshpande V, Zaleski A, Farinatti P, Santos LP, Taylor BA, O'Neill RJ, Thompson PD, Pescatello LS (2019) Furin variant associations with postexercise hypotension are intensity and race dependent. Physiol Rep 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13952
Peña C, Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Rincon J, Pedreañez A, Viera N, Mosquera J (2013) Proinflammatory role of angiotensin II in mercuric induced nephropathy in rats. J Immunotoxicol 10:125–132. https://doi.org/10.3109/1547691X.2012.699478
134, Vargas R, Rincon J, Pedreañez A, Viera N, Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Peña C, Mosquera J (2012) Role of Angiotensin II in the brain inflammatory events during experimental diabetes in rats. Brain Res 1453:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.03.021
Muñoz M, Rincon J, Pedreañez A, Viera N, Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Mosquera J (2011) Proinflammatory role of angiotensin II in a rat nephrosis model induced by adriamycin. J Ren Ang Ald Syst 12:404–412. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470320311410092
Acknowledgements
We thank Instituto de Investigaciones Cllnicas Dr. Américo Negrette, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Zulia, Maracaibo, Venezuela.
Funding
No financial support was received for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JM-S and AP conceived the subject matter and contributed to the design of the work. JM-S, AP, YC, JPH-F, and RV contributed to the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data. JM-S and AP wrote the original draft. JM-S, AP, YC, RV, and JPH-F critically revised the first draft. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Eiji Morita.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pedreañez, A., Carrero, Y., Vargas, R. et al. Role of angiotensin II in cellular entry and replication of dengue virus. Arch Virol 169, 121 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-024-06040-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-024-06040-4