Abstract
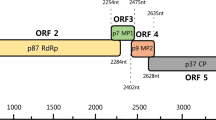
A novel varicosa-like virus was identified in a tall morning glory (Ipomoea purpurea) plant by high-throughput sequencing and tentatively named "morning glory varicosavirus" (MGVV). The complete genome of MGVV contains two segments of negative-sense single-stranded RNA of 6409 (RNA1) and 5288 (RNA2) nucleotides. RNA1 encodes a 224.3-kDa large protein (224K), and RNA2 encodes four putative proteins of 48.6 kDa (49K), 46.4 kDa (46K), 35.7 kDa (36K), and 36.8 kDa (37K), respectively. The 224K and 49K proteins show amino acid sequence similarity to the large protein (39.4%) and the 49K protein (22.6%), respectively, of red clover-associated varicosavirus, and the 36K protein shares 19.6% amino acid sequence similarity with protein 3 of lettuce big-vein associated virus. The 46K and 37K proteins share no significant sequence similarity to known functional viral sequences. Phylogenetic analysis based on the large protein of MGVV and other rhabdoviruses showed that MGVV clustered with the varicosaviruses. These analyses indicate that MGVV is a novel member of the genus Varicosavirus in the family Rhabdoviridae.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dietzgen RG, Kondo H, Goodin MM, Kurath G, Vasilakis N (2017) The family Rhabdoviridae: mono- and bipartite negative-sense RNA viruses with diverse genome organization and common evolutionary origins. Virus Res 227:158–170
Dietzgen RG, Bejerman NE, Goodin MM, Higgins CM, Huot OB, Kondo H, Martin KM, Whitfield AE (2020) Diversity and epidemiology of plant rhabdoviruses. Virus Res 281:197942
Verbeek M, Dullemans AM, van Bekkum PJ, van der Vlugt RAA (2013) Evidence for Lettuce big-vein associated virus as the causal agent of a syndrome of necrotic rings and spots in lettuce. Plant Pathol 62:444–451
Koloniuk I, Fránová J, Sarkisova T, Pribylová J, Lenz O, Petrzik K, Špak J (2018) Identification and molecular characterization of a novel varicosa-like virus from red clover. Arch Virol 163:2213–2218
Sabbadin F, Glover R, Stafford R, Rozado-Aguirre Z, Boonham N, Adams I, Mumford R, Edwards R (2017) Transcriptome sequencing identifies novel persistent viruses in herbicide resistant wild-grasses. Sci Rep 7:41978
Nabeshima T, Abe J (2021) High-Throughput Sequencing Indicates Novel Varicosavirus, Emaravirus, and Deltapartitivirus Infections in Vitis coignetiae. Viruses 13:827
Yang CX, Wu ZJ, Xie LH (2009) First report of the occurrence of sweet potato leaf curl virus in tall morning glory (Ipomoea purpurea) in China. Plant Dis 93:764–764
Zerbino DR, Birney E (2008) Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 18:821–829
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by China Agriculture Research Systems of MOF and MARA (CARS-10-B13) and the Science-Technology Foundation for Outstanding Young Scientists of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2020YQ23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any research involving humans or animals.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Ralf Georg Dietzgen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, F., Liu, H., Qiao, Q. et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel varicosavirus infecting tall morning glory (Ipomoea purpurea). Arch Virol 166, 3225–3228 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-021-05240-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-021-05240-6