Abstract
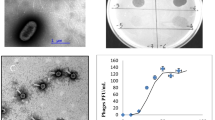
Bacteriophage Deep-Purple, isolated from an agricultural soil in Belgium, lyses the emetic Bacillus weihenstephanensis strain LH002 and exhibits a lytic activity against 55% of emetic Bacillus cereus and B. weihenstephanensis strains. Deep-Purple is able to complete its lytic cycle within 45 min and is stable to a large range of pHs and temperatures below 60 °C. It possesses an icosahedral head of about 63 nm in diameter and a non-contractile tail of approximately 165 nm in length. The genome of this newly classifiable Siphoviridae family member is 36,278 bp long, with a G+C content of 38.36% and 40 putative CDSs. Most CDSs do not display similarity with other B. cereus group phages supporting the idea that Deep-Purple belongs to a new and currently uncharacterised Siphoviridae subfamily.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
EFSA and ECDC (2016) The European Union Summary Report on Trends and Sources of Zoonoses, Zoonotic Agents and food-borne Outbreaks in 2015. EFSA J 14:12
Dierick K, Van Coillie E, Swiecicka I, Meyfroidt G, Devlieger H et al (2005) Fatal family outbreak of Bacillus cereus food poisoning. J Clin Microbiol 43:4277–4279
Naranjo M, Denayer S, Botteldoorn N, Delbrassinne L, Veys J et al (2011) Sudden death of a young adult associated with Bacillus cereus food poisoning. J Clin Microbiol 49:4379–4381
Lee WJ, Billington C, Hudson JA, Heinemann JA (2011) Isolation and characterization of phages infecting Bacillus cereus. Lett Appl Microbiol 52:456–464
Shin H, Bandara N, Shin E, Ryu S, Kim KP (2011) Prevalence of Bacillus cereus bacteriophages in fermented foods and characterization of phage JBP901. Res Microbiol 162:791–797
Kong M, Ryu S (2015) Bacteriophage PBC1 and its endolysin as an antimicrobial agent against Bacillus cereus. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:2274–2283
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (3-volume set). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Kajitani R, Toshimoto K, Noguchi H, Toyoda A, Ogura Y et al (2014) Efficient de novo assembly of highly heterozygous genomes from whole-genome shotgun short reads. Genome Res 24:1384–1395
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: A DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M et al (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649
Delcher AL, Harmon D, Kasif S, White O, Salzberg SL (1999) Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucl Acids Res 27:4636–4641
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T et al (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucl Acids Res 29:2607–2618
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE:a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucl Acids Res 25:955–964
Zankari E, Hasman H, Cosentino S, Vestergaard M, Rasmussen S et al (2012) Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J Antimicrob Chemother 67:2640–2644
Cosentino S, Larsen MV, Aarestrup FM, Lund O (2013) PathogenFinder—distinguishing friend from foe using bacterial whole genome sequence data. PloS One 8:e77302
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView Server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucl Acids Res 36:W181–W184
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl Acid Res 32:1792–1797
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lee YD, Park JH (2010) Genomic sequence of temperate phage 250 isolated from emetic B. cereus and cloning of putative endolysin. Food Sci Biotechnol 19:1643–1648
Smeesters PR, Drèze PA, Bousbata S, Parikka KJ, Timmery S et al (2011) Characterization of a novel temperate phage originating from a cereulide-producing Bacillus cereus strain. Res Microbiol 162:446–459
Nyunoya H, Lusty CJ (1983) The carB gene of Escherichia coli: a duplicated gene coding for the large subunit of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4629–4633
Gillis A, Mahillon J (2014) Phages preying on Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus thuringiensis: past, present and future. Viruses 6:2623–2672
Gillis A, Guo S, Bolotin A, Makart L, Sorokin A et al (2017) Detection of the cryptic prophage-like molecule pBtic235 in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Res Microbiol 168:319–330
Clokie M, Kropinski A (2009) Bacteriophages: methods and protocols, Vol 1: isolation, characterization and interactions, vol 501. Humana Press, New York, pp 307
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to P. Lipnik and D. Magnin for their technical assistance with transmission electron microscopy.
Funding
This study was funded by the FRIA (Fonds pour la formation à la Recherche dans l’Industrie et dans l’Agriculture) through a grant to L. Hock, the FNRS (National Fund for Scientific Research) through grants to A. Gillis and J. Mahillon, the Université catholique de Louvain and the Research Department of the Communauté française de Belgique (Concerted Research Action, ARC12_17-046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
L. Hock, A. Gillis and J. Mahillon declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Chan-Shing Lin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hock, L., Gillis, A. & Mahillon, J. Complete genome sequence of bacteriophage Deep-Purple, a novel member of the family Siphoviridae infecting Bacillus cereus. Arch Virol 163, 2555–2559 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3865-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3865-z