Abstract
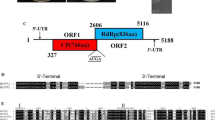
Mycoviruses are widely distributed in fungi, but only a few mycoviruses have been reported in basal fungi to date. Here, we characterized a novel totivirus isolated from the basal fungus Conidiobolus heterosporus, and we designated this virus as “Conidiobolus heterosporus totivirus 1” (ChTV1). The complete genome of ChTV1 contains two discontinuous open reading frames (ORFs), ORF1 and ORF2, encoding a putative coat protein (CP) and a putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP), respectively. Phylogenetic analysis based on RdRP sequences showed that ChTV1 clustered with members of the genus Totivirus. The RdRP of ChTV1 has 51% sequence identity to that of Trichoderma koningiopsis totivirus 1 (TkTV1), which is the highest among mycoviruses. However, TkTV1 formed a distinct cluster with Wuhan insect virus 27, with 63% RdRP sequence identity, although Wuhan insect virus 27 has not been described, and its host represents a different kingdom. Therefore, we propose that ChTV1 is a new member of the genus Totivirus, family Totiviridae.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghabrial SA, Castón JR, Jiang DH, Nibert ML, Suzuki N (2015) 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 479:356–368
King AM, Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ et al (eds) (2011) Virus taxonomy. In: IXth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, 9th edn. Elsevier, Waltham
Huang Y, Guo X, Zhang S, Zhao Q, Sun Q, Zhou H, Zhang J, Tong Y (2018) Discovery of two novel totiviruses from Culex tritaeniorhynchus classifiable in a distinct clade with arthropod-infecting viruses within the family Totiviridae. Arch Virol 163:2899–2902
Yang X, Zhang Y, Ge X, Yuan J, Shi Z (2012) A novel totivirus-like virus isolated from bat guano. Arch Virol 157:1093–1099
Zhai Y, Attoui H, Mohd Jaafar F, Wang HQ, Cao YX, Fan SP, Sun YX, Liu LD, Mertens PP, Meng WS, Wang D, Liang G (2010) Isolation and full-length sequence analysis of Armigeres subalbatus totivirus, the first totivirus isolate from mosquitoes representing a proposed novel genus (Artivirus) of the family Totiviridae. J Gen Virol 91:2836–2845
Yang G, Hu F, Shi N, Wang P, Huang B (2020) A novel non-segmented double-stranded RNA virus isolated from the basal fungus Conidiobolus sp. Arch Virol 165:1919–1923
Spatafora JW, Chang Y, Benny GL, Lazarus K, Smith ME, Berbee ML, Bonito G, Corradi N, Grigoriev I, Gryganskyi A, James TY, O’Donnell K, Roberson RW, Taylor TN, Uehling J, Vilgalys R, White MM, Stajich JE (2016) A phylum-level phylogenetic classifcation of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia 108:1028–10462
Nie Y, Yu D-S, Wang C-F, Liu X-Y, Huang B (2020) A taxonomic revision of the genus Conidiobolus (Ancylistaceae, Entomophthorales): four clades including three new genera. MycoKeys 66:55–81
Nibert ML, Debat HJ, Manny AR, Grigoriev IV, De Fine Licht HH (2019) Mitovirus and mitochondrial coding sequences from basal fungus Entomophthora muscae. Viruses 11:351
Herrero N, Dueñas E, Quesada-Moraga E, Zabalgogeazcoa I (2012) Prevalence and diversity of viruses in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:8523–8530
Yang J, Yang F, Ren L, Xiong Z, Wu Z, Dong J, Sun L, Zhang T, Hu Y, Du J, Wang J, Jin Q (2011) Unbiased parallel detection of viral pathogens in clinical samples by use of a metagenomic approach. J Clin Microbiol 49:3463–3469
Coutts RHA, Livieratos IC (2003) A rapid method for sequencing the 5′- and 3′-termini of double-stranded RNA viral templates using RLM-RACE. J Phytopathol 151:525–527
Katoh K, Rozewicki J, Yamada KD (2019) MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief Bioinform 20:1160–1166
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K, Battistuzzi FU (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Fujimura T, Esteban R (2011) Cap-snatching mechanism in yeast L-A double-stranded RNA virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:17667–17671
Fujimura T, Esteban R (2013) Cap snatching in yeast L-BC double-stranded RNA totivirus. J Biol Chem 288:23716–23724
Kozlakidis Z, Herrero N, Ozkan S, Kanhayuwa L, Jamal A, Bhatti MF, Coutts RH (2013) Sequence determination of a quadripartite dsRNA virus isolated from Aspergillus foetidus. Arch Virol 158:267–272
Bruenn ERAJA (1998) Functions of conserved motifs in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of a yeast double-stranded RNA virus. J Virol 72:4427–4429
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 31772226, 31471821 and 30770008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Massimo Turina.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
705_2021_5054_MOESM3_ESM.tif
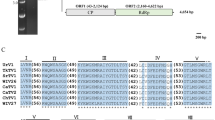
(A) A region extracted from a multiple amino acid (aa) sequence alignments of coat proteins (CPs) of ChTV1 and other totiviruses, showing the position of the histidine (His) residue required for the cap-snatching mechanism of totiviral CPs in red (Supplementary Data 2). (B) Conserved amino acid sequence analysis of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRPs) of totiviruses. Identical residues are indicated by the same background color and are represented by an asterisk. Virus abbreviations are shown in Supplementary Table 1 (TIF 1110 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Shi, N., Yang, G. et al. Molecular characterization of a novel totivirus infecting the basal fungus Conidiobolus heterosporus. Arch Virol 166, 1801–1804 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-021-05054-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-021-05054-6