Abstract
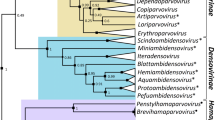
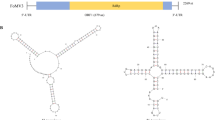
A new cytorhabdovirus, tentatively named “chelidonium yellow mottle associated virus” (CheYMaV), was identified in Chelidonium majus with yellow mottle symptoms by high-throughput sequencing and RT-PCR. Its genome is 12,121 nucleotides in length and contains eight open reading frames (ORFs) in the order 3ʹ-N-Pʹ-P-P3-M-G-P6-L-5ʹ. Amino acid sequence comparisons between the putative proteins of CheYMaV and the corresponding proteins of other cytorhabdoviruses showed that it shares the highest sequence similarity with Trifolium pratense virus A (TpVA, MH982250) and Glehnia littoralis virus 1 (GllV1, BK014304), but with sequence identity values below the species demarcation threshold for cytorhabdoviruses (< 80%). Phylogenetic analysis showed that CheYMaV is most closely related to TpVA and GllV1. CheYMaV should therefore be considered a new member of the genus Cytorhabdovirus. This is the first report of a cytorhabdovirus identified in Chelidonium majus.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Walker PJ, Freitas-Astúa J, Bejerman N, Blasdell KR, Breyta R, Dietzgen RG, Fooks AR, Kondo H, Kurath G, Kuzmin IV, Ramos-González PL, Shi M, Stone DM, Tesh RB, Tordo N, Vasilakis N, Whitfield AE, Ictv Report Consortium (2022) ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Rhabdoviridae 2022. J Gen Virol 103(6):https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.001689
Bejerman N, Dietzgen RG, Debat H (2021) Illuminating the plant rhabdovirus landscape through metatranscriptomics data. Viruses 13(7):1304
Fránová J, Sarkisova T, Jakešová H, Koloniuk I (2019) Molecular and biological properties of two putative new cytorhabdoviruses infecting Trifolium pratense. Plant Physiol 68(7):1276–1286
Bejerman N, Acevedo RM, de Breuil S, Ruiz OA, Sansberro P, Dietzgen RG, Nome C, Debat H (2020) Molecular characterization of a novel cytorhabdovirus with a unique genomic organization infecting yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) in Argentina. Arch Virol 165(6):1475–1479
Bejerman N, Giolitti F, de Breuil S, Trucco V, Nome C, Lenardon S, Dietzgen RG (2015) Complete genome sequence and integrated protein localization and interaction map for alfalfa dwarf virus, which combines properties of both cytoplasmic and nuclear plant rhabdoviruses. Virol 483:275–283
Koloniuk I, Fránová J, Sarkisova T, Přibylová J (2018) Complete genome sequences of two divergent isolates of strawberry crinkle virus coinfecting a single strawberry plant. Arch Virol 163(9):2539–2542
Dietzgen RG, Bejerman NE, Goodin MM, Higgins CM, Huot OB, Kondo H, Martin KM, Whitfield AE (2020) Diversity and epidemiology of plant rhabdoviruses. Virus Res 281:197942
Bolus S, Al Rwahnih M, Grinstead SC, Mollov D (2021) Rose virus R, a cytorhabdovirus infecting rose. Arch Virol 166(2):655–658
Read DA, Strydom E, Slippers B, Steenkamp E, Pietersen G (2022) Genomic characterization of soybean blotchy mosaic virus, a cytorhabdovirus from South Africa. Arch Virol 167(11):2359–2363
Šafářová D, Candresse T, Navrátil M (2022) Complete genome sequence of a novel cytorhabdovirus infecting elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) in the Czech Republic. Arch Virol 167(7):1589–1592
Petrzik K, Přibylová J, Špak J, Sarkisova T, Fránová J, Holub J, Skalík J, Koloniuk I (2022) Mixed infection of blackcurrant with a novel cytorhabdovirus and black currant-associated nucleorhabdovirus. Viruses 14(11):2456
Di DP, Zhang YL, Yan C, Yan T, Zhang AH, Yang F, Cao XL, Li DW, Lu YG, Wang XB, Miao HQ (2014) First report of barley yellow striate mosaic virus on wheat in China. Plant Dis 98(10):1450
Liu Y, Du Z, Wang H, Zhang S, Cao M, Wang X (2018) Identification and characterization of wheat yellow striate virus, a novel leafhopper-transmitted nucleorhabdovirus infecting wheat. Front Microbiol 9:468
Wang Y, Wang G, Bai J, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wen S, Li L, Yang Z, Hong N (2021) A novel actinidia cytorhabdovirus characterized using genomic and viral protein interaction features. Mol Plant Pathol 22(10):1271–1287
Zhang S, Huang A, Zhou X, Li Z, Dietzgen RG, Zhou C, Cao M (2021) Natural defect of a plant rhabdovirus glycoprotein gene: a case study of virus-plant coevolution. Phytopathology 111(1):227–236
Du SL, Li LR, Gu S, Cai MC, Li X (2022) Progress in the comprehensive research on pharmacological actions of celandine. Jilin J Tradit Chin Med 42(01):84–87
Bečák J (1979) Isolates of cucumber mosaic virus from spontaneously infected plants of Chelidonium majus and Impatiens parviflora. Biol Plant 21:220–223
Zhao F, Yoo RH, Lim S, Igori D, Lee SH, Moon JS (2015) Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of a new proposed crinivirus, tetterwort vein chlorosis virus. Arch Virol 160(11):2899–2902
Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M, Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber M, MacManes MD, Ott M, Orvis J, Pochet N, Strozzi F, Weeks N, Westerman R, William T, Dewey CN, Henschel R, LeDuc RD, Friedman N, Regev A (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat Protoc 8(8):1494–1512
Joubert DA, Blasdell KR, Audsley MD, Trinidad L, Monaghan P, Dave KA, Lieu KG, Amos-Ritchie R, Jans DA, Moseley GW, Gorman JJ, Walker PJ (2014) Bovine ephemeral fever rhabdovirus α1 protein has viroporin-like properties and binds importin β1 and importin 7. J Virol 88(3):1591–1603
Liu Q, Jin J, Yang L, Zhang S, Cao M (2021) Molecular characterization of a novel cytorhabdovirus associated with chrysanthemum yellow dwarf disease. Arch Virol 166(4):1253–1257
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38(7):3022–3027
Freitas-Astúa J, Dietzgen RG, Walker PJ, Blasdell KR, Breyta R, Fooks ARKH, Kurath G, Kuzmin IV, Stone DM, Tesh RB, Tordo NVN, Whitfeld AE, Ramos-González PL (2020) Create twelve new species in the genus Cytorhabdovirus, family Rhabdoviridae. approved ICTV proposal. 2019.030M
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funds from the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2021-MS-341) and the Program for Young and Middle-Aged Scientific and Technological Innovation Talents of Shenyang City (RC210161).
Funding
This work was supported by funds from the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2021-MS-341) and the Program for Young and Middle-Aged Scientific and Technological Innovation Talents of Shenyang City (RC210161).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any experiments involving humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Ralf Georg Dietzgen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Cui, X., An, W. et al. The complete genome sequence of a putative novel cytorhabdovirus identified in Chelidonium majus in China. Arch Virol 169, 56 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-024-05969-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-024-05969-w