Summary.
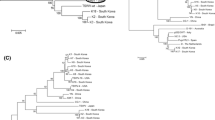
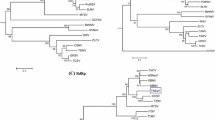
The complete S-RNA sequences of four Bulgarian and one German isolate of tomato spotted wilt tospovirus were determined. All isolates show a high conservation in their N proteins, while the NSs proteins and the intergenic regions (IGR) are more variable. The Bulgarian isolate 10HK96 has the largest S-RNA (3364 nucleotides) among tomato spotted wilt viruses reported so far. The enlargement is based on an insertion of 365 nts in the IGR that may have resulted from stuttering of the viral polymerase or non-homologous recombination. This insertion is present in the N protein gene subgenomic messenger, upstream of a proposed transcription termination signal.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received November 29, 2001; accepted July 2, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinze, C., Willingmann, P., Schwach, F. et al. An unusual large intergenic region in the S-RNA of a Bulgarian tomato spotted wilt virus isolate. Arch Virol 148, 199–205 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0882-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0882-7