Abstract
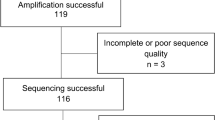
Resistance to antiretroviral agents is a significant concern in the clinical management of HIV-infected individuals, particularly in areas of the world where treatment options are limited. In this study, we aimed to identify HIV drug-resistance-associated mutations in 40 drug-naïve patients and 62 patients under antiretroviral therapy (ART) referred to the Shiraz HIV/AIDS Research Center – the first such data available for the south of Iran. HIV reverse transcriptase and protease genes were amplified and sequenced to determine subtypes and antiretroviral- resistance-associated mutations (RAMs). Subtype CRF35-AD recombinant was the most prevalent in all patients (98 of 102, 96 %), followed by subtype A1, and subtype B (one each, 2 %). Among the 40 ART-naïve patients, two mutations associated with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) resistance (two with Y115F and T215I) and three associated with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance (two with G190S and Y181C, four with V179T) were found. Among ART-experienced patients, four mutations associated with resistance to NRTI, four with NNRTI, and five with protease inhibitors (PI) were found. Twenty patients with high levels of resistance were already on second-line therapy. We document for the first time in this region of Iran high levels of ART resistance to multiple drugs. Our findings call for more vigilant systematic ART resistance surveillance, increased resistance testing, careful management of patients with existing regimens, and strong advocacy for expansion of available drugs in Iran.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clavel F, Hance AJ (2004) HIV drug resistance. N Engl J Med 350(10):1023–1035
Cortez KJ, Maldarelli F (2011) Clinical management of HIV drug resistance. Viruses 3(4):347–378
Richman DD, Morton SC, Wrin T, Hellmann N, Berry S, Shapiro MF et al (2004) The prevalence of antiretroviral drug resistance in the United States. Aids 18(10):1393–1401
Thomson MM, Pérez-Álvarez L, Nájera R (2002) Molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 genetic forms and its significance for vaccine development and therapy. Lancet Infect Dis 2(8):461–471
Kaleebu P, French N, Mahe C, Yirrell D, Watera C, Lyagoba F et al (2002) Effect of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 envelope subtypes A and D on disease progression in a large cohort of HIV-1—positive persons in Uganda. J Infect Dis 185(9):1244–1250
Alaeus A, Lidman K, Björkman A, Giesecke J, Albert J (1999) Similar rate of disease progression among individuals infected with HIV-1 genetic subtypes AD. Aids 13(8):901–907
Pieniazek D, Rayfield M, Hu DJ, Nkengasong J, Wiktor SZ, Downing R et al (2000) Protease sequences from HIV-1 group M subtypes A–H reveal distinct amino acid mutation patterns associated with protease resistance in protease inhibitor-naive individuals worldwide. Aids 14(11):1489–1495
Frater AJ, Dunn DT, Beardall AJ, Ariyoshi K, Clarke JR, McClure MO et al (2002) Comparative response of African HIV-1-infected individuals to highly active antiretroviral therapy. Aids 16(8):1139–1146
Pennings PS (2012) HIV drug resistance: problems and perspectives. arXiv preprint arXiv:12115807
Frentz D, Boucher C, Van De Vijver D (2012) Temporal changes in the epidemiology of transmission of drug-resistant HIV-1 across the world. AIDs Rev 14(1):17–27
Baesi K, Ravanshad M, Ghanbarisafari M, Saberfar E, SeyedAlinaghi S, Volk JE (2014) Antiretroviral drug resistance among antiretroviral-naïve and treatment experienced patients infected with HIV in Iran. J Med Virol 86(7):1093–1098
Jahanbakhsh F, Hattori J, Matsuda M, Ibe S, Monavari S-HR, Memarnejadian A et al (2013) Prevalence of transmitted HIV drug resistance in Iran between 2010 and 2011. PloS One 8(4):e61864
Mousavi SM, Hamkar R, Gouya MM, Safaie A, Zahraei SM, Yazdani Z et al (2010) Surveillance of HIV drug resistance transmission in Iran: experience gained from a pilot study. Arch Virol 155(3):329–334
Baesi K, Moallemi S, Farrokhi M, Alinaghi SAS, Truong HHM (2014) Subtype classification of Iranian HIV-1 sequences registered in the HIV databases, 2006–2013. PloS One 9(9):e105098
Stuyver L (1999) Method for detection of drug-selected mutations in the HIV protease gene. Google Patents
Edelstein RE, Nickerson DA, Tobe VO, Manns-Arcuino LA, Frenkel LM (1998) Oligonucleotide ligation assay for detecting mutations in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 polGene that are associated with resistance to zidovudine, didanosine, and lamivudine. J Clin Microbiol 36(2):569–572
Rhee S-Y, Gonzales MJ, Kantor R, Betts BJ, Ravela J, Shafer RW (2003) Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase and protease sequence database. Nucleic Acids Res 31(1):298–303
Sarrami-Forooshani R, Das SR, Sabahi F, Adeli A, Esmaeili R, Wahren B et al (2006) Molecular analysis and phylogenetic characterization of HIV in Iran. J Med Virol 78(7):853–863
Hamkar R, Mohraz M, Lorestani S, Aghakhani A, Truong H-HM, McFarland W et al (2010) Assessing subtype and drug-resistance-associated mutations among antiretroviral-treated HIV-infected patients. Aids 24:S85–S91
Soheilli ZS, Ataiee Z, Tootian S, Zadsar M, Amini S, Abadi K et al (2009) Presence of HIV-1 CRF35_AD in Iran. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 25(1):123–125
Baesi k, Moradbeigi M, Ravanshad M, Baghban A (2016) Phylogeny and drug resistance of HIV PR gene among HIV patients receiving RT inhibitors in Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. doi:10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.12.020
Gholami M, Sadeghi L, Baesi K, Rouzbahani NH, Mohraz M (2015) Survey of antiretroviral drug resistance pattern among HIV-infected patients with treatment failure in Iran. J Hum Virol Retrovir 3(1):1–6
Memarnejadian A, Menbari S, Mansouri SA, Sadeghi L, Vahabpour R, Aghasadeghi MR et al (2015) Transmitted drug resistance mutations in antiretroviral-naïve injection drug users with chronic HIV-1 infection in Iran. PloS One 10(5):e0126955
Weinstein MC, Goldie SJ, Losina E, Cohen CJ, Baxter JD, Zhang H et al (2001) Use of genotypic resistance testing to guide HIV therapy: clinical impact and cost-effectiveness. Ann Intern Med 134(6):440–450
Smith D, Moini N, Pesano R, Cachay E, Aiem H, Lie Y et al (2007) Clinical utility of HIV standard genotyping among antiretroviral-naive individuals with unknown duration of infection. Clin Infect Dis 44(3):456–458
World Health Organization (2012) The HIV drug resistance report-2012. World Health Organization, Geneva
Marconi VC, Sunpath H, Lu Z, Gordon M, Koranteng-Apeagyei K, Hampton J et al (2008) Prevalence of HIV-1 drug resistance after failure of a first highly active antiretroviral therapy regimen in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa. Clin Infect Dis 46(10):1589–1597
Baesi K, Ravanshad M, Hosseini Y, Abdolbaghi MH (2012) Drug resistance profile and subtyping of HIV-1 RT gene in Iranian patients under treatment. Iran J Biotechnol 10(1)
Lee N, Hogg RS, Yip B, Harrigan PR, Harris M, O’Shaughnessy MV et al (2003) Rates of disease progression among human immunodeficiency virus-infected persons initiating multiple-drug rescue therapy. J Infect Dis 188(1):137–141
Schuurman R, Nijhuis M, van Leeuwen R, Schipper P, de Jong D, Collis P et al (1995) Rapid changes in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA load and appearance of drug-resistant virus populations in persons treated with lamivudine (3TC). J Infect Dis 171(6):1411–1419
Durant J, Clevenbergh P, Halfon P, Delgiudice P, Porsin S, Simonet P et al (1999) Drug-resistance genotyping in HIV-1 therapy: the VIRAD APT randomised controlled trial. Lancet 353(9171):2195–2199
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge Golestan University of Medical Sciences for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding source
Golestan University of Medical Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naziri, H., Baesi, K., Moradi, A. et al. Antiretroviral drug resistance mutations in naïve and experienced patients in Shiraz, Iran, 2014. Arch Virol 161, 2503–2509 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-2955-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-2955-z