Abstract
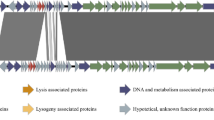
In this study, we present the characterization and genomic data of three Achromobacter phages belonging to the family Siphoviridae. Phages 83-24, JWX and JWF were isolated from sewage samples in Paris and Braunschweig, respectively, and infect Achromobacter xylosoxidans, an emerging nosocomial pathogen in cystic fibrosis patients. Analysis of morphology and growth parameters revealed that phages 83-24 and JWX have similar properties, both have nearly the same head and tail measurements, and both have a burst size between 85 and 100 pfu/cell. In regard to morphological properties, JWF had a much longer and more flexible tail compared to other phages. The linear double-stranded DNAs of all three phages are terminally redundant and not circularly permutated. The complete nucleotide sequences consist of 81,541 bp for JWF, 49,714 bp for JWX and 48,216 bp for 83-24. Analysis of the genome sequences showed again that phages JWX and 83-24 are quite similar. Comparison to the GenBank database via BLASTN revealed partial similarities to Roseobacter phage RDJL phi1 and Burkholderia phage BcepGomr. In contrast, BLASTN analysis of the genome sequence of phage JWF revealed only few similarities to non-annotated prophage regions in different strains of Burkholderia and Mesorhizobium.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yabuuchi E, Oyama A (1971) Achromobacter xylosoxidans n. sp. from human ear discharge. Jpn J Microbiol 15(5):477–481
Busse HJ, Auling G (2005) Genus II. Achromobacter Yabuuchi and Yano 1981, 477VP emend. Yabuuchi, Kawamura, Kosako and Ezaki 1998a, 1083. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. Springer, New York, pp 658–662
Spear JB, Fuhrer J, Kirby BD (1988) Achromobacter xylosoxidans (Alcaligenes xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans) bacteremia associated with a well-water source: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Microbiol 26(3):598–599
Mahenthiralingam E (2014) Emerging cystic fibrosis pathogens and the microbiome. Paediatr Respir Rev 15(Suppl 1):13–15. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2014.04.006
Trancassini M, Iebba V, Citera N, Tuccio V, Magni A, Varesi P, De Biase RV, Totino V, Santangelo F, Gagliardi A, Schippa S (2014) Outbreak of Achromobacter xylosoxidans in an Italian Cystic fibrosis center: genome variability, biofilm production, antibiotic resistance, and motility in isolated strains. Front Microbiol 5:138. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00138
Ahmed MS, Nistal C, Jayan R, Kuduvalli M, Anijeet HK (2009) Achromobacter xylosoxidans, an emerging pathogen in catheter-related infection in dialysis population causing prosthetic valve endocarditis: a case report and review of literature. Clin Nephrol 71(3):350–354
van Hal S, Stark D, Marriott D, Harkness J (2008) Achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans prosthetic aortic valve infective endocarditis and aortic root abscesses. J Med Microbiol 57(Pt 4):525–527. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.47496-0
Behrens-Muller B, Conway J, Yoder J, Conover CS (2012) Investigation and control of an outbreak of Achromobacter xylosoxidans bacteremia. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 33(2):180–184. doi:10.1086/663710
Tena D, Carranza R, Barbera JR, Valdezate S, Garrancho JM, Arranz M, Saez-Nieto JA (2005) Outbreak of long-term intravascular catheter-related bacteremia due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans subspecies xylosoxidans in a hemodialysis unit. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 24(11):727–732. doi:10.1007/s10096-005-0028-4
Park JH, Song NH, Koh JW (2012) Achromobacter xylosoxidans keratitis after contact lens usage. Korean J Ophthalmol 26(1):49–53. doi:10.3341/kjo.2012.26.1.49
Reddy AK, Garg P, Shah V, Gopinathan U (2009) Clinical, microbiological profile and treatment outcome of ocular infections caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Cornea 28(10):1100–1103. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181a1658f
Tena D, Gonzalez-Praetorius A, Perez-Balsalobre M, Sancho O, Bisquert J (2008) Urinary tract infection due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans: report of 9 cases. Scand J Infect Dis 40(2):84–87. doi:10.1080/00365540701558714
Wittmann J, Dreiseikelmann B, Rohde C, Rohde M, Sikorski J (2014) Isolation and characterization of numerous novel phages targeting diverse strains of the ubiquitous and opportunistic pathogen Achromobacter xylosoxidans. PLoS One 9(1):e86935. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086935
Abedon ST, Kuhl SJ, Blasdel BG, Kutter EM (2011) Phage treatment of human infections. Bacteriophage 1(2):66–85. doi:10.4161/bact.1.2.15845
Johnson RP, Gyles CL, Huff WE, Ojha S, Huff GR, Rath NC, Donoghue AM (2008) Bacteriophages for prophylaxis and therapy in cattle, poultry and pigs. Anim Health Res Rev 9(2):201–215. doi:10.1017/s1466252308001576
Zaczek M, Weber-Dabrowska B, Gorski A (2014) Phages in the global fruit and vegetable industry. J Appl Microbiol. doi:10.1111/jam.12700
Jones PT, Pretorius GHJ (1981) Achromobacter sp. 2 Phage a3: a physical characterization. J Gen Virol 55:275–281
Thomson JA, Woods DR (1974) Bacteriophages and cryptic lysogeny in Achromobacter. J Gen Virol 22(1):153–157
Wittmann J, Klumpp J, Moreno Switt AI, Yagubi A, Ackermann HW, Wiedmann M, Svircev A, Nash JH, Kropinski AM (2015) Taxonomic reassessment of N4-like viruses using comparative genomics and proteomics suggests a new subfamily—”Enquartavirinae”. Arch Virol 160(12):3053–3062. doi:10.1007/s00705-015-2609-6
Wittmann J, Dreiseikelmann B, Rohde M, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Bunk B, Rohde C (2014) First genome sequences of Achromobacter phages reveal new members of the N4 family. Virol J 11:14. doi:10.1186/1743-422x-11-14
Li E, Zhao J, Ma Y, Wei X, Li H, Lin W, Wang X, Li C, Shen Z, Zhao R, Jiang A, Yang H, Yuan J, Zhao X (2016) Characterization of a novel Achromobacter xylosoxidans specific siphoviruse: phiAxp-1. Sci Rep 6:21943. doi:10.1038/srep21943
Ma Y, Li E, Qi Z, Li H, Wei X, Lin W, Zhao R, Jiang A, Yang H, Yin Z, Yuan J, Zhao X (2016) Isolation and molecular characterisation of Achromobacter phage phiAxp-3, an N4-like bacteriophage. Sci Rep 6:24776. doi:10.1038/srep24776
Beilstein F, Dreiseikelmann B (2006) Bacteriophages of freshwater Brevundimonas vesicularis isolates. Res Microbiol 157(3):213–219. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2005.07.005
Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP (2013) Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 14(2):178–192. doi:10.1093/bib/bbs017
Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, Rajandream MA, Barrell B (2000) Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 16(10):944–945
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25(5):955–964
Laslett D, Canback B (2004) ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32(1):11–16. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh152
Park M, Lee JH, Shin H, Kim M, Choi J, Kang DH, Heu S, Ryu S (2012) Characterization and comparative genomic analysis of a novel bacteriophage, SFP10, simultaneously inhibiting both Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(1):58–69. doi:10.1128/aem.06231-11
Wittmann J, Gartemann KH, Eichenlaub R, Dreiseikelmann B (2011) Genomic and molecular analysis of phage CMP1 from Clavibacter michiganensis subspecies michiganensis. Bacteriophage 1(1):6–14. doi:10.4161/bact.1.1.13873
Valentine RC, Shapiro BM, Stadtman ER (1968) Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 7(6):2143–2152
Jakobsen TH, Hansen MA, Jensen PO, Hansen L, Riber L, Cockburn A, Kolpen M, Ronne Hansen C, Ridderberg W, Eickhardt S, Hansen M, Kerpedjiev P, Alhede M, Qvortrup K, Burmolle M, Moser C, Kuhl M, Ciofu O, Givskov M, Sorensen SJ, Hoiby N, Bjarnsholt T (2013) Complete genome sequence of the cystic fibrosis pathogen Achromobacter xylosoxidans NH44784-1996 complies with important pathogenic phenotypes. PLoS One 8(7):e68484. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0068484
Strnad H, Ridl J, Paces J, Kolar M, Vlcek C, Paces V (2011) Complete genome sequence of the haloaromatic acid-degrading bacterium Achromobacter xylosoxidans A8. J Bacteriol 193(3):791–792. doi:10.1128/JB.01299-10
Rocha EP, Danchin A (2002) Base composition bias might result from competition for metabolic resources. Trends Genet 18(6):291–294. doi:10.1016/s0168-9525(02)02690-2
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30(14):2068–2069. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Zhou Y, Liang Y, Lynch KH, Dennis JJ, Wishart DS (2011) PHAST: a fast phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 39((Web Server issue)):W347–W352. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr485
Ceyssens PJ, Mesyanzhinov V, Sykilinda N, Briers Y, Roucourt B, Lavigne R, Robben J, Domashin A, Miroshnikov K, Volckaert G, Hertveldt K (2008) The genome and structural proteome of YuA, a new Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage resembling M6. J Bacteriol 190(4):1429–1435. doi:10.1128/jb.01441-07
Seguritan V, Feng IW, Rohwer F, Swift M, Segall AM (2003) Genome sequences of two closely related Vibrio parahaemolyticus phages, VP16T and VP16C. J Bacteriol 185(21):6434–6447
Groth AC, Calos MP (2004) Phage integrases: biology and applications. J Mol Biol 335(3):667–678
Casjens SR, Gilcrease EB, Winn-Stapley DA, Schicklmaier P, Schmieger H, Pedulla ML, Ford ME, Houtz JM, Hatfull GF, Hendrix RW (2005) The generalized transducing Salmonella bacteriophage ES18: complete genome sequence and DNA packaging strategy. J Bacteriol 187(3):1091–1104. doi:10.1128/jb.187.3.1091-1104.2005
Fouts DE, Klumpp J, Bishop-Lilly KA, Rajavel M, Willner KM, Butani A, Henry M, Biswas B, Li M, Albert MJ, Loessner MJ, Calendar R, Sozhamannan S (2013) Whole genome sequencing and comparative genomic analyses of two Vibrio cholerae O139 Bengal-specific Podoviruses to other N4-like phages reveal extensive genetic diversity. Virol J 10:165. doi:10.1186/1743-422x-10-165
Merrill BD, Grose JH, Breakwell DP, Burnett SH (2014) Characterization of Paenibacillus larvae bacteriophages and their genomic relationships to firmicute bacteriophages. BMC Genom 15:745. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-745
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305(3):567–580. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315
Young R (2002) Bacteriophage holins: deadly diversity. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4(1):21–36
Stewart CR, Casjens SR, Cresawn SG, Houtz JM, Smith AL, Ford ME, Peebles CL, Hatfull GF, Hendrix RW, Huang WM, Pedulla ML (2009) The genome of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO1. J Mol Biol 388(1):48–70. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.009
Ong KS, Aw YK, Gan HM, Yule CM, Lee SM (2014) Draft genome sequences of two antimicrobial-producing Burkholderia sp. strains, MSh1 and MSh2, isolated from Malaysian Tropical Peat Swamp Forest Soil. Genome Announc. doi:10.1128/genomeA.01032-14
Summer EJ, Berry J, Tran TA, Niu L, Struck DK, Young R (2007) Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts. J Mol Biol 373(5):1098–1112. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.045
Mahadevan P, King JF, Seto D (2009) CGUG: in silico proteome and genome parsing tool for the determination of “core” and unique genes in the analysis of genomes up to ca. 1.9 Mb. BMC Res Notes 2:168. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-2-168
Lavigne R, Seto D, Mahadevan P, Ackermann HW, Kropinski AM (2008) Unifying classical and molecular taxonomic classification: analysis of the Podoviridae using BLASTP-based tools. Res Microbiol 159(5):406–414. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2008.03.005
Hatfull GF (2008) Bacteriophage genomics. Curr Opin Microbiol 11(5):447–453. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.004
Casjens SR, Thuman-Commike PA (2011) Evolution of mosaically related tailed bacteriophage genomes seen through the lens of phage P22 virion assembly. Virology 411(2):393–415. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2010.12.046
Maynaud G, Brunel B, Mornico D, Durot M, Severac D, Dubois E, Navarro E, Cleyet-Marel JC, Le Quere A (2013) Genome-wide transcriptional responses of two metal-tolerant symbiotic Mesorhizobium isolates to zinc and cadmium exposure. BMC Genom 14:292. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-292
Lohr JE, Chen F, Hill RT (2005) Genomic analysis of bacteriophage PhiJL001: insights into its interaction with a sponge-associated alpha-proteobacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1598–1609. doi:10.1128/aem.71.3.1598-1609.2005
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Simone Severitt, Nicole Heyer and Anja Meier for technical assistance. We further thank Professor Ed Moore (CCUG Culture Collection, University of Gothenburg, Sweden) and Dr. Danielle Janssens (BCCM/LMG, Laboratory for Microbiology, University of Gent, Belgium) for providing us with strains of Achromobacter xylosoxidans, and Professor Sylvain Moineau (Félix d`Hérelle Reference Center for Bacterial Viruses, Université Laval, Canada) for phage 83-24.
Author contributions
BD conceived and designed the experiments and wrote the paper, BB and CS performed sequencing and genome analysis, MR performed morphological analysis via TEM microscopy, MN analyzed the peptide mass fingerprinting data, JW conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreiseikelmann, B., Bunk, B., Spröer, C. et al. Characterization and genome comparisons of three Achromobacter phages of the family Siphoviridae . Arch Virol 162, 2191–2201 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3347-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3347-8