Abstract
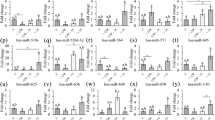
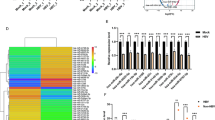
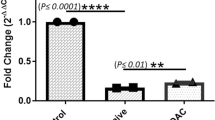
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important host molecules involved in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) can affect the miRNA expression profile, but differentially expressed miRNAs still remain to be identified. In this study, we used gene chips to analyze miRNA expression profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from ART-naive HIV-1 patients and those receiving ART, as well as from uninfected individuals. We measured differences in miRNA expression by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) in an expanded sample. We found significant differences in the expression of has-miR-191-5p among the three groups (P < 0.05). Furthermore, we showed that hsa-miR-191-5p has an inhibitory effect on HIV-1 replication in cell models in vitro. We identified CCR1 and NUP50 as target molecules of hsa-miR-191-5p and found that hsa-miR-191-5p inhibits the expression of CCR1 and NUP50. Knockdown of NUP50 resulted in significant inhibition of HIV-1 replication. In summary, our research shows that hsa-miR-191-5p expression is reduced in HIV-1-infected patients and acts an inhibitor of HIV-1 infection via a mechanism that may involve targeted repression of NUP50 expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The SPSS data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- PCAF:
-
P300/CBP-associated factor
- TNPO3:
-
Transportin 3
- 3'UTR:
-
3 Untranslated region
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- ART:
-
Antiretroviral therapy
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- MAGIA:
-
MiRNA and genes integrated analysis
References
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120(1):15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035
Swaminathan S, Murray DD, Kelleher AD (2013) miRNAs and HIV: unforeseen determinants of host-pathogen interaction. Immunol Rev 254(1):265–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12077
Triboulet R, Mari B, Lin Y-L et al (2007) Suppression of microRNA-silencing pathway by HIV-1 during virus replication. Science 315(5818):1579–1582. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1136319
Sung T-L, Rice AP (2009) miR-198 inhibits HIV-1 gene expression and replication in monocytes and its mechanism of action appears to involve repression of cyclin T1. PLoS Pathog 5(1):e1000263. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000263
Houzet L, Yeung ML, de Lame V, Desai D, Smith SM, Jeang KT (2008) MicroRNA profile changes in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) seropositive individuals. Retrovirology 5:118. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4690-5-118
Witwer KW, Watson AK, Blankson JN, Clements JE (2012) Relationships of PBMC microRNA expression, plasma viral load, and CD4+T-cell count in HIV-1-infected elite suppressors and viremic patients. Retrovirology 9:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4690-9-5
Coiras M, López-Huertas MR, Pérez-Olmeda M, Alcamí J (2009) Understanding HIV-1 latency provides clues for the eradication of long-term reservoirs. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(11):798–812. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2223
Ahluwalia JK, Khan SZ, Soni K et al (2008) Human cellular microRNA hsa-miR-29a interferes with viral nef protein expression and HIV-1 replication. Retrovirology 5:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4690-5-117
Nathans R, Chu CY, Serquina AK, Lu CC, Cao H, Rana TM (2009) Cellular microRNA and P bodies modulate host-HIV-1 interactions. Mol Cell 34(6):696–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.003
Sun G, Li H, Wu X et al (2012) Interplay between HIV-1 infection and host microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 40(5):2181–2196. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr961
Bochnakian A, Zhen A, Zisoulis DG et al (2019) Interferon-inducible MicroRNA miR-128 modulates HIV-1 replication by targeting TNPO3 mRNA. J Virol 93:20. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00364-19
Shah MY, Pan X, Fix LN, Farwell MA, Zhang B (2011) 5-Fluorouracil drug alters the microrna expression profiles in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 226(7):1868–1878. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22517
Reid RW, Fodor AA (2008) Determining gene expression on a single pair of microarrays. BMC Bioinform 9(1):489. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-489
Hsu SD, Tseng YT, Shrestha S et al (2014) MiRTarBase update 2014: an information resource for experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D78-85. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1266
Bisognin A, Sales G, Coppe A, Bortoluzzi S, Romualdi C (2012) MAGIA2: from miRNA and genes expression data integrative analysis to microRNA-transcription factor mixed regulatory circuits (2012 update). Nucleic Acids Res 40(Web Server issue):W13-21. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks460
Ako-Adjei D, Fu W, Wallin C, Katz KS, Song G, Darji D, Brister JR, Ptak RG, Pruitt KD (2015) HIV-1, human interaction database: current status and new features. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D566-570. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1126
Konig R, Zhou Y, Elleder D et al (2008) Global analysis of host-pathogen interactions that regulate early-stage HIV-1 replication. Cell 135(1):49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.032
Zhou H, Xu M, Huang Q et al (2008) Genome-scale RNAi screen for host factors required for HIV replication. Cell Host Microbe 4(5):495–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2008.10.004
Krüger J, Rehmsmeier M (2006) RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Web Server issue):W451–W454. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl243
Sheth U, Parker R (2003) Decapping and decay of messenger RNA occur in cytoplasmic processing bodies. Science 300(5620):805–808. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1082320
Pedersen IM, Cheng G, Wieland S, Volinia S, Croce CM, Chisari FV, David M (2007) Interferon modulation of cellular microRNAs as an antiviral mechanism. Nature 449(7164):919–922. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06205
Egana-Gorrono L, Escriba T, Boulanger N, Guardo AC, León A, Bargalló ME, Garcia F, Gatell JM, Plana M, Arnedo M (2014) Differential microRNA expression profile between stimulated PBMCs from HIV-1 infected elite controllers and viremic progressors. PLoS ONE 9(9):e106360. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106360
Nagpal N, Kulshreshtha R (2014) MiR-191: an emerging player in disease biology. Front Genet 5:99. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00099
Sisk JM, Clements JE, Witwer KW (2012) MiRNA profiles of monocyte-lineage cells are consistent with complicated roles in HIV-1 restriction. Viruses 4(10):1844–1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4101844
Shen C-J, Jia Y-H, Tian R-R et al (2012) Translation of Pur-α is targeted by cellular miRNAs to modulate the differentiation-dependent susceptibility of monocytes to HIV-1 infection. FASEB J 26(11):4755–4764. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-209023
Coley W, Van Duyne R, Carpio L, Guendel I, Kehn-Hall K, Chevalier S, Narayanan A, Luu T, Lee N, Klase Z, Kashanchi F (2010) Absence of DICER in monocytes and its regulation by HIV-1. J Biol Chem 285(42):31930–31943. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.101709
Klase Z, Kale P, Winograd R, Gupta MV, Heydarian M, Berro R, McCaffrey T, Kashanchi F (2007) HIV-1 TAR element is processed by Dicer to yield a viral micro-RNA involved in chromatin remodeling of the viral LTR. BMC Mol Biol 8:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-8-63
Swaminathan G, Rossi F, Sierra L-J, Gupta A, Martín SN, García JM (2012) A role for microRNA-155 modulation in the anti-HIV-1 effects of Toll-like receptor 3 stimulation in macrophages. PLoS Pathog 8(9):e1002937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002937
Swaminathan S, Zaunders J, Wilkinson J, Suzuki K, Kelleher AD (2007) Does the presence of anti-HIV miRNAs in monocytes explain their resistance to HIV-1 infection? Leuk Lymphoma 113(20):5029–5030. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-01-196741
Zhao J, Cheng-Rui Q, Sheng Y, Li X, Yang Y, Zhu D, Zhang C, Liu D, Wu K, Zhao S (2017) A novel pathway in NSCLC cells: miR-191, targeting NFIA, is induced by chronic hypoxia, and promotes cell proliferation and migration. Mol Med Rep 15(3):1319–1325. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6100
Zhang X, Wu M, Chong Q, Zhang W, Qian P, Yan H, Qian W, Zhang M, Lobie PE, Zhu T (2018) Amplification of hsa-miR-191/425 locus promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting DICER1. Carcinogenesis 39(12):1506–1516. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgy102
Xu G, Zhang Y, Jia H, Li J, Liu X, Engelhardt JF, Wang Y (2009) Cloning and identification of microRNAs in bovine alveolar macrophages. Mol Cell Biochem 332(1–2):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0168-4
Di Leva G, Croce CM (2013) miRNA profiling of cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 23:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2013.01.004
Saba R, Goodman CD, Huzarewich R, Huzarewich R, Robertson C, Booth SA (2008) A miRNA signature of prion induced neurodegeneration. PLoS ONE 3(11):e3652. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003652
Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, Yao W, Shen L, Wang C, Hu Z, Zhuang R, Ning G, Zhang C, Yuan Y, Li Z, Zen K, Ba Y, Zhang C (2012) Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem 58:610–618. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2011.172767
Collins AL, Wojcik S, Liu J, Frankel WL, Alder H, Yu L, Schmittgen TD, Croce CM, Bloomston M (2014) A differential microRNA profile distinguishes cholangiocarcinoma from pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 21(1):133–138. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3240-y
Hunter MP, Ismail N, Zhang X, Aguda B, Lee E, Yu L, Xiao T, Schafer J, Lee M, Schmittgen T, Sinkam S, Jarjoura D, Marsh C (2008) Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS ONE 3(11):e3694. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003694
Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD (2008) MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol 9(8):839–845. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.f.209
Gupta P, Saksena NK (2013) miRNAs: small molecules with a big impact on HIV infection and pathogenesis. Future Virology 8(8):769–781. https://doi.org/10.2217/fvl.13.59
Munshi SU, Panda H, Holla P, Rewari BB, Jameel S (2014) MicroRNA-150 is a potential biomarker of HIV/AIDS disease progression and therapy. PLoS ONE 9(5):e95920. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095920
Patel RS, Jakymiw A, Yao B, Pauley BA, Carcamo WC, Katz J, Cheng JQ, Chan E (2011) High resolution of microRNA signatures in human whole saliva. Arch Oral Biol 56(12):1506–1513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.05.015
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N (2008) Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 455(7209):58–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07228
Ekimler S, Sahin K (2014) Computational methods for microRNA target prediction. Genes 5(3):671–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-748-8_12
Woodward CL, Chow SA (2010) The nuclear pore complex: a new dynamic in HIV-1 replication. Nucleus 1(1):18–22. https://doi.org/10.4161/nucl.1.1.10571
Chan EY, Qian W-J, Diamond DL, Liu T, Gritsenko MA, Monroe ME, Camp DG, Smith RD, Katze MG (2007) Quantitative analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected CD4+ cell proteome: dysregulated cell cycle progression and nuclear transport coincide with robust virus production. J Virol 81(14):7571–7583. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00288-07
Rotger M, Dang KK, Fellay J, Heinzen LE, Feng S, Descombes P, Shianna K, Ge D, Günthard HF, Goldstein D, Telenti A (2010) Genome-wide mRNA expression correlates of viral control in CD4+T-cells from HIV-1-infected individuals. PLoS Pathog 6(2):e1000781. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000781
Konig R, Zhou Y, Elleder D, Diamond T, Bonamy G, Irelan J, Chiang C, Tu B, Jesus P, Lilley C, Seidel S, Opaluch A, Caldwell J, Weitzman M, Kuhen K, Bandyopadhyay S, Ideker T, Orth A, Miraglia L, Bushman F, Young J, Chandaet S (2008) Global analysis of host-pathogen interactions that regulate early-stage HIV-1 replication. Cell 135(1):49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.032
Acknowledgements
Yanghao Zheng, Zongxing Yang, Changzhong Jin, and Nanping Wu designed and supervised the experiments. Yanghao Zheng, Zongxing Yang, and Chaoyu Chen performed the tests and prepared the figures. Yanghao Zheng and Zongxing Yang drafted the manuscript, and Changzhong Jin revised it for valuable intellectual content. We would like to thank the native English-speaking scientists of Elixigen Company (Huntington Beach, California) for editing our manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project during the 13th Five-Year Plan of China (Grant no. 2017ZX10202101-004-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures were done in accordance with ethical standards.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Carolina Scagnolari.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Yang, Z., Jin, C. et al. hsa-miR-191-5p inhibits replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by downregulating the expression of NUP50. Arch Virol 166, 755–766 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04899-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04899-7