Abstract
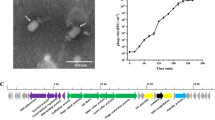
A novel bacteriophage, JX01, specifically infecting bovine Streptococcus agalactiae was isolated from milk of mastitis-affected cattle. The phage morphology showed that JX01 belongs to the family Siphoviridae, and this phage demonstrated a broad host range. Microbiological characterization demonstrated that nearly 90 % of JX01 phage particles were adsorbed after 2.5 min of incubation, that the burst size was 20 virions released per infected host cell, and that there was a latent period of 30 min. JX01 was thermal sensitive and showed acid and alkaline resistance (pH 3–11). The genome of JX01 was found to consist of a linear, double-stranded 43,028-bp DNA molecule with a GC content of 36.81 % and 70 putative open reading frames (ORFs) plus one tRNA. Comparative genome analysis revealed high similarity between JX01 and the prophage 315.2 of Streptococcus pyogenes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MH (1959) Bacteriophages. Interscience, New York
Ajitkumar P, Barkema HW, De Buck J (2012) Rapid identification of bovine mastitis pathogens by high-resolution melt analysis of 16S rDNA sequences. Vet Microbiol 155:332–340
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2607–2618
Bowater RO, Forbes-Faulkner J, Anderson IG, Condon K, Robinson B, Kong F, Gilbert GL, Reynolds A, Hyland S, McPherson G, Brien JO, Blyde D (2012) Natural outbreak of Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) infection in wild giant Queensland grouper, Epinephelus lanceolatus (Bloch), and other wild fish in northern Queensland, Australia. J Fish Dis 35:173–186
Boyd EF, Brussow H (2002) Common themes among bacteriophage-encoded virulence factors and diversity among the bacteriophages involved. Trends Microbiol 10:521–529
Bradley A (2002) Bovine mastitis: an evolving disease. Vet J 164:116–128
Brussow H, Desiere F (2001) Comparative phage genomics and the evolution of Siphoviridae: insights from dairy phages. Mol Microbiol 39:213–222
Carlson K (2005) Working with Bacteriophages: common techniques and methodological approaches. In: Kutter E, Sulakvelidze A (eds) Bacteriophages: biology and application. CRC Press, Florida, pp 437–494
Casjens SR, Gilcrease EB (2009) Determining DNA packaging strategy by analysis of the termini of the chromosomes in tailed-bacteriophage virions. Methods Mol Biol 502:91–111
Cheng Q, Nelson D, Zhu S, Fischetti VA (2005) Removal of group B streptococci colonizing the vagina and oropharynx of mice with a bacteriophage lytic enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:111–117
Davies MR, McMillan DJ, Van Domselaar GH, Jones MK, Sriprakash KS (2007) Phage 3396 from a Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis pathovar may have its origins in streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol 189:2646–2652
Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC, Salzberg SL (2007) Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 23:673–679
Delisle AL, Guo M, Chalmers NI, Barcak GJ, Rousseau GM, Moineau S (2012) Biology and genome sequence of Streptococcus mutans phage M102AD. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:2264–2271
Domelier AS, van der Mee-Marquet N, Sizaret PY, Hery-Arnaud G, Lartigue MF, Mereghetti L, Quentin R (2009) Molecular characterization and lytic activities of Streptococcus agalactiae bacteriophages and determination of lysogenic-strain features. J Bacteriol 191:4776–4785
Elias AO, Cortez A, Brandao PE, da Silva RC, Langoni H (2011) Molecular detection of Streptococcus agalactiae in bovine raw milk samples obtained directly from bulk tanks. Res Vet Sci 93(1):34–38
Garcia JC, Klesius PH, Evans JJ, Shoemaker CA (2008) Non-infectivity of cattle Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus and channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Aquaculture 281:151–154
Groth AC, Calos MP (2004) Phage integrases: biology and applications. J Mol Biol 335:667–678
Haug RH, Gudding R, Bakken G (1981) Serotyping and bacteriophage typing of human and bovine group-B streptococci. J Med Microbiol 14:479–482
Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ (2010) Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics 11:119
Iguchi A, Iyoda S, Terajima J, Watanabe H, Osawa R (2006) Spontaneous recombination between homologous prophage regions causes large-scale inversions within the Escherichia coli O157:H7 chromosome. Gene 372:199–207
Jamalludeen N, Johnson RP, Friendship R, Kropinski AM, Lingohr EJ, Gyles CL (2007) Isolation and characterization of nine bacteriophages that lyse O149 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vet Microbiol 124:47–57
Jardine PJ, Anderson DL (2006) DNA packaging in double-stranded DNA phages. Oxford University Press, USA
Kropinski A (2009) Measurement of the rate of attachment of bacteriophage to cells. In: Clokie MJ, Kropinski A (eds) Bacteriophages. Humana Press, New York, pp 151–155
Laslett D, Canback B (2004) ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:11–16
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964
Lu G, Moriyama EN (2004) Vector NTI, a balanced all-in-one sequence analysis suite. Brief Bioinform 5:378–388
Ma YL, Lu CP (2008) Isolation and identification of a bacteriophage capable of infecting Streptococcus suis type 2 strains. Vet Microbiol 132:340–347
Marchler-Bauer A, Lu S, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C, Fong JH, Geer LY, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Lanczycki CJ, Lu F, Marchler GH, Mullokandov M, Omelchenko MV, Robertson CL, Song JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zhang N, Zheng C, Bryant SH (2011) CDD: a Conserved Domain Database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D225–D229
Martinez G, Harel J, Gottschalk M (2001) Specific detection by PCR of Streptococcus agalactiae in milk. Can J Vet Res 65:68–72
Matthews BW, Ohlendorf DH, Anderson WF, Fisher RG, Takeda Y (1983) Cro repressor protein and its interaction with DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 47(Pt 1):427–433
Nakagawa I, Kurokawa K, Yamashita A, Nakata M, Tomiyasu Y, Okahashi N, Kawabata S, Yamazaki K, Shiba T, Yasunaga T, Hayashi H, Hattori M, Hamada S (2003) Genome sequence of an M3 strain of Streptococcus pyogenes reveals a large-scale genomic rearrangement in invasive strains and new insights into phage evolution. Genome Res 13:1042–1055
Pereira UP, Mian GF, Oliveira IC, Benchetrit LC, Costa GM, Figueiredo HC (2010) Genotyping of Streptococcus agalactiae strains isolated from fish, human and cattle and their virulence potential in Nile tilapia. Vet Microbiol 140:186–192
Pritchard DG, Dong S, Baker JR, Engler JA (2004) The bifunctional peptidoglycan lysin of Streptococcus agalactiae bacteriophage B30. Microbiology 150:2079–2087
Pritchard DG, Dong S, Kirk MC, Cartee RT, Baker JR (2007) LambdaSa1 and LambdaSa2 prophage lysins of Streptococcus agalactiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7150–7154
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry J, Tate J, Boursnell C, Pang N, Forslund K, Ceric G, Clements J, Heger A, Holm L, Sonnhammer EL, Eddy SR, Bateman A, Finn RD (2012) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D290–D301
Raya Rl, H’bert E (2009) Isolation of Phage via Induction of Lysogens. In: Clokie MJ, Kropinski A (eds) Bacteriophages. Humana Press, New York, pp 23–32
Richards VP, Lang P, Bitar PD, Lefebure T, Schukken YH, Zadoks RN, Stanhope MJ (2011) Comparative genomics and the role of lateral gene transfer in the evolution of bovine adapted Streptococcus agalactiae. Infect Genet Evol 11:1263–1275
Romero P, Croucher NJ, Hiller NL, Hu FZ, Ehrlich GD, Bentley SD, Garcia E, Mitchell TJ (2009) Comparative genomic analysis of ten Streptococcus pneumoniae temperate bacteriophages. J Bacteriol 191:4854–4862
Russell H, Norcross NL, Kahn DE (1969) Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus agalactiae bacteriophage. J Gen Virol 5:315–317
Salloum M, van der Mee-Marquet N, Domelier AS, Arnault L, Quentin R (2010) Molecular characterization and prophage DNA contents of Streptococcus agalactiae strains isolated from adult skin and osteoarticular infections. J Clin Microbiol 48:1261–1269
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY
Shi Y, Yan Y, Ji W, Du B, Meng X, Wang H, Sun J (2012) Characterization and determination of holin protein of Streptococcus suis bacteriophage SMP in heterologous host. Virol J 9:70
Stanley E, Fitzgerald GF, Le Marrec C, Fayard B, van Sinderen D (1997) Sequence analysis and characterization of phi O1205, a temperate bacteriophage infecting Streptococcus thermophilus CNRZ1205. Microbiology 143(Pt 11):3417–3429
Stringer J (1980) The development of a phage-typing system for group-B streptococci. J Med Microbiol 13:133–143
Swanson MM, Reavy B, Makarova KS, Cock PJ, Hopkins DW, Torrance L, Koonin EV, Taliansky M (2012) Novel bacteriophages containing a genome of another bacteriophage within their genomes. PLoS ONE 7:e40683
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28:33–36
Tavares P, Zinn-Justin S, Orlova EV (2012) Genome gating in tailed bacteriophage capsids. Adv Exp Med Biol 726:585–600
Tettelin H, Masignani V, Cieslewicz MJ, Eisen JA, Peterson S, Wessels MR, Paulsen IT, Nelson KE, Margarit I, Read TD, Madoff LC, Wolf AM, Beanan MJ, Brinkac LM, Daugherty SC, DeBoy RT, Durkin AS, Kolonay JF, Madupu R, Lewis MR, Radune D, Fedorova NB, Scanlan D, Khouri H, Mulligan S, Carty HA, Cline RT, Van Aken SE, Gill J, Scarselli M, Mora M, Iacobini ET, Brettoni C, Galli G, Mariani M, Vegni F, Maione D, Rinaudo D, Rappuoli R, Telford JL, Kasper DL, Grandi G, Fraser CM (2002) Complete genome sequence and comparative genomic analysis of an emerging human pathogen, serotype V Streptococcus agalactiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12391–12396
Tettelin H, Masignani V, Cieslewicz MJ, Donati C, Medini D, Ward NL, Angiuoli SV, Crabtree J, Jones AL, Durkin AS, Deboy RT, Davidsen TM, Mora M, Scarselli M, Margarit y Ros I, Peterson JD, Hauser CR, Sundaram JP, Nelson WC, Madupu R, Brinkac LM, Dodson RJ, Rosovitz MJ, Sullivan SA, Daugherty SC, Haft DH, Selengut J, Gwinn ML, Zhou L, Zafar N, Khouri H, Radune D, Dimitrov G, Watkins K, O’Connor KJ, Smith S, Utterback TR, White O, Rubens CE, Grandi G, Madoff LC, Kasper DL, Telford JL, Wessels MR, Rappuoli R, Fraser CM (2005) Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: implications for the microbial “pan-genome”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13950–13955
Twest R, Kropinski A (2009) Bacteriophage Enrichment from Water and Soil. In: Clokie MJ, Kropinski A (eds) Bacteriophages. Humana Press, New York, pp 15–21
van der Mee-Marquet N, Domelier AS, Mereghetti L, Lanotte P, Rosenau A, van Leeuwen W, Quentin R (2006) Prophagic DNA fragments in Streptococcus agalactiae strains and association with neonatal meningitis. J Clin Microbiol 44:1049–1058
Wang IN, Smith DL, Young R (2000) Holins: the protein clocks of bacteriophage infections. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:799–825
Zamri-Saad M, Amal MN, Siti-Zahrah A (2010) Pathological changes in red tilapias (Oreochromis spp.) naturally infected by Streptococcus agalactiae. J Comp Pathol 143:227–229
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zhu L, Suzuki M, Inouye M (2004) Interference of mRNA function by sequence-specific endoribonuclease PemK. J Biol Chem 279:20678–20684
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Moineau and Tillett for their support and suggestions during the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of Ministry of Education of China (NCET-110671), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nucleotide sequence data reported are available in the GenBank database under the accession number JX409895.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Q., Zhang, W., Yang, Y. et al. Characterization and genome sequencing of a novel bacteriophage infecting Streptococcus agalactiae with high similarity to a phage from Streptococcus pyogenes . Arch Virol 158, 1733–1741 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1667-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1667-x