Abstract
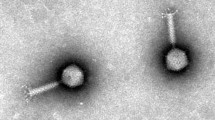
Members of the bacterial genus Aeromonas are important aquatic pathogens that cause severe fish diseases. Here, we characterize a novel lytic phage, Aeromonas virus phiA8-29, isolated from the alimentary tract of a freshwater fish. Transmission electron microscopy showed that phiA8-29 has a long contractile tail and thus can be classified as a member of the family Myoviridae. The phage genome was identified as a double-stranded DNA molecule of 144,974 bp containing 185 open reading frames and nine tRNA-encoding genes. Comparative genomic analysis revealed that the phiA8-29 genome has little similarity to any of the currently sequenced Aeromonas phage genomes. Our data indicate that phiA8-29 is a novel lytic Myoviridae phage that does not belong to any of the known genera.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedon ST, Garcia P, Mullany P, Aminov R (2017) Editorial: phage therapy: past, present and future. Front Microbiol 8:981
Chan BK, Abedon ST, Loc-Carrillo C (2013) Phage cocktails and the future of phage therapy. Future Microbiol 8:769–783
Deng Y, Wu Y, Jiang L, Tan A, Zhang R, Luo L (2016) Multi-drug resistance mediated by class 1 integrons in Aeromonas isolated from farmed freshwater animals. Front Microbiol 7:935
Fernandez J, Bert F, Nicolas-Chanoine MH (2016) The challenges of multi-drug-resistance in hepatology. J Hepatol 65:1043–1054
He Y, Yang H (2015) The gastrointestinal phage communities of the cultivated freshwater fishes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnu027
Holmfeldt K, Solonenko N, Shah M, Corrier K, Riemann L, Verberkmoes NC, Sullivan MB (2013) Twelve previously unknown phage genera are ubiquitous in global oceans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:12798–12803
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2010) The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:35–73
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31370205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Chan-Shing Lin.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Huang, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Characterization of a novel lytic myophage, phiA8-29, infecting Aeromonas strains. Arch Virol 164, 893–896 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-4109-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-4109-y