Abstract
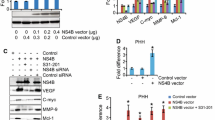
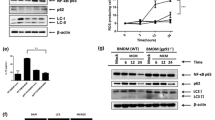
HBx acts as a multifunctional regulator that modulates various cellular responses, which can lead to development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we show that the HBx protein is also localized to peroxisomes, and this increases cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) to levels that are higher than when HBx is localized to other organelles. The elevated ROS strongly activated nuclear factor (NF)-κB. In addition, the peroxisome-localized HBx increased the expressions of matrix metalloproteinases and decreased the expression of E-cadherin, which increased the invasive ability of HCC cells. Thus, a specific distribution of HBx to peroxisomes may contribute to HCC progression by increasing the invasive ability of HCC cells through elevation of the cellular ROS level.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- AP-1:
-
Activation protein-1
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor κB
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- HA:
-
Hemagglutinin
- FIS1:
-
Mitochondrial fission 1 protein
- mAb:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- pAb:
-
Polyclonal antibody
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- IRES:
-
Internal ribosome entry site
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- MAVS:
-
Mitochondrial antiviral signaling
- NAC:
-
N-Acetyl cysteine
- PEX5:
-
Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 5
References
Baes M, Gressens P, Baumgart E, Carmeliet P, Casteels M, Fransen M, Evrard P, Fahimi D, Declercq PE, Collen D, van Veldhoven PP, Mannaerts GP (1997) A mouse model for Zellweger syndrome. Nat Genet 17:49–57
Chung TW, Lee YC, Kim CH (2004) Hepatitis B viral HBx induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression through activation of ERK and PI-3K/AKT pathways: involvement of invasive potential. FASEB J 18:1123–1125
Clippinger AJ, Bouchard MJ (2008) Hepatitis B virus HBx protein localizes to mitochondria in primary rat hepatocytes and modulates mitochondrial membrane potential. J Virol 82:6798–6811
Delille HK, Alves R, Schrader M (2009) Biogenesis of peroxisomes and mitochondria: linked by division. Histochem Cell Biol 131:441–446
Dixit E, Boulant S, Zhang Y, Lee AS, Odendall C, Shum B, Hacohen N, Chen ZJ, Whelan SP, Fransen M, Nibert ML, Superti-Furga G, Kagan JC (2010) Peroxisomes are signaling platforms for antiviral innate immunity. Cell 141:668–681
Jeong SP, Kang JA, Park SG (2012) Intestinal intraepithelial TCRgammadelta(+) T cells are activated by normal commensal bacteria. J Microbiol 50:837–841
Kim CM, Koike K, Saito I, Miyamura T, Jay G (1991) HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 351:317–320
Kim SY, Lee PY, Shin HJ, Kim do H, Kang S, Moon HB, Kang SW, Kim JM, Park SG, Park BC, Yu DY, Bae KH, Lee SC (2009) Proteomic analysis of liver tissue from HBx-transgenic mice at early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis. Proteomics 9:5056–5066
Kumar M, Jung SY, Hodgson AJ, Madden CR, Qin J, Slagle BL (2011) Hepatitis B virus regulatory HBx protein binds to adaptor protein IPS-1 and inhibits the activation of beta interferon. J Virol 85:987–995
Lim SO, Gu JM, Kim, Kim HS, Park YN, Park CK, Cho JW, Park YM, Jung G (2008) Epigenetic changes induced by reactive oxygen species in hepatocellular carcinoma: methylation of the E-cadherin promoter. Gastroenterology 135:2128–2140 (2140 e2121–2128)
Liu LP, Liang HF, Chen XP, Zhang WG, Yang SL, Xu T, Ren L (2010) The role of NF-kappaB in Hepatitis b virus X protein-mediated upregulation of VEGF and MMPs. Cancer Investig 28:443–451
Liu Y, Tong Z, Li T, Chen Q, Zhuo L, Li W, Wu RC, Yu C (2012) Hepatitis B virus X protein stabilizes amplified in breast cancer 1 protein and cooperates with it to promote human hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasiveness. Hepatology 56:1015–1024
Liu YN, Lee WW, Wang CY, Chao TH, Chen Y, Chen JH (2005) Regulatory mechanisms controlling human E-cadherin gene expression. Oncogene 24:8277–8290
Ma J, Sun T, Park S, Shen G, Liu J (2011) The role of hepatitis B virus X protein is related to its differential intracellular localization. Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica 43:583–588
Morgan MJ, Liu ZG (2011) Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Res 21:103–115
Ng SA, Lee C (2011) Hepatitis B virus X gene and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol 46:974–990
Park SG, Ryu HM, Lim SO, Kim YI, Hwang SB, Jung G (2005) Interferon-gamma inhibits hepatitis B virus-induced NF-kappaB activation through nuclear localization of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase. Gastroenterology 128:2042–2053
Park SG, Chung C, Kang H, Kim JY, Jung G (2006) Up-regulation of cyclin D1 by HBx is mediated by NF-kappaB2/BCL3 complex through kappaB site of cyclin D1 promoter. J Biol Chem 281:31770–31777
Schrader M, Fahimi HD (2004) Mammalian peroxisomes and reactive oxygen species. Histochem Cell Biol 122:383–393
Schrader M, Fahimi HD (2006) Peroxisomes and oxidative stress. Biochimica et biophysica acta 1763:1755–1766
Tang H, Oishi N, Kaneko S, Murakami S (2006) Molecular functions and biological roles of hepatitis B virus x protein. Cancer Sci 97:977–983
Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P (2009) Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:579–591
Wanders RJ, Waterham HR (2006) Biochemistry of mammalian peroxisomes revisited. Annu Rev Biochem 75:295–332
Waris G, Huh KW, Siddiqui A (2001) Mitochondrially associated hepatitis B virus X protein constitutively activates transcription factors STAT-3 and NF-kappa B via oxidative stress. Mol Cellular Biol 21:7721–7730
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A111838) and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST)(NRF-2013R1A1A2010995).
Conflict of interest
We confirm that all authors fulfill all conditions required for authorship. We also confirm that there is no potential conflict of interest or financial dependence regarding this publication, as described in the Instructions for Authors. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J.-M. Han and J.-A. Kang contributed equally to this paper
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, JM., Kang, JA., Han, MH. et al. Peroxisome-localized hepatitis Bx protein increases the invasion property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Arch Virol 159, 2549–2557 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2105-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2105-4