Abstract
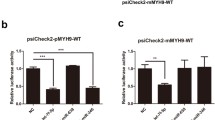
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV, species Betaarterivirus suid 1 or 2) is a major pathogen affecting pigs on farms throughout the world. miR-296-3p is a multifunctional microRNA involved in the regulation of the inflammatory response in mice and humans. However, little is known about the biological functions of miR-296-3p in pigs. In this study, we used a highly pathogenic PRRSV-2 (species Betaarterivirus suid 2) strain to show that PRRSV infection robustly downregulates the expression of miR-296-3p in porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs). Furthermore, we demonstrated that overexpression of miR-296-3p increases the replication of highly pathogenic (HP)-PRRSV in PAMs. Notably, the overexpression of miR-296-3p inhibited the induction of TNF-α, even with increased viral replication, compared with that in the HP-PRRSV-infected control group. We also demonstrated that miR-296-3p targets IRF1-facilitated viral infection and modulates the expression of TNF-α in PAMs during HP-PRRSV infection and that IRF1 regulates the expression of TNF-α by activating the TNF promoter via IRF1 response elements. In summary, these findings show that HP-PRRSV infection activates the IRF1/TNF-α signaling axis in PAMs by downregulating host miR-296-3p. This extends our understanding of the inflammatory response induced by HP-PRRSV infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li H, Ouyang XP, Jiang T, Zheng XL, He PP, Zhao GJ (2018) MicroRNA-296: a promising target in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis? Mol Med (Camb, Mass) 24(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-018-0012-y
Zhai H, Sui M, Jiang L, Hu J, Jiang X, Yuan Y, Li M, Yu Z, Hu S (2016) MiR-296 promotes colorectal cancer cells growth through regulating NF-κB. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 9(4):4391–4396
Yoon AR, Gao R, Kaul Z, Choi IK, Ryu J, Noble JR, Kato Y, Saito S, Hirano T, Ishii T, Reddel RR, Yun CO, Kaul SC, Wadhwa R (2011) MicroRNA-296 is enriched in cancer cells and downregulates p21WAF1 mRNA expression via interaction with its 3′ untranslated region. Nucleic Acids Res 39(18):8078–8091. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr492
Lee H, Shin CH, Kim HR, Choi KH, Kim HH (2017) MicroRNA-296-5p promotes invasiveness through downregulation of nerve growth factor receptor and caspase-8. Mol Cells 40(4):254–261. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.2270
Zhou X, Michal JJ, Jiang Z, Liu B (2017) MicroRNA expression profiling in alveolar macrophages of indigenous Chinese Tongcheng pigs infected with PRRSV in vivo. J Appl Genet 58(4):539–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-017-0410-9
Gulyaeva A, Dunowska M, Hoogendoorn E, Giles J, Samborskiy D, Gorbalenya AE (2017) Domain organization and evolution of the highly divergent 5′ coding region of genomes of arteriviruses, including the novel possum nidovirus. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02096-16
Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ, King AMQ, Harrach B, Harrison RL, Knowles NJ, Kropinski AM, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Mushegian AR, Nibert M, Sabanadzovic S, Sanfaçon H, Siddell SG, Simmonds P, Varsani A, Zerbini FM, Gorbalenya AE, Davison AJ (2017) Changes to taxonomy and the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2017). Arch Virol 162(8):2505–2538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3358-5
Tian K, Yu X, Zhao T, Feng Y, Cao Z, Wang C, Hu Y, Chen X, Hu D, Tian X, Liu D, Zhang S, Deng X, Ding Y, Yang L, Zhang Y, Xiao H, Qiao M, Wang B, Hou L, Wang X, Yang X, Kang L, Sun M, Jin P, Wang S, Kitamura Y, Yan J, Gao GF (2007) Emergence of fatal PRRSV variants: unparalleled outbreaks of atypical PRRS in China and molecular dissection of the unique hallmark. PLoS One 2(6):e526. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000526
Guo B, Lager KM, Henningson JN, Miller LC, Schlink SN, Kappes MA, Kehrli ME Jr, Brockmeier SL, Nicholson TL, Yang HC, Faaberg KS (2013) Experimental infection of United States swine with a Chinese highly pathogenic strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virology 435(2):372–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2012.09.013
Hu SP, Zhang Z, Liu YG, Tian ZJ, Wu DL, Cai XH, He XJ (2013) Pathogenicity and distribution of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in pigs. Transbound Emerg Dis 60(4):351–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1865-1682.2012.01354.x
Morgan SB, Frossard JP, Pallares FJ, Gough J, Stadejek T, Graham SP, Steinbach F, Drew TW, Salguero FJ (2016) Pathology and virus distribution in the lung and lymphoid tissues of pigs experimentally inoculated with three distinct type 1 PRRS virus isolates of varying pathogenicity. Transbound Emerg Dis 63(3):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.12272
Liu F, Du Y, Feng WH (2017) New perspective of host microRNAs in the control of PRRSV infection. Vet Microbiol 209:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.01.004
An TQ, Li JN, Su CM, Yoo D (2020) Molecular and cellular mechanisms for PRRSV pathogenesis and host response to infection. Virus Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2020.197980m
Chen J, Shi X, Zhang X, Wang A, Wang L, Yang Y, Deng R, Zhang GP (2017) MicroRNA 373 facilitates the replication of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by its negative regulation of type I interferon induction. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01311-16
Liu F, Wang H, Du L, Wei Z, Zhang Q, Feng WH (2018) MicroRNA-30c targets the interferon-alpha/beta receptor beta chain to promote type 2 PRRSV infection. J Gen Virol 99(12):1671–1680. https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.001166
Qi P, Liu K, Wei J, Li Y, Li B, Shao D, Wu Z, Shi Y, Tong G, Qiu Y, Ma Z (2017) Nonstructural protein 4 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus modulates cell surface swine leukocyte antigen class I expression by downregulating β2-microglobulin transcription. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01755-16
Shi Z, Wei J, Deng X, Li S, Qiu Y, Shao D, Li B, Zhang K, Xue F, Wang X, Ma Z (2014) Nitazoxanide inhibits the replication of Japanese encephalitis virus in cultured cells and in a mouse model. Virol J 11:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422x-11-10
Neal LM, Qiu Y, Chung J, Xing E, Cho W, Malachowski AN, Sandysloat AR, Osterholzer JJ, Maillard I, Olszewski MA (2017) T cell–restricted notch signaling contributes to pulmonary Th1 and Th2 immunity during Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol 199(2):643–655
Ma F, Liu X, Li D, Wang P, Li N, Lu L, Cao X (2010) MicroRNA-466l upregulates IL-10 expression in TLR-triggered macrophages by antagonizing RNA-binding protein tristetraprolin-mediated IL-10 mRNA degradation. J Immunol 184(11):6053–6059. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0902308
Qiu Y, Shen Y, Li X, Liu Q, Ma Z (2008) Polyclonal antibody to porcine p53 protein: a new tool for studying the p53 pathway in a porcine model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377(1):151–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.09.117
Messeguer X, Escudero R, Farré D, Núñez O, Martínez J, Albà MM (2002) PROMO: detection of known transcription regulatory elements using species-tailored searches. Bioinformatics (Oxf, Engl) 18(2):333–334. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/18.2.333
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS (2003) MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol 5(1):R1. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2003-5-1-r1
Bao D, Wang R, Qiao S, Wan B, Wang Y, Liu M, Shi X, Guo J, Zhang G (2013) Antibody-dependent enhancement of PRRSV infection down-modulates TNF-α and IFN-β transcription in macrophages. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 156(1–2):128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2013.09.006
Van Reeth K, Labarque G, Nauwynck H, Pensaert M (1999) Differential production of proinflammatory cytokines in the pig lung during different respiratory virus infections: correlations with pathogenicity. Res Vet Sci 67(1):47–52. https://doi.org/10.1053/rvsc.1998.0277
Han D, Hu Y, Li L, Tian H, Chen Z, Wang L, Ma H, Yang H, Teng K (2014) Highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection results in acute lung injury of the infected pigs. Vet Microbiol 169(3–4):135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.12.022
Zhang L, Liu J, Bai J, Wang X, Li Y, Jiang P (2013) Comparative expression of Toll-like receptors and inflammatory cytokines in pigs infected with different virulent porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolates. Virol J 10:135. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422x-10-135
Li Y, Wu Z, Liu K, Qi P, Xu J, Wei J, Li B, Shao D, Shi Y, Qiu Y, Ma Z (2017) Proteomic analysis of the secretome of porcine alveolar macrophages infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Proteomics. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201700080
Lu Y, Zhang Y, Xiang X, Sharma M, Liu K, Wei J, Shao D, Li B, Tong G, Olszewski MA, Ma Z, Qiu Y (2020) Notch signaling contributes to the expression of inflammatory cytokines induced by highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (HP-PRRSV) infection in porcine alveolar macrophages. Dev Comp Immunol 108:103690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2020.103690
Zhang F, Lin X, Yang X, Lu G, Zhang Q, Zhang C (2019) MicroRNA-132-3p suppresses type I IFN response through targeting IRF1 to facilitate H1N1 influenza A virus infection. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20192769
Hazra B, Kumawat KL (2017) The host microRNA miR-301a blocks the IRF1-mediated neuronal innate immune response to Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Sci Signal 10(466):eaaf5185. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaf5185
Xie Y, He S, Wang J (2018) MicroRNA-373 facilitates HSV-1 replication through suppression of type I IFN response by targeting IRF1. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother 97:1409–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.071
Acknowledgements
This study was supported, in part, by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972693), the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0500101), the Chinese Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest (no. 2020JB04), and the Elite Program of CAAS (to YQ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YQ conceived and designed the experiments; YZ performed the experiments; XX, YL, HL, AW, MS, KL, JW, ZL, DS, and BL contributed to the preparation of samples and reagents/materials; YZ, ZM, and YQ wrote the paper. All of the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Sheela Ramamoorthy.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xiang, X., Lu, Y. et al. Downregulation of miR-296-3p by highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus activates the IRF1/TNF-α signaling axis in porcine alveolar macrophages. Arch Virol 166, 511–519 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04921-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04921-y