Abstract
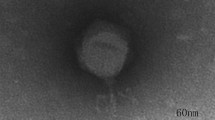
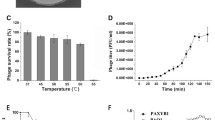
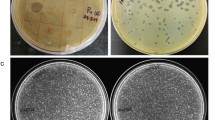
A lytic Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage, vB_PaeP_Lx18 (Lx18), was isolated from the sewage of a dairy farm. Biological characterization revealed that Lx18 was stable from 40 °C to 60 °C and over a wide range of pH values from 4 to 10. It was able to lyse 63.6% (21/33) of the P. aeruginosa strains tested and was able to reduce and disperse biofilms, with a biofilm reduction rate of 76.8%. Whole-genome sequencing showed that Lx18 is a dsDNA virus with a genome of 42,735 bp and G+C content of 62.16%. The genome contains 54 open reading frames (ORFs), 28 of which have known functions, including DNA replication and modification, transcriptional regulation, structural and packaging proteins, and host cell lysis. No virulence or tRNA genes were identified. Phylogenetic analysis showed that phage Lx18 belongs to the genus Phikmvvirus. The lysozyme of Lx18, Lys18, was cloned and expressed. The combined action of Lys18 and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) had antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The study of phage Lx18 and its lysozyme will provide basic information for further research on the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ceyssens PJ, Lavigne R (2010) Bacteriophages of Pseudomonas. Future Microbiol 5:1041–1055
Hilker R, Munder A, Klockgether J, Losada PM, Chouvarine P, Cramer N, Davenport CF, Dethlefsen S, Fischer S, Peng H, Schönfelder T, Türk O, Wiehlmann L, Wölbeling F, Gulbins E, Goesmann A, Tümmler B (2015) Interclonal gradient of virulence in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pangenome from disease and environment. Environ Microbiol 17:29–46
Martins SAM, Martins VC, Cardoso FA, Germano J, Rodrigues M, Duarte C, Bexiga R, Cardoso S, Freitas PP (2019) Biosensors for on-farm diagnosis of mastitis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:186
Meng L, Zhang Y, Liu H, Zhao S, Wang J, Zheng N (2017) Characterization of Pseudomonas spp. and associated proteolytic properties in raw milk stored at low temperatures. Front Microbiol 8:2158
Schauer B, Wald R, Urbantke V, Loncaric I, Baumgartner M (2021) Tracing mastitis pathogens-epidemiological investigations of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mastitis outbreak in an Austrian Dairy Herd. Animals (Basel) 11(2):279
Subedi D, Vijay AK, Willcox M (2018) Overview of mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an ocular perspective. Clin Exp Optom 101(2):162–171
Lister PD, Wolter DJ, Hanson ND (2009) Antibacterial-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa: clinical impact and complex regulation of chromosomally encoded resistance mechanisms. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:582–610
Zahedi Bialvaei A, Rahbar M, Hamidi-Farahani R, Asgari A, Esmailkhani A, Mardani Dashti Y, Soleiman-Meigooni S (2021) Expression of RND efflux pumps mediated antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains. Microb Pathog 153:104789
Pang Z, Raudonis R, Glick BR, Lin TJ, Cheng Z (2019) Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol Adv 37(1):177–192
Roy R, Tiwari M, Donelli G, Tiwari V, Tiwari V (2018) Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: a focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action. Virulence 9(1):522–554
Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, Righi E, Guery B (2018) How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs Context 7:212527
Breitbart M, Rohwer F (2005) Here a virus, there a virus, everywhere the same virus? Trends Microbiol 13:278–284
Huff WE, Huff GR, Rath NC, Balog JM, Donoghue AM (2005) Alternatives to antibiotics: utilization of bacteriophage to treat colibacillosis and prevent foodborne pathogens. Poult Sci 84(4):655–659
Alves DR, Perez-Esteban P, Kot W, Bean JE, Arnot T, Hansen LH, Enright MC, Jenkins AT (2016) A novel bacteriophage cocktail reduces and disperses Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms under static and flow conditions. Microb Biotechnol 9(1):61–74
Pires DP, Vilas Boas D, Sillankorva S, Azeredo J (2015) Phage therapy: a step forward in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Virol 89:7449–7456
Young R (2014) Phage lysis: three steps, three choices, one outcome. J Microbiol 52:243–258
Oliveira H, Thiagarajan V, Walmagh M, Sillankorva S, Lavigne R, Neves-Petersen MT, Kluskens LD, Azeredo J (2014) A thermostable Salmonella phage endolysin, Lys68 with broad bactericidal properties against gram-negative pathogens in presence of weak acids. PLoS ONE 9(10):e108376
Azeredo J, Sillankorva S, Pires DP (2014) Pseudomonas bacteriophage isolation and production. Methods Mol Biol 1149:23–32
Ackermann HW (2009) Basic phage electron microscopy. Methods Mol Biol 501:113–126
Zhou W, Feng Y, Zong Z (2018) Two new lytic bacteriophages of the myoviridae family against carbapenem-resistant Aci netobacter baumannii. Front Microbiol 9:850
Yang Z, Liu X, Shi Y, Yin S, Shen W, Chen J, Chen Y, Chen Y, You B, Gong Y, Luo X, Zhang C, Yuan Z, Peng Y (2019) Characterization and genome annotation of a newly detected bacteriophage infecting multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Adv Virol 164(6):1527–1533
Tang C, Deng C, Zhang Y, Xiao C, Wang J, Rao X, Hu F, Lu S (2018) Characterization and genomic analyses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa podovirus TC6: establishment of genus Pa11virus. Front Microbiol 9:2561
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:75
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evolut 33(7):1870–1874
Wu M, Hu K, Xie Y, Liu Y, Mu D, Guo H, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Chang D, Shi Y (2019) A novel phage PD-6A3, and its endolysin Ply6A3, with extended lytic activity against Acinetobacter baumannii. Front Microbiol 9:3302
Guo M, Feng C, Ren J, Zhuang X, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Dong K, He P, Guo X, Qin J (2017) A Novel Antimicrobial Endolysin, LysPA26, against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol 8:293
Han H, Li X, Zhang T, Wang X, Zou J, Zhang C, Tang H, Zou Y, Cheng B, Wang R (2019) Bioinformatic analyses of a potential Salmonella-virus-FelixO1 biocontrol phage BPS15S6 and the characterisation and anti-Enterobacteriaceae-pathogen activity of its endolysin LyS15S6. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 112(11):1577–1592
Zhang C, Wang Y, Sun H, Ren H (2015) Multiple-site mutations of phage Bp7 endolysin improves its activities against target bacteria. Virol Sin 30(5):386–395
Kropinski AM, Prangishvili D, Lavigne R (2009) Position paper: the creation of a rational scheme for the nomenclature of viruses of Bacteria and Archaea. Environ Microbiol 11(11):2775–2777
Yang Y, Lu S, Shen W, Zhao X, Shen M, Tan Y, Li G, Li M, Wang J, Hu F, Le S (2016) Characterization of the first double-stranded RNA bacteriophage infecting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 6:38795
Lefkowitz EJ, Dempsey DM, Hendrickson RC, Orton RJ, Siddell SG, Smith DB (2018) Virus taxonomy: the database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucl Acids Res 46:D708–D717
Bachta KER, Allen JP, Cheung BH, Chiu CH, Hauser AR (2020) Systemic infection facilitates transmission of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. Nat Commun 11(1):543
Klaas IC, Zadoks RN (2018) An update on environmental mastitis: challenging perceptions. Transbound Emerg Dis 65(Suppl 1):166–185
Lin DM, Koskella B, Lin HC (2017) Phage therapy: an alternative to antibiotics in the age of multi-drug resistance. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 8(3):162–173
Wang Z, Xue Y, Gao Y, Guo M, Liu Y, Zou X, Cheng Y, Ma J, Wang H, Sun J, Yan Y (2021) Phage vB_PaeS-PAJD-1 Rescues Murine Mastitis Infected With Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:689770
Wu Y, Wang R, Xu M et al (2019) A novel polysaccharide depolymerase encoded by the phage SH-KP152226 confers specific activity against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via biofilm degradation. Front Microbiol 10:2768
Lavigne R, Burkal’tseva MV, Robben J, Sykilinda NN, Kurochkina LP, Grymonprez B, Jonckx B, Krylov VN, Mesyanzhinov VV, Volckaert G (2003) The genome of bacteriophage phiKMV, a T7-like virus infecting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Virology 312(1):49–59
Cao Z, Zhang J, Niu YD, Cui N, Ma Y, Cao F, Jin L, Li Z, Xu Y (2015) Isolation and characterization of a “phiKMV-like” bacteriophage and its therapeutic effect on mink hemorrhagic pneumonia. PLoS ONE 10(1):e0116571
Lavigne R, Briers Y, Hertveldt K, Robben J, Volckaert G (2004) Identification and characterization of a highly thermostable bacteriophage lysozyme. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(21):2753–2759
Schneider CL (2017) Bacteriophage-mediated horizontal gene transfer: transduction. Bacteriophages 9:1–42
Shi Y, Yan Y, Ji W, Du B, Meng X, Wang H, Sun J (2012) Characterization and determination of holin protein of Streptococcus suis bacteriophage SMP in heterologous host. Virol J 22(9):70
Ghose C, Euler CW (2020) Gram-negative bacterial lysins. Antibiotics (Basel). 9(2):74
Lai WCB, Chen X, Ho MKY, Xia J, Leung SSY (2020) Bacteriophage-derived endolysins to target gram-negative bacteria. Int J Pharm 15(589):119833
Larpin Y, Oechslin F, Moreillon P, Resch G, Entenza JM, Mancini S (2018) In vitro characterization of PlyE146, a novel phage lysin that targets Gram-negative bacteria. PLoS ONE 13(2):e0192507
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Dr Zongzhu Liu for collecting samples for the experiments, and we thank the staff of the Central Lab of Qingdao Agricultural University for their assistance with TEM.
Funding
This study was supported by Shandong Province modern agricultural industrial technology system cattle industry innovation team project (No. SDAIT-09-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL conceived and designed the experiments and critically evaluated the manuscript. YY carried out the data analysis and wrote the manuscript. XW and ZM carried out the experiments. HR evaluated the experimental design and helped with experiments and the revision of manuscript. CZ evaluated the experimental design and gave advice about the manuscript. LZ provided reagents and instruments. HL provided financial support for the experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Handling Editor: T. K. Frey.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Y., Wang, X., Mou, Z. et al. Characterization and genome analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage vB_PaeP_Lx18 and the antibacterial activity of its lysozyme. Arch Virol 167, 1805–1817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-022-05472-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-022-05472-0