Summary
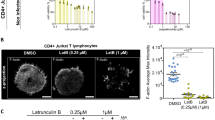
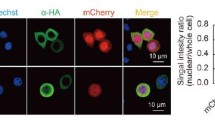
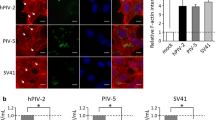
We present evidence that actin is necessary for the successful assembly of HaNPV virions. Purified nucleocapsid protein Ha-VP39 of Heliothis armigera nuclear polyhedrosis virus (HaNPV) was found to be able to bind to actin in vitro without assistance, as demonstrated by Western blot and isothermal titration calorimeter. ΔH and binding constants (K) detected by isothermal titration calorimeter strongly suggested that Ha-VP39 first binds actin to seed the formation of hexamer complex of actin, and the hexamers then link to each other to form filaments, and the filaments finally twist into cable structures. The proliferation of HaNPV was completely inhibited in Hz-AM1 cells cultivated in the medium containing 0.5 µg/ml cytochalasin D (CD) to prevent polymerization of actin, while its yield was reduced to 10−4 in the presence of 0.1 µg/ml CD. Actin concentration and the viral DNA synthesis were not significantly affected by CD even though the progeny virions assembled in the CD treated cells were morphologically different from normal ones and resulted in fewer plaques in plaque assay
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors equally contributed to the work.
The authors equally contributed to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, S., Ge, G. & Qi, Y. Ha-VP39 binding to actin and the influence of F-actin on assembly of progeny virions. Arch Virol 149, 2187–2198 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-004-0361-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-004-0361-4