Abstract
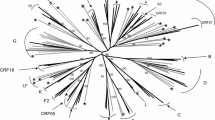
Modalities of intra-familial transmission of HIV-1 are not always clear. Here we describe an uncommon case of HIV transmission in a family setting, analyzed using clinical, epidemiological and nucleic-acid-based methods, and assess risk factors for intrafamilial transmission of HIV-1 infection. All sequences from the father and the daughter were grouped in the same cluster with a 100 % bootstrap value, which means that the father and his daughter were infected with highly homologous CRF01_AE. The diversity of genetic clones between env and pol genes was insignificant (p > 0.05). Moreover, the results of analysis of drug-resistance-associated mutation positions of the two viral isolates were almost identical, indicating that both were susceptible to the first-line anti-HIV drugs prior to the initiation of antiretroviral treatment (ART), and this presented additional evidence of a high similarity between the two family members’ HIV-1 quasispecies. In this family, HIV-1 isolates from a father and his daughter had very highly genetic relatedness. By combining their clinical histories, we could draw the conclusion that the daughter was probably infected via contact with her father’s blood or other body fluids, but no obvious transmission route was found, suggesting that HIV-1 infection in similar household settings should be taken into consideration whenever the origin of HIV-1 infection cannot be identified.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1994) Human immunodeficiency virus transmission in household settings—United States. JAMA 271:1897–1899
Blank S, Simonds RJ, Weisfuse I, Rudnick J, Chiasson MA, Thomas P (1994) Possible nosocomial transmission of HIV. Lancet 344:512–514
Berthier A, Chamaret S, Fauchet R et al (1986) Transmissibility of human immunodeficiency virus in haemophilic and non-haemophilic children living in a private school in France. Lancet 2:598–601
Shao J, Chen J, Shen Y et al (2013) Identification of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) transmission from a 29-year-old daughter to her mother in Shanghai, China. Arch Virol 158(1):11–17
Delwart EL, Herring B, Rodrigo AG, Mullins JI (1995) Genetic subtyping of human immunodeficiency virus using a heteroduplex mobility assay. PCR Methods Appl 4:S202–S216
Parreira R, Padua E, Piedade J, Venenno T, Paixao MT, Esteves A (2005) Genetic analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nef in Portugal: subtyping, identification of mosaic genes, and amino acid sequence variability. J Med Virol 77:8–16
Schulter E, Oette M, Balduin M et al (2011) HIV prevalence and route of transmission in Turkish immigrants living in North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany. Med Microbiol Immunol 200:219–223
Gershon RR, Vlahov D, Nelson KE (1990) The risk of transmission of HIV-1 through non-percutaneous, non-sexual modes–a review. AIDS 4:645–650
French MA, Herring BL, Kaldor JM et al (2003) Intrafamilial transmission of HIV-1 infection from individuals with unrecognized HIV-1 infection. AIDS 17:1977–1981
Tubiana R, Le Chenadec J, Rouzioux C et al (2010) Factors associated with mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 despite a maternal viral load <500 copies/ml at delivery: a case-control study nested in the French perinatal cohort (EPF-ANRS CO1). Clin Infect Dis 50:585–596
Little KM, Hu DJ, Dominguez KL (2012) HIV-1 and breastfeeding in the United States. Adv Exp Med Biol 743:261–270
Yu X, Yuan L, Huang Y et al (2011) Susceptibility of HIV-1 subtypes B′, CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE that are predominantly circulating in China to HIV-1 entry inhibitors. PLoS One 6:e17605
Rudikoff D (2002) The relationship between HIV infection and atopic dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2:275–281
Salvatori F, De Martino M, Galli L, Vierucci A, Chieco-Bianchi L, De Rossi A (1998) Horizontal transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from father to child. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 14:1679–1685
Han Y, Wu N, Zhu W et al (2011) Detection of HIV-1 viruses in tears of patients even under long-term HAART. AIDS 25:1925–1927
Rou K, Sullivan SG, Liu P, Wu Z (2010) Scaling up prevention programmes to reduce the sexual transmission of HIV in China. Int J Epidemiol 39(Suppl 2):ii38–ii46
Shao JS, Zhang YZ, Tang YW et al (2011) Pearls and pitfalls of HIV-1 serologic laboratory testing. Microbes, viruses and parasites in AIDS process, InTech, pp 55–66
Nicolosi A, Correa Leite ML, Musicco M, Arici C, Gavazzeni G, Lazzarin A (1994) The efficiency of male-to-female and female-to-male sexual transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus: a study of 730 stable couples. Italian Study Group on HIV Heterosexual Transmission. Epidemiology 5:570–575
Sendi P, Gunthard HF, Simcock M, Ledergerber B, Schupbach J, Battegay M (2007) Cost-effectiveness of genotypic antiretroviral resistance testing in HIV-infected patients with treatment failure. PLoS One 2:e173
Si XF, Huang HL, Wei M et al (2004) Prevalence of drug resistance mutations among antiretroviral drug-naive HIV-1-infected patients in China. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi 18:308–311
Ye JR, Lu HY, Wang WS et al (2012) The prevalence of drug resistance mutations among treatment-naive HIV-infected individuals in Beijing, China. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 28:418–423
Mothe B, Perez I, Domingo P et al (2009) HIV-1 infection in subjects older than 70: a multicenter cross-sectional assessment in Catalonia, Spain. Curr HIV Res 7:597–600
Muck B, Trapana G, Jager H (2012) HIV in elderly. MMW Fortschr Med 154(Suppl 1):26–28
Vouri SM, Blaszczyk AT (2012) HIV: a growing concern in the elderly population. Consult Pharm 27:358–364
Major K, Clerc O, Rochat S, Cavassini M, Bula C (2011) HIV infection and the elderly. Rev Med Suisse 7(2170):2–5
Chan YJ (2011) HIV in the elderly: an emergent challenge. J Chin Med Assoc 74:195–196
Lazaryan A, Lobashevsky E, Mulenga J et al (2006) Human leukocyte antigen B58 supertype and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in native Africans. J Virol 80:6056–6060
Laeyendecker O, Zhang GW, Quinn TC et al (2005) Molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 subtypes in southern China. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 38:356–362
Li XJ, Kusagawa S, Xia X et al (2005) Molecular epidemiology of the heterosexual HIV-1 transmission in Kunming, Yunnan Province of China suggests origin from the local IDU epidemic. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 21:977–980
Meng Z, Xing H, He X, Ma L, Xu W, Shao Y (2007) Genetic characterization of three newly isolated CRF07_BC near full-length genomes in China. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 23:1049–1054
Acknowledgments
Dr. Jiangrong Wang contributed equally to the paper. We are indebted to the three members in the family who volunteered for this study; we also acknowledge the contributions of Fengdi Zhang, Tangkai Qi, Xinlei Wang, and Xueyan Jiang.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest, and the study is funded by Twelve Fifth Key Research grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology, People’s Republic of China (2012ZX10001-003).
Ethical standards
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center Affiliated to Fudan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, J., Wang, J., Abubakar, Y.F. et al. Genetic relatedness of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) strains in a 12-year-old daughter and her father in a household setting. Arch Virol 159, 1385–1391 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1963-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1963-5