Abstract
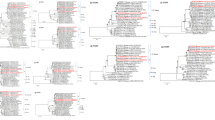
Introduction of animal group A rotavirus (RVA) gene segments into the human RVA population is a major factor shaping the genetic landscape of human RVA strains. The VP6 and NSP4 genes of 74 G/P-genotyped RVA isolates collected in Rawalpindi during 2010 were analyzed, revealing the presence of VP6 genotypes I1 (60.8%) and I2 (39.2%) and NSP4 genotypes E1 (60.8%), E2 (28.3%) and E-untypable (10.8%) among the circulating human RVA strains. The typical human RVA combinations I1E1 and I2E2 were found in 59.4% and 24.3% of the cases, respectively, whereas 5.4% of the RVA strains were reassortants, i.e., either I1E2 or I2E1. The phylogeny of the NSP4 gene showed that one G2P[4] and two G1P[6] RVA strains clustered with porcine E1 RVA strains or RVA strains that were considered to be (partially) of porcine origin. In addition, the NSP4 gene segment of the unusual human G6P[1] RVA strains clustered closely with bovine E2 RVA strains, further strengthening the hypothesis of an interspecies transmission event. The study further demonstrates the role of genomic re-assortment and the involvement of interspecies transmission in the evolution of human RVA strains. The VP6 and NSP4 nucleotide sequences analyzed in the study received the GenBank accession numbers KC846908- KC846971 and KC846972-KC847037, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crawford SE, Patel DG, Cheng E, Berkova Z, Hyser JM, Ciarlet M, Finegold MJ, Conner ME, Estes MK (2006) Rotavirus viremia and extraintestinal viral infection in the neonatal rat model. J Virol 80:4820–4832
Estes MK, Greenberg HB (2013) Rotaviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM et al (eds) Fields Virology, 6th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1347–1401
Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Heiman E, Arijs I, Delbeke T, McDonald SM, Palombo EA, Iturriza-Gomara M, Maes P, Patton JT, Rahman M, Van Ranst M (2008) Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-Like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J Virol 82:3204–3219
Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, McDonald SM, Attoui H, Banyai K, Brister JR, Buesa J, Esona MD, Estes MK, Gentsch JR, Iturriza-Gomara M, Johne R, Kirkwood CD, Martella V, Mertens PP, Nakagomi O, Parreno V, Rahman M, Ruggeri FM, Saif LJ, Santos N, Steyer A, Taniguchi K, Patton JT, Desselberger U, Van Ranst M (2011) Uniformity of rotavirus strain nomenclature proposed by the Rotavirus Classification Working Group (RCWG). Arch Virol 156:1397–1413
Matthijnssens J, Mino S, Papp H, Potgieter C, Novo L, Heylen E, Zeller M, Garaicoechea L, Badaracco A, Lengyel G, Kisfali P, Cullinane A, Collins PJ, Ciarlet M, O’Shea H, Parreno V, Banyai K, Barrandeguy M, Van Ranst M (2012) Complete molecular genome analyses of equine rotavirus A strains from different continents reveal several novel genotypes and a largely conserved genotype constellation. J Gen Virol 93:866–875
Papp H, Al-Mutairi LZ, Chehadeh W, Farkas SL, Lengyel G, Jakab F, Martella V, Szucs G, Banyai K (2012) Novel NSP4 genotype in a camel G10P[15] rotavirus strain. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 59:411–421
Trojnar E, Sachsenroder J, Twardziok S, Reetz J, Otto PH, Johne R (2013) Identification of an avian group A rotavirus containing a novel VP4 gene with a close relationship to those of mammalian rotaviruses. J Gen Virol 94:136–142
Heiman EM, McDonald SM, Barro M, Taraporewala ZF, Bar-Magen T, Patton JT (2008) Group A human rotavirus genomics: evidence that gene constellations are influenced by viral protein interactions. J Virol 82:11106–11116
McDonald SM, Matthijnssens J, McAllen JK, Hine E, Overton L, Wang S, Lemey P, Zeller M, Van Ranst M, Spiro DJ, Patton JT (2009) Evolutionary dynamics of human rotaviruses: balancing reassortment with preferred genome constellations. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000634
Iturriza-Gómara M, Isherwood B, Desselberger U, Gray J (2001) Reassortment in vivo: driving force for diversity of human rotavirus strains isolated in the United Kingdom between 1995 and 1999. J of virol 75:3696–3705
Settembre EC, Chen JZ, Dormitzer PR, Grigorieff N, Harrison SC (2011) Atomic model of an infectious rotavirus particle. EMBO J 30(2):408–416
Mihalov-Kovács E, Gellért Á, Marton S, Farkas SL, Fehér E, Oldal M, Jakab F, Martella V, Bányai K (2015) Candidate new rotavirus species in sheltered dogs, Hungary. Emerg Infect Dis 21(4):660–663
Benati FJ, Maranhao AG, Lima RS, da Silva RC, Santos N (2010) Multiplegene characterization of rotavirus strains: evidence of genetic linkage among the VP7-, VP4-, VP6-, and NSP4-encoding genes. J Med Virol 82:1797–1802
Khamrin P, Maneekarn N, Malasao R, Nguyen TA, Ishida S, Okitsu S, Ushijima H (2010) Genotypic linkages of VP4, VP6, VP7, NSP4, NSP5 genes of rotaviruses circulating among children with acute gastroenteritis in Thailand. Infect Genet Evol 10:467–472
Matthijnssens J, Rahman M, Ciarlet M, Zeller M, Heylen E, Nakagomi T, Uchida R, Hassan Z, Azim T, Nakagomi O, Van Ranst M (2010) Reassortment of human rotavirus gene segments into G11 rotavirus strains. Emerg Infect Dis 16:625–630
Solberg OD, Hasing ME, Trueba G, Eisenberg JN (2009) Characterization of novel VP7, VP4, and VP6 genotypes of a previously untypeable group A rotavirus. Virology 385:58–67
Esona MD, Mijatovic-Rustempasic S, Conrardy C, Tong S, Kuzmin IV, Agwanda B, Breiman RF, Banyai K, Niezgoda M, Rupprecht CE, Gentsch JR, Bowen MD (2010) Reassortant group A rotavirus from straw-colored fruit bat (Eidolon helvum). Emerg Infect Dis 16:1844–1852
Ghosh S, Shintani T, Kobayashi N (2012) Evidence for the porcine origin of equine rotavirus strain H-1. Vet Microbiol 158:410–414
Guo D, Liu J, Lu Y, Sun Y, Yuan D, Jiang Q, Lin H, Li C, Si C, Qu L (2012) Full genomic analysis of rabbit rotavirus G3P[14] strain N5 in China: identification of a novel VP6 genotype. Infect Genet Evol 12:1567–1576
Berkova Z, Crawford SE, Trugnan G, Yoshimori T, Morris AP, Estes MK (2006) Rotavirus NSP4 induces a novel vesicular compartment regulated by calcium and associated with viroplasms. J Virol 80:6061–6071
Chen F, Wang H, He H, Song L, Wu J, Gao Y, Liu X, He C, Yang H, Chen L, Wang L, Li G, Li Y, Kaplan DE, Zhong J (2011) Short hairpin RNAmediated silencing of bovine rotavirus NSP4 gene prevents diarrhoea in suckling mice. J Gen Virol 92:945–951
Rajasekaran D, Sastri NP, Marathahalli JR, Indi SS, Pamidimukkala K, Suguna K, Rao CD (2008) The flexible C terminus of the rotavirus non-structural protein NSP4 is an important determinant of its biological properties. J Gen Virol 89:1485–1496
Silvestri LS, Tortorici MA, Vasquez-Del Carpio R, Patton JT (2005) Rotavirus glycoprotein NSP4 is a modulator of viral transcription in the infected cell. J Virol 79:15165–15174
Ball JM, Tian P, Zeng CQ, Morris AP, Estes MK (1996) Age-dependent diarrhea induced by a rotaviral nonstructural glycoprotein. Science 272:101–104
Au KS, Chan WK, Burns JW, Estes MK (1989) Receptor activity of rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. J Virol 63:4553–4562
Meyer JC, Bergmann CC, Bellamy AR (1989) Interaction of rotavirus cores with the nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. Virology 171:98–107
Zhang M, Zeng CQ, Dong Y, Ball JM, Saif LJ, Morris AP, Estes MK (1998) Mutations in rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NSP4 are associated with altered virus virulence. J Virol 72:3666–3672
Araujo IT, Heinemann MB, Mascarenhas JD, Assis RM, Fialho AM, Leite JP (2007) Molecular analysis of the NSP4 and VP6 genes of rotavirus strains recovered from hospitalized children in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Med Microbiol 56:854–859
Ghosh S, Gatheru Z, Nyangao J, Adachi N, Urushibara N, Kobayashi N (2011) Full genomic analysis of a simian SA11-like G3P[2] rotavirus strain isolated from an asymptomatic infant: identification of novel VP1, VP6 and NSP4 genotypes. Infect Genet Evol 11:57–63
Matthijnssens J, Rahman M, Martella V, Xuelei Y, De Vos S, De Leener K, Ciarlet M, Buonavoglia C, Van Ranst M (2006) Full genomic analysis of human rotavirus strain B4106 and lapine rotavirus strain 30/96 provides evidence for interspecies transmission. J Virol 80:3801–3810
Sharma S, Paul VK, Bhan MK, Ray P (2009) Genomic characterization of nontypeable rotaviruses and detection of a rare G8 strain in Delhi, India. J Clin Microbiol 47:3998–4005
Rahman M, Goegebuer T, De Leener K, Maes P, Matthijnssens J, Podder G, Azim T, Van Ranst M (2004) Chromatography paper strip method for collection, transportation, and storage of rotavirus RNA in stool samples. J Clin Microbiol 42:1605–1608
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. 2016. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874
Tamim S, Hasan F, Matthijnssens J, Sharif S, Shaukat S, Alam MM, Angez M, Suleman Rana M, Khurshid A, Zaidi SS (2013) Epidemiology and phylogenetic analysis of VP7 and VP4 genes of rotaviruses circulating in Rawalpindi, Pakistan during 2010. Infect Genet Evol 14:161–168
Iturriza-Gomara M, Anderton E, Kang G, Gallimore C, Phillips W, Desselberger U, Gray J (2003) Evidence for genetic linkage between the gene segments encoding NSP4 and VP6 proteins in common and reassortant human rotavirus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 41:3566–3573
Au KS, Mattion NM, Estes MK (1993) A subviral particle binding domain on the rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. Virology 194:665–673
Ghosh S, Varghese V, Samajdar S, Bhattacharya SK, Kobayashi N, Naik TN (2007) Evidence for independent segregation of the VP6- and NSP4- encoding genes in porcine group A rotavirus G6P[13] strains. Arch Virol 152:423–429
Iturriza Gomara M, Wong C, Blome S, Desselberger U, Gray J (2002) Molecular characterization of VP6 genes of human rotavirus isolates: correlation of genogroups with subgroups and evidence of independent segregation. J Virol 76:6596–6601
Mukherjee A, Ghosh S, Bagchi P, Dutta D, Chattopadhyay S, Kobayashi N, Chawla-Sarkar M (2010) Full genomic analyses of human rotavirus G4P[4], G4P[6], G9P[19] and G10P[6] strains from North-eastern India: evidence for interspecies transmission and complex reassortment events. Clin Microbiol Infect 17:1343–1346
Tatte VS, Chitambar SD (2012) Evidence of discordant genetic linkage in the VP4, VP6, VP7 and NSP4 encoding genes of rotavirus strains from adolescent and adult patients with acute gastroenteritis. Infect Genet Evol 12:1630–1634
Banerjee I, Iturriza-Gomara M, Rajendran P, Primrose B, Ramani S, Gray JJ, Brown DW, Kang G (2007) Molecular characterization of G11P[25] and G3P[3] human rotavirus strains associated with asymptomatic infection in South India. J Med Virol 79:1768–1774
Rahman M, Matthijnssens J, Nahar S, Podder G, Sack DA, Azim T, Van Ranst M (2005) Characterization of a novel P[25], G11 human group a rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol 43:3208–3212
Doan YH, Nakagomi T, Aboudy Y, Silberstein I, Behar-Novat E, Nakagomi O, Shulman LM (2013) Identification by full-genome analysis of a bovine rotavirus transmitted directly to and causing diarrhea in a human child. J Clin Microbiol 51:182–189
Komoto S, Tacharoenmuang R, Guntapong R, Ide T, Haga K, Katayama K, Kato T, Ouchi Y, Kurahashi H et al (2015) Emergence and characterization of unusual DS-1-like G1P[8] rotavirus strains in children with diarrhea in Thailand. PLoS One 10:739
Fujii Y, Nakagomi T, Nishimura N, Noguchi A, Miura S, Ito H, Doan YH, Takahashi T, Ozaki T et al (2014) Spread and predominance in Japan of novel G1P[8] double-reassortant rotavirus strains possessing a DS-1-like genotype constellation typical of G2P[4] strains. Infect Genet Evol 28:426–433
Nakagomi T, Nguyen MQ, Gauchan P, Agbemabiese CA, Kaneko M, Do LP, Vu TD, Nakagomi O (2017) Evolution of DS-1-like G1P[8] double-gene reassortant rotavirus A strains causing gastroenteritis in children in Vietnam in 2012/2013. Arch Virol. 162(3):739–748
Jere KC, Chaguza C, Bar-Zeev N, Lowe J, Peno C, Kumwenda B, Nakagomi O, Tate JE, Parashar UD, Heyderman RS, French N, Cunliffe N, Iturriza-Gomara M (2018) Emergence of double- and triple-gene reassortant G1P[8] rotaviruses possessing a DS-1-like backbone after rotavirus vaccine introduction in Malawi. J Virol 92(3):17
Acknowledgements
Sana Tamim was supported by a PhD stipend and mobility grant from the Higher Education Commission (HEC) for research work at the Rega Institute for Medical Research, KU Leuven University, Leuven, Belgium. M.Z. was supported by the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT Vlaanderen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists that could inappropriately influence their work during the submission process.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Tim Skern.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamim, S., Matthijnssens, J., Heylen, E. et al. Evidence of zoonotic transmission of VP6 and NSP4 genes into human species A rotaviruses isolated in Pakistan in 2010. Arch Virol 164, 1781–1791 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04271-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04271-4