Abstract
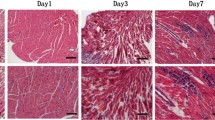
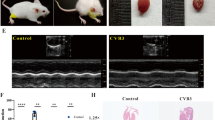
Viral myocarditis (VMC) is a common cardiovascular disease, and microRNAs (miRNAs) have been postulated to be involved in its pathology. Using microarrays, we observed that miRNA-21 and -146b were upregulated in a murine model of VMC. We also found that miRNA-451 was downregulated. In vivo silencing of miRNA-21 and -146b resulted in less-severe VMC. Overexpression of miRNA-451 did not ameliorate the severity of VMC. Further work revealed that inhibition of miRNA-21 and -146b decreased the expression levels of Th17 and RORγt . Overexpression of miRNA-451 had no effect on IL-17 and RORγt expression. Inhibition of miRNA-21 and -146b might ameliorate myocardium inflammation by mediating downregulation of RORγt expression, indicating that these miRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of murine VMC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta S, Markham DW, Drazner MH, Mammen PP (2008) Fulminant myocarditis. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 51:693–706
Fairweather D, Frisancho-Kiss S, Yusung SA, Barrett MA, Davis SE, Gatewood SJ, Njoku DB, Rose NR (2004) Interferon-γ protects against chronic viral myocarditis by reducing mast cell degranulation, fibrosis, and the profibrotic cytokines transforming growth factor-ß1, interleukin-1ß, and interleukin-4 in the heart. Am J Pathol 165:1883–1894
Fairweather D, Frisancho-Kiss S, Yusung SA, Barrett MA, Davis SE, Steele RA, Gatewood SJ, Rose NR (2005) IL-12 Protects against Coxsackievirus B3-Induced Myocarditis by Increasing IFN-gamma and macrophage and neutrophil populations in the heart. J Immunol 174:261–269
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2009) IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu Rev Immunol 27:485–517
Miossec P (2009) IL-17 and Th17 cells in human inflammatory diseases. Microbes Infect 11:625–630
Yuan J, Yu M, Lin QW, Cao AL, Yu X, Dong JH, Wang JP, Zhang JH, Wang M, Guo HP, Liao YH (2010) Neutralization of IL-17 inhibits the production of anti-ANT autoantibodies in CVB3-induced acute viral myocarditis. Int Immunopharmacol 10:272–276
Fan Y, Weifeng W, Yuluan Y, Qing K, Yu P (2011) Huang Yanlan: treatment with a neutralizing anti-murine interleukin-17 antibody after the onset of coxsackie virus b3-induced viral myocarditis reduces myocardium inflammation. Virol J 8(1):17
Yang F, Lin S, Huang YL, Wu WF (2010) Alteration of Th17 cells in mice with coxsackie virus induced myocarditis. Chinese J Cardiol 38:790–793
Ichiyama K et al (2008) Foxp3 inhibits RORgammat-mediated IL-17A mRNA transcription through direct interaction with RORgammat. J Biol Chem 283(25):17003–17008
Llave C, Xie Z, Kasschau KD et al (2002) Cleavage of scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. J Sci 297(5589):2053–2056
Zhou X et al (2008) Selective miRNA disruption in T reg cells leads to uncontrolled autoimmunity. J Exp Med 205:1983–1991
Chong MM, Rasmussen JP, Rudensky AY, Littman DR (2008) The RNAseIII enzyme Drosha is critical in T cells for preventing lethal inflammatory disease. J Exp Med 205:2005–2017
Du C, Liu C, Kang J, Zhao G, Ye Z, Huang S, Li Z, Wu Z, Pie G (2009) MicroRNA miR-326 regulates TH-17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Nature immunol 10:1252–1260
Evdokimov AG, Pokross ME, Egorov NS et al (2006) Structural basis for the fast maturation of Arthropoda green fluorescent protein. EMBO Rep 7(10):1006–1012
Mikkola H, Woods NB, Sjögren M et al (2000) Lentivirus gene transfer in murine hematopoietic progenitor cells is compromised by a delay in proviral integration and results in transduction mosaicism and heterogeneous gene expression in progeny cells. J Virol 74(24):11911–11918
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B (2006) TGF-β in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24:179–189
Mangan PR, Harrington LE, O’Quinn DB, Helms WS, Bullard DC, Elson CO, Hatton RD, Wahl SM, Schoeb TR, Weaver CT (2006) Transforming growth factor-β induces development of the TH17 lineage. Nature 441:231–234
Korn T, Bettelli E, Gao W, Awasthi A, Jäger A, Strom TB, Oukka M (2007) Kuchroo VK:IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory TH17 cells. Nature 448:484–487
Yang XO, Pappu BP, Nurieva R, Akimzhanov A, Kang HS, Chung Y, Ma L, Shah B, Panopoulos AD, Schluns KS, Watowich SS, Tian Q, Jetten AM, Dong C (2008) Thelper 17 lineage differentiation is programmed by orphan nuclear receptors RORα and RORγ. Immunity 28:29–39
Yang XO, Panopoulos AD, Nurieva R, Chang SH, Wang D, Watowich SS (2007) Dong C:STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J Biol Chem 282:9358–9363
Jetten AM (2009) Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs): critical roles in development, immunity, circadian rhythm, and cellular metabolism. Nucl Recept Signal 7:e003
Veldhoen M et al (2006) Signals mediated by transforming growth factor-beta initiate autoimmune encephalomyelitis, but chronic inflammation is needed to sustain disease. Nat Immunol 7(11):1151–1156
Malhotra N, Kang J (2010) SMAD2 is essential for TGF beta mediated Th17 cell generation. J Biol Chem 285(38):29044–29048
Takimoto T et al (2010) Smad2 and Smad3 are redundantly essential for the TGF-beta-mediated regulation of regulatory T plasticity and Th1 development. J Immunol 185(2):842–855
Li QJ et al (2007) miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 129:147–161
Sheedy FJ, Palsson-McDermott E, Hennessy EJ, Martin C, O’Leary JJ, Ruan Q et al (2010) Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miRNA-21. Nat Immunol 11:141–147
Stagakis E, Bertsias G, Verginis P, Nakou M, Hatziapostolou M, Kritikos H, Iliopoulos D, Boumpas DT (2011) Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to human lupus disease activity and pathogenesis:miRNA-21 regulates aberrant T cell responses through regulation of PDCD4 expression. Ann Rheum Dis 70(8):1496–1506
Narducci MG, Arcelli D, Picchio MC, Lazzeri C, Pagani E, Sampogna F, Scala E, Fadda P, Cristofoletti C, Facchiano A, Frontani M, Monopoli A, Ferracin M, Negrini M, Lombardo GA, Caprini E, Russo G (2011) MicroRNA profiling reveals that miRNA-21, miR486 and miRNA-214 are upregulated and involved in cell survival in Sézary syndrome. Cell Death Dis 2(4):e151
Lu TX, Hartner J, Lim EJ, Fabry V, Mingler MK, Cole ET, Orkin SH, Aronow BJ, Rothenberg ME (2011) MicroRNA-21 limits in vivo immune response-mediated activation of the IL-12/IFN-gamma pathway, Th1 polarization, and the severity of delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol 187(6):3362–3373
Garchow BG, BartulosEncinas O, Leung YT, Tsao PY, Eisenberg RA, Caricchio R, Obad S, Petri A, Kauppinen S, Kiriakidou M (2011) Silencing of microRNA-21 in vivo ameliorates autoimmune splenomegaly in lupus mice. EMBO Mol Med 3(10):605–615
Van der Fits L, van Kester MS, Qin Y, Out-Luiting JJ, Smit F, Zoutman WH, Willemze R, Tensen CP, Vermeer MH (2011) MicroRNA-21 expression in CD4+ T cells is regulated by STAT3 and is pathologically involved in Sézary syndrome. J Invest Dermatol 131(3):762–768
Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Okubo A et al (2008) Expression of MicmRNA-146 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Tissue[J]. Arthritis Rheum 58(5):1284–1292
Stanczyk J, Pedrioli DM, Brentano F et al (2008) Altered Expression of MicrRNA in Synovial Fibmblasts and Synovial Tissue in Rheumatoid Arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum 58(4):1001–1009
Tang Y, Luo X, Cui H et al (2009) MicmRNA-146a Contributes to Abnormal Activation of the Type I Interferon Pathway in Human Lupus by Targeting the Key Signaling Proteins. Arthritis Rheum 60(4):1065–1075
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jiao Lan, Xiu-Jiu Liang, and Qi-Guang Huang for their technical assistance. LY coordinated the study, carried out data collection, performed the statistical analysis, interpreted data, and drafted the manuscript. WW participated in the conception and design of the study, coordinated the study, and reviewed the manuscript. XY, GM, YY, KQ, PY and YF carried out data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30960129).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests, and had no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y.L., Wu, W., Xue, Y. et al. MicroRNA-21 and -146b are involved in the pathogenesis of murine viral myocarditis by regulating TH-17 differentiation. Arch Virol 158, 1953–1963 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1695-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1695-6