Abstract
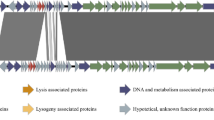
Bacteriophage TEM126, a newly isolated temperate phage from a mitomycin-C-induced lysate of wild-type Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food, has an isometric head, a noncontractile tail, and a double-stranded DNA genome with a length of 33,540 bp and a G+C content of 33.94%. Bioinformatics analysis of the phage genome revealed 44 putative open reading frames (ORFs). Predicted protein products of the ORFs were determined and described. Temperate phage TEM126 can be classified as a member of the family Siphoviridae by morphology and genome structure. Temperate phage TEM126 showed 84% similarity with Staphylococcus phage phiNM1. To our knowledge, this is the first report of genomic sequencing and characterization of temperate phage TEM126 from a wild-type S. aureus isolated from foods in Korea.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akoh CC, Lee GC, Liaw YC, Huang TH, Shaw JF (2004) GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res 43:534–552
Altekruse SF, Cohen ML, Swerdlow DL (1997) Emerging food borne disease. Emerg Infect Dis 3:285–293
Brussow H, Canchaya C, Hardt WD (2004) Phages and the evolution of bacterial pathogens: from genomic rearrangements to lysogenic conversion. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:560–602
Carolyn MT, Derek GF (1996) Interactions between coat and scaffolding proteins of phage P22 are altered in vitro by amino acid substitutions in coat protein that cause a cold-sensitive phenotype. Biochemistry 35:14831–14840
Christiane W, Wolfgang W, Christiane W, Christiane G (2010) Insertion of host DNA into PVL-encoding phages of the Staphylococcus aureus lineage ST80 by intra-chromosomal recombination. Virology 406:322–327
Katsura I, Hendrix RW (1984) Length determination in bacteriophage lambda tails. Cell 39:691–698
Kwan T, Liu J, DuBow M, Gros P, Pelletier J (2005) The complete genomes and proteomes of 27 Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(14):5174–5179
Lee YD, Moon BY, Park JH, Chang HI, Kim WJ (2007) Expression of enterotoxin genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates based on mRNA analysis. J Microbiol Biotech 17:461–467
Le Loir Y, Baron F, Gautier M (2003) Staphylococcus aureus and food poisoning. Genet Mol Res 31:63–76
Lina G, Piémont Y, Godail-Gamot F, Bes M, Peter MO, Gauduchon V, Vandenesch F, Etienne (1999) Involvement of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis 29:1128–1132
Mahdi AA, Sharples GJ, Mandal TN, Lloyd RG (1996) Holliday junction resolvases encoded by homologous rusA genes in Escherichia coli K-12 and phage 82. J Mol Biol 257:561–573
Manfioletti G, Schneider C (1988) A new and fast method for preparing high quality lambda DNA suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 16:2873–2884
Novick RP (2003) Mobile genetic elements and bacterial toxinoses: the superantigen-encoding pathogenicity islands of Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid 49:93–105
Rao VB, Feiss M (2008) The bacteriophage DNA packaging motor. Annu Rev Genet 42:647–681
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Stiles BG, Krakauer T (2005) Staphylococcal enterotoxins: a purging experience in review, part I. Clin Microbiol Newslett 27:179–186
van Wamel WJ, Rooijakkers SH, Ruyken M, van Kessel KP, van Strijp JA (2006) The innate immune modulators staphylococcal complement inhibitor and chemotaxis inhibitory protein of Staphylococcus aureus are located on β-hemolysin-converting bacteriophages. J Bacteriol 188:1310–1315
Vollmer W, Joris B, Charlier P, Foster S (2008) Bacterial peptidoglycan (murein) hydrolases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:259–286
Wood WB, Conley MP, Lyle HL, Dickson RC (1978) Attachment of tail fibers in bacteriophage T4 assembly. J Biol Chem 253:2437–2445
Yu J, Moffitt J, Hetherington CL, Bustamante C, Oster G (2010) Mechanochemistry of a viral DNA packaging motor. J Mol Biol 400:186–203
Young R (1992) Bacteriophage lysis: mechanism and regulation. Microbiol Rev 56:430–481
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (20100016898)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hyo-Ihl Chang and Jong-Hyun Park contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YD., Chang, HI. & Park, JH. Genomic sequence of temperate phage TEM126 isolated from wild type S. aureus . Arch Virol 156, 717–720 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-0923-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-0923-1