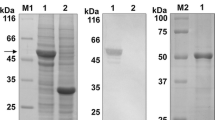
Abstract
Chinese sacbrood disease (CSBD) is a highly pathogenic infectious disease in bees that is caused by Chinese sacbrood virus (CSBV). Although several molecular detection methods have been developed for CSBV, there are no commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. We therefore developed a sandwich ELISA to detect CSBV antigens. To this end, monoclonal antibodies were produced using VP2 as an immunogen and subsequently characterized. Hybridomas were screened for the secretion of immunoglobulin G (IgG). Using an unlabeled monoclonal antibody (mAb) for coating and a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled mAb for detection, a CSBV sandwich ELISA method was established. This method showed specificity for CSBV and did not show cross-reactivity with other bee viruses. The detection limit of the sandwich ELISA was 3.675 × 104 copies/µL. Sixty bee larvae were tested using our sandwich ELISA method, and the presence of CSBV was verified by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The total coincidence rate was 90%. Thus, a sandwich ELISA method with high specificity and accuracy and a detection limit of 3.675 × 104 copies/µL has been successfully developed and can be used for the clinical detection of CSBV. This method will support rapid diagnosis, real-time monitoring, and early warning of CSBD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma MX (2014) New insights of sacbrood virus. Virologica Sinica 29(6):410–413
Berényi O, Bakonyi T, Derakhshifar I, Köglberger H, Nowotny N (2006) Occurrence of six honeybee viruses in diseased austrian apiaries. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(4):2414–2420
Hassanyar AK, Huang S, Li Z et al (2019) Prevalence of bee viruses in Apis cerana cerana population from different locations in the Fujian Province of China. Microbiol Open 8(9):e00830
Li M, Fei D, Sun L, Ma M (2019) Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of Chinese sacbrood virus isolates from Apis mellifera. Peer J 7:e8003
Sun L, Li M, Fei D, Hu Y, Ma M (2017) Chinese sacbrood virus infection in Apis mellifera, Shandong, China, 2016. Virus Res 242:96–99
Ma MX, Li M, Cheng J, Yang S, Wang SD, Li PF (2011) Molecular and biological characterization of Chinese sacbrood virus LN isolate. Comp Funct Genom 2011:409386
Ma MX, Ma C, Cheng J, Xie Z, Li M, Fei DL (2011) Prediction and identification of structural proteins of chinese sacbrood virus LN isolate. Chem J Chin Univ 32(8):1768–1773
Fei DL, Zhang H, Diao QY, Jiang LL, Wang Q, Zhong Y, Fan ZB, Ma MX (2015) Correction: codon optimization, expression in escherichiacoli, and immunogenicity of recombinant Chinese Sacbrood virus (CSBV) structural proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3. PloS One 10:e0128486
Li FB, Fei DL, Zhang H, Hu Y, Wei D, Zhang H, Yue JJ, Ma MX (2017) Optimized expression of the VP2 code of the structural protein of CSBV and its immunogenicity. Chin J Virol 02:108–114
Zhang XY, Fei DL, Sun L, Li M, Ma YY, Wang C, Huang SC, Ma MX (2019) Identification of the novel host protein interacting with the structural protein vp1 of chinese sacbrood virus by yeast two-hybrid screening. Front Microbiol 10:2192
Fei DL, Wei D, Yu XL, Yue JJ, Li M, Sun L, Jiang LL, Li Y, Diao QY, Ma MX (2018) Screening of binding proteins that interact with chinese sacbrood virus vp3 capsid protein in, apis cerana, larvae cdna library by the yeast two-hybrid method. Virus Res 248:24–30
Xia X, Zhou B, Wei T (2015) Complete genome of Chinese sacbrood virus from Apis cerana and analysis of the 3C-like cysteine protease. Virus Genes 50(2):277–285
Zhang J, Feng J, Liang Y, Zhang Q, Lu X, Chen D, Zhou Z (2001) Three-dimensional structure of the Chinese Sacbrood bee virus. Sci China C Life Sci 44(4):443–448
Zhang H (2018) Preparation of monoclonal antibody against Saccharomyces cerevisiae larvirus and establishment of agar diffusion assay. Dissertation, Jinzhou Medical University
Mingxiao M, Jinhua L, Yingjin S, Li L, Yongfei L (2013) TaqMan MGB probe fluorescence real-time quantitative PCR for rapid detection of Chinese Sacbrood virus. PLoS One 8(2):e52670
Ma MX, Li M, Yuan CY (2010) Development of a rt-pcr method for determination of chinese sacbrood virus. Chin J Biol 23(4):425–427
Song Z, Wang Z, Feng X, Liu J, Wei C, Cai Y, Meng Q, Zhou L (2010) A real-time TaqMan PCR assay to detect Sacbrood virus in honeybee and honeybee peoducts. Acta Entomol Sinica 53(8):920–925
Ma MX, Ma C, Li M, Wang S, Yang S, Wang S (2011) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of Chinese sacbrood virus. J Virol Methods 176(1):115–119
Li Y, Ma MX, Song Y, Li Y (2014) Development of helicase-dependent amplification method for detection of Chinese sacbrood virus. Chin J Biol 27(02):267–271
Xie Z, Qin C, Xie L, Liu J, Pang Y, Deng X et al (2010) Recombinant protein-based elisa for detection and differentiation of antibodies against avian reovirus in vaccinated and non-vaccinated chickens. J Virol Methods 165(1):108–111
Chen L, Ruan F, Sun Y, Chen H (2019) Establishment of sandwich ELISA for detecting the H7 subtype influenza A virus. J Med Virol 1:25408
Zhang L, Du W, Chen C, Chen Z, Zhang L, Han Q, Xia X, Song Y, Zhang J (2018) Development and characterization of double-antibody sandwich ELISA for detection of zika virus infection. Viruses 10(11):v10110634
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31772760 and 31972626), an award for “Distinguished Professor of Liaoning Province,” the Liaoning Education Department Fund (L2015315), and the Natural Science Fund of Liaoning Province (No. 20180550289).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: T. K. Frey.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Sun, L., Ma, Y. et al. Development of a sandwich ELISA for the detection of Chinese sacbrood virus infection. Arch Virol 165, 1551–1556 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04634-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04634-2