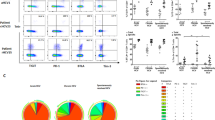
Summary.
PHA-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are widely used for investigating replication and neutralization of HIV primary isolates in vitro. The objective of this study was to identify the T lymphocyte subset(s) that are found infected after one replication cycle by either R5- or X4-HIV-1 variants in PHA-stimulated PBMCs from healthy donors. Infected T lymphocytes were detected by intracellular p24 staining and characterized by cell surface immunophenotyping using flow cytometry. The predominant lymphocyte subset expressing p24 after 24 h of infection with either R5 or X4 HIV-1 strains was found to exhibit mainly the memory CD45RO phenotype, a greater percentage of CD62L+CD45RO+ central memory T lymphocytes was infected with X4 HIV strains. Although some CD45RA+ lymphocytes were also infected, these cells co-expressed CD45RO+. The proportion of lymphocytes expressing CD4 and CD4/CD45RO decreased by 20% after 24 h of infection. A 2-fold decrease of CD4+CD8+ T lymphocytes could also be recorded, even though this subset accounted for less than 5% of total lymphocytes in control cultures. Moreover, CD4+CD8+ T cells further decreased by 90% after 4 days of infection, a time at which they scored p24+. Therefore, our results indicate that the in vitro infection system of PHA-stimulated PBMC utilized in neutralization assays provides an appropriate model for the study of infected CD45RO+ lymphocytes but not CD45RA+ lymphocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HH Birdsall J Trial HJ Lin DM Green GW Sorrentino EB Siwak AL de Jong RD Rossen (1997) ArticleTitleTransendothelial migration of lymphocytes from HIV-1-infected donors: a mechanism for extravascular dissemination of HIV-1 J Immunol 158 5968–5977 Occurrence Handle9190951 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktVWgtrk%3D
H Blaak AB van Wout M Brouwer B Hooibrink E Hovenkamp H Schuitemaker (2000) ArticleTitleIn vivo HIV-1 infection of CD45RA(+)CD4(+) T cells is established primarily by syncytium-inducing variants and correlates with the rate of CD4(+) T cell decline Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 1269–1274 Occurrence Handle10655520 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.97.3.1269 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXpvFeksw%3D%3D
DC Douek (2003) ArticleTitleDisrupting T-cell homeostasis: how HIV-1 infection causes disease AIDS Rev 5 172–177 Occurrence Handle14598566
DC Douek MR Betts BJ Hill SJ Little R Lempicki JA Metcalf J Casazza C Yoder JW Adelsberger RA Stevens MW Baseler P Keiser DD Richman RT Davey RA Koup (2001) ArticleTitleEvidence for increased T cell turnover and decreased thymic output in HIV infection J Immunol 167 6663–6668 Occurrence Handle11714838 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXovVChsLY%3D
DC Douek JM Brenchley MR Betts DR Ambrozak BJ Hill Y Okamoto JP Casazza J Kuruppu K Kunstman S Wolinsky Z Grossman M Dybul A Oxenius DA Price M Connors RA Koup (2002) ArticleTitleHIV preferentially infects HIV-specific CD4+ T cells Nature 417 95–98 Occurrence Handle11986671 Occurrence Handle10.1038/417095a Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjsFOgtbY%3D
DA Eckstein ML Penn YD Korin DD Scripture-Adams JA Zack JF Kreisberg M Roederer MP Sherman PS Chin MA Goldsmith (2001) ArticleTitleHIV-1 actively replicates in naive CD4(+) T cells residing within human lymphoid tissues Immunity 15 671–682 Occurrence Handle11672548 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1074-7613(01)00217-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXotVegtbs%3D
L Flamand RW Crowley P Lusso S Colombini-Hatch DM Margolis RC Gallo (1998) ArticleTitleActivation of CD8+ T lymphocytes through the T cell receptor turns on CD4 gene expression: implications for HIV pathogenesis Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 3111–3116 Occurrence Handle9501224 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.95.6.3111 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitV2itL4%3D
E Gemmell B Feldner GJ Seymour (1992) ArticleTitleCD45RA and CD45RO positive CD4 cells in human peripheral blood and peridontal disease tissue before and after stimulation with peridontopathic bacteria Oral Microbiol Immunol 7 84–88 Occurrence Handle1356262 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38vgvFalsA%3D%3D
F Gondois-Rey A Biancotte MA Fernandez L Bettendroffer J Blazkova K Trejbalova M Pion I Hirsch (2006) ArticleTitleR5 variants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preferentially infect CD62L-CD4+ T cells and are potentially resistant to nucleaside reverse transcriptase inhibitors J Virol 80 854–865 Occurrence Handle16378987 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.80.2.854-865.2006 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XivVOruw%3D%3D
F Gondois-Rey JC Grivel A Biancotto M Pion R Vigne LB Margolis I Hirsch (2002) ArticleTitleSegregation of R5 and X4 HIV-1 variants to memory T cell subsets differentially expressing CD62L in ex vivo infected human lymphoid tissue AIDS 16 1245–1249 Occurrence Handle12045489 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-200206140-00006 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlsFOrurw%3D
JC Grivel LB Margolis (1999) ArticleTitleCCR5- and CXCR4-tropic HIV-1 are equally cytopathic for their T-cell targets in human lymphoid tissue Nat Med 5 344–346 Occurrence Handle10086394 Occurrence Handle10.1038/6565 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7osVWqug%3D%3D
SL Heath JG Tew AK Szakal GF Burton (1995) ArticleTitleFollicular dendritic cells and human immunodeficiency virus infectivity Nature 377 740–744 Occurrence Handle7477265 Occurrence Handle10.1038/377740a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXovFygu70%3D
V Holl S Hemmerter R Burrer S Schmidt A Bohbot AM Aubertin C Moog (2004) ArticleTitleInvolvement of FcgammaR I (CD64) in the mechanism of HIV-1 inhibition by polyclonal IgG purified from infected patients in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages J Immunol 173 6274–6283 Occurrence Handle15528366 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXpt1Oltro%3D
GH Holm C Zheng PR Gorry K Peden D Schols E De Clercq D Gabuzda (2004) ArticleTitleApoptosis of bystander T cells induced by HIV-1 with increased envelope/ receptor affinity and coreceptor binding site exposure J Virol 78 4541–4551 Occurrence Handle15078935 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.78.9.4541-4551.2004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjsVKisr0%3D
S Imlach S McBreen T Shirafuji C Leen JE Bell P Simmonds (2001) ArticleTitleActivated peripheral CD8 lymphocytes express CD4 in vivo and are targets for infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 J Virol 75 11555–11564 Occurrence Handle11689637 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.75.23.11555-11564.2001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXotlaqsr0%3D
SG Kitchen YD Korin MD Roth A Landay JA Zack (1998) ArticleTitleCostimulation of naive CD8(+) lymphocytes induces CD4 expression and allows human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection J Virol 72 9054–9060 Occurrence Handle9765450 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmslahsrk%3D
JR Mascola MK Louder C Winter R Prabhakara SC De Rosa DC Douek BJ Hill D Gabuzda M Roederer (2002) ArticleTitleHuman immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization measured by flow cytometric quantitation of single-round infection of primary human T cells J Virol 76 4810–4821 Occurrence Handle11967298 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.76.10.4810-4821.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xjtlerurk%3D
JM McCune (2001) ArticleTitleThe dynamics of CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV disease Nature 410 974–979 Occurrence Handle11309627 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35073648 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjt1Kru7s%3D
MS Melzer HE Gendelman (1992) ArticleTitleMononuclear phagocytes as targets, tissue reservoirs, and immunoregulatory cells in human immunodeficiency virus disease Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 181 239–263
C Moog C Spenlehauer H Fleury F Heshmati S Saragosti F Letourneur A Kirn AM Aubertin (1997) ArticleTitleNeutralization of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates: a study of parameters implicated in neutralization in vitro AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 13 19–27 Occurrence Handle8989423 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7ktlCisA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1089/aid.1997.13.19
M Nascimbeni EC Shin L Chiriboga DE Kleiner B Rehermann (2004) ArticleTitlePeripheral CD4+CD8+ T cells are differentiated effector memory cells with antiviral functions Blood 104 478–486 Occurrence Handle15044252 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood-2003-12-4395 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXlvFSnurs%3D
MA Ostrowski TW Chun SJ Justement I Motola MA Spinelli J Adelsberger LA Ehler SB Mizell CW Hallahan AS Fauci (1999) ArticleTitleBoth memory and CD45RA+/CD62L+ naive CD4(+) T cells are infected in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals J Virol 73 6430–6435 Occurrence Handle10400736 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXksFKntrY%3D
G Pantaleo C Graziosi JF Demarest L Butini M Montroni CH Fox JM Orenstein DP Kotler AS Fauci (1993) ArticleTitleHIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease Nature 362 355–358 Occurrence Handle8455722 Occurrence Handle10.1038/362355a0 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s3gsFWhsQ%3D%3D
S Patterson NR English H Longhurst P Balfe M Helbert AJ Pinching SC Knight (1998) ArticleTitleAnalysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) variants and levels of infection in dendritic and T cells from symptomatic HIV-1-infected patients J Gen Virol 79 247–257 Occurrence Handle9472609 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXotVGjtg%3D%3D
T Pierson J McArthur RF Siliciano (2000) ArticleTitleReservoirs for HIV-1: mechanisms for viral persistence in the presence of antiviral immune responses and antiretroviral therapy Annu Rev Immunol 18 665–708 Occurrence Handle10837072 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.665 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjs1Gmtrs%3D
DD Richman SA Bozzette (1994) ArticleTitleThe impact of the syncytium-inducing phenotype of human immunodeficiency virus on disease progression J Infect Dis 169 968–974 Occurrence Handle7909549 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2c3itlWjsw%3D%3D
JL Riley BL Levine N Craighead T Francomano D Kim RG Carroll CH June (1998) ArticleTitleNaive and memory CD4 T cells differ in their susceptibilities to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection following CD28 costimulation: implications for transmission and pathogenesis J Virol 72 8273–8280 Occurrence Handle9733871 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmt1Shtbc%3D
M Roederer PA Raju DK Mitra LA Herzenberg (1997) ArticleTitleHIV does not replicate in naive CD4 T cells stimulated with CD3/CD28 J Clin Investig 99 1555–1564 Occurrence Handle9119999 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXitlantLs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1172/JCI119318
S Rowland-Jones (1999) ArticleTitleHIV infection: where have all the T cells gone? Lancet 354 5–7 Occurrence Handle10406356 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(99)90017-X Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mzjt12ruw%3D%3D
NK Saksena SJ Potter (2003) ArticleTitleReservoirs of HIV-1 in vivo: implications for antiretroviral therapy AIDS Rev 5 3–18 Occurrence Handle12875103
SM Schnittman HC Lane J Greenhouse JS Justement M Baseler AS Fauci (1990) ArticleTitlePreferential infection of CD4+ memory T cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1: evidence for a role in the selective T-cell functional defects observed in infected individuals Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87 6058–6062 Occurrence Handle2385584 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.87.16.6058 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3czkvFGmtg%3D%3D
G Semenzato C Agostini L Ometto R Zambello L Trentin L Chieco-Bianchi A De Rossi (1995) ArticleTitleCD8+ T lymphocytes in the lung of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients harbor human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Blood 85 2308–2314 Occurrence Handle7727764 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXlt1Omur0%3D
JW Sleasman LF Aleixo A Morton S Skoda-Smith MM Goodenow (1996) ArticleTitleCD4+ memory T cells are the predominant population of HIV-1-infected lymphocytes in neonates and children AIDS 10 1477–1484 Occurrence Handle8931781 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s%2FosFKqtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-199611000-00004
CM Steffens EZ Managlia A Landay L Al-Harthi (2002) ArticleTitleIL-7-treated naive T cells can be productively infected by T-cell-adapted and primary isolates of HIV Blood 99 3310–3318 Occurrence Handle11964298 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood.V99.9.3310 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjtlGqsL0%3D
YB Sullivan AL Landay JA Zack SG Kitchen L Al-Harthi (2001) ArticleTitleUpregulation of CD4 on CD8+ T cells: CD4dimCD8bright T cells constitute an activated phenotype of CD8+ T cells Immunology 103 270–280 Occurrence Handle11454056 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01243.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXltlaqsr0%3D
JA Zack AM Haislip P Krogstad IS Chen (1992) ArticleTitleIncompletely reverse-transcribed human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes in quiescent cells can function as intermediates in the retroviral life cycle J Virol 66 1717–1725 Occurrence Handle1371173 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38Xht1Clurw%3D
JY Zhou DC Montefiori (1997) ArticleTitleAntibody-mediated neutralization of primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is not affected by the initial activation state of the cells J Virol 71 2512–2517 Occurrence Handle9032392 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXht1ajt7k%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holl, V., Schmidt, S., Aubertin, AM. et al. The major population of PHA-stimulated PBMC infected by R5 or X4 HIV variants after a single cycle of infection is predominantly composed of CD45RO+CD4+ T lymphocytes. Arch Virol 152, 507–518 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-006-0873-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-006-0873-1