Abstract
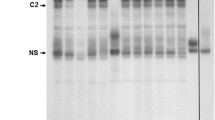
We have previously described a cis enhancing sequence (CES) in the gp41 region of the HIV-1 env gene. It could enhance HIV-1 Gag expression via both rev-dependent and CTE (constitutive transport element)-dependent pathways. We identified a functionally important and conserved region in the CES that contained a predicted binding sequence for an SR protein, ASF/SF2. We show here that ASF/SF2 bound to this sequence in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay and that the putative ASF/SF2-binding sequence was required for the enhancement of Gag expression by CES and might play a role in HIV-1 posttranscriptional regulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cartegni L, Wang J, Zhu Z, Zhang MQ, Krainer AR (2003) ESEfinder: a web resource to identify exonic splicing enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3568–3571
Damgaard CK, Kahns S, Lykke-Andersen S, Nielsen AL, Jensen TH, Kjems J (2008) A 5′ splice site enhances the recruitment of basal transcription initiation factors in vivo. Mol Cell 29:271–278
Expert-Bezancon A, Sureau A, Durosay P, Salesse R, Groeneveld H, Lecaer JP, Marie J (2004) hnRNP A1 and the SR proteins ASF/SF2 and SC35 have antagonistic functions in splicing of beta-tropomyosin exon 6B. J Biol Chem 279:38249–38259
Graveley BR (2000) Sorting out the complexity of SR protein functions. Rna 6:1197–1211
Huang Y, Gattoni R, Stevenin J, Steitz JA (2003) SR splicing factors serve as adapter proteins for TAP-dependent mRNA export. Mol Cell 11:837–843
Huang Y, Yario TA, Steitz JA (2004) A molecular link between SR protein dephosphorylation and mRNA export. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9666–9670
Huang Y, Steitz JA (2005) SRprises along a messenger’s journey. Mol Cell 17:613–615
Jacquenet S, Decimo D, Muriaux D, Darlix JL (2005) Dual effect of the SR proteins ASF/SF2, SC35 and 9G8 on HIV-1 RNA splicing and virion production. Retrovirology 2:33
Lai MC, Tarn WY (2004) Hypophosphorylated ASF/SF2 binds TAP and is present in messenger ribonucleoproteins. J Biol Chem 279:31745–31749
Lemaire R, Prasad J, Kashima T, Gustafson J, Manley JL, Lafyatis R (2002) Stability of a PKCI-1-related mRNA is controlled by the splicing factor ASF/SF2: a novel function for SR proteins. Genes Dev 16:594–607
Nishimori H, Shiratsuchi T, Urano T, Kimura Y, Kiyono K, Tatsumi K, Yoshida S, Ono M, Kuwano M, Nakamura Y, Tokino T (1997) A novel brain-specific p53-target gene, BAI1, containing thrombospondin type 1 repeats inhibits experimental angiogenesis. Oncogene 15:2145–2150
Paca-Uccaralertkun S, Damgaard CK, Auewarakul P, Thitithanyanont A, Suphaphiphat P, Essex M, Kjems J, Lee TH (2006) The effect of a single nucleotide substitution in the splicing silencer in the tat/rev intron on HIV type 1 envelope expression. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 22:76–82
Rodgers JT, Patel P, Hennes JL, Bolognia SL, Mascotti DP (2000) Use of biotin-labeled nucleic acids for protein purification and agarose-based chemiluminescent electromobility shift assays. Anal Biochem 277:254–259
Saltarelli MJ, Hadziyannis E, Hart CE, Harrison JV, Felber BK, Spira TJ, Pavlakis GN (1996) Analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mRNA splicing patterns during disease progression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from infected individuals. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 12:1443–1456
Sanford JR, Gray NK, Beckmann K, Caceres JF (2004) A novel role for shuttling SR proteins in mRNA translation. Genes Dev 18:755–768
Sanford JR, Ellis J, Caceres JF (2005) Multiple roles of arginine/serine-rich splicing factors in RNA processing. Biochem Soc Trans 33:443–446
Sanford JR, Ellis JD, Cazalla D, Caceres JF (2005) Reversible phosphorylation differentially affects nuclear and cytoplasmic functions of splicing factor 2/alternative splicing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15042–15047
Suptawiwat O, Sutthent R, Lee TH, Auewarakul P (2003) Intragenic HIV-1 env sequences that enhance gag expression. Virology 309:1–9
Suptawiwat O, Lee TH, Auewarakul P (2005) HIV-1 Cis Enhancing Sequence (CES) enhances CTE-dependent Gag expression. Virology 342:111–118
Swartz JE, Bor YC, Misawa Y, Rekosh D, Hammarskjold ML (2007) The shuttling SR protein 9G8 plays a role in translation of unspliced mRNA containing a constitutive transport element. J Biol Chem 282:19844–19853
Takeb EY, Kusagawa S, Motomura K (2004) Molecular epidemiology of HIV: tracking AIDS pandemic. Pediatr Int 46:236–244
Tange TO, Damgaard CK, Guth S, Valcarcel J, Kjems J (2001) The hnRNP A1 protein regulates HIV-1 tat splicing via a novel intron silencer element. EMBO J 20:5748–5758
Xiao SH, Manley JL (1998) Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation differentially affects activities of splicing factor ASF/SF2. EMBO J 17:6359–6367
Zahler AM, Damgaard CK, Kjems J, Caputi M (2004) SC35 and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B proteins bind to a juxtaposed exonic splicing enhancer/exonic splicing silencer element to regulate HIV-1 tat exon 2 splicing. J Biol Chem 279:10077–10084
Zhu J, Mayeda A, Krainer AR (2001) Exon identity established through differential antagonism between exonic splicing silencer-bound hnRNP A1 and enhancer-bound SR proteins. Mol Cell 8:1351–1361
Acknowledgments
O. Suptawiwat and C. Boonarkart were supported by the postdoctoral and research assistant program of the Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital. The project was supported by a research grant from Thailand Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suptawiwat, O., Boonarkart, C. & Auewarakul, P. A novel SR protein binding site in a cis-regulatory element of HIV-1. Arch Virol 155, 1789–1795 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0765-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0765-2