Summary
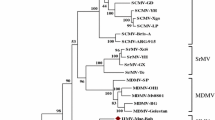
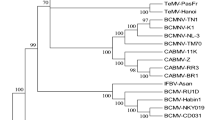
Potyvirus isolates from asparagus bean (Vigna sesquipedalis) plants in Zhejiang province, China, caused either rugose and vein banding mosaic symptoms (isolate R) or severe yellowing (isolate Y) in this host, but were otherwise similar in host range. Both isolates were completely sequenced and shown to be isolates of Bean common mosaic virus (BCMV). The complete sequences were 9992 (R) or 10062 (Y) nucleotides long and shared 91.7% identical nucleotides (93.2% identical amino acids) in their genomes and were more distantly related to the BCMV-Peanut stripe virus sequence (PStV). The isolates were much less similar to one another in the 5′-UTR and the N-terminal region of the P1 protein. In the P1, isolate Y was closer to PStV (76.1% identical amino acids) than to isolate R (64.8%). Phylogenetic analyses of the coat protein region showed that the new isolates grouped with other isolates from Vigna spp., forming the blackeye cowpea mosaic strain subgroup of BCMV with 94–98% nucleotides (96–99% amino acids) identical to one another and about 90% identity to other BCMV isolates. Other significant subgroupings amongst published BCMV isolates were detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received September 14, 2001 accepted January 25, 2002¶Published online April 22, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Chen, J., Chen, J. et al. Bean common mosaic virus isolates causing different symptoms in asparagus bean in China differ greatly in the 5′-parts of their genomes. Arch. Virol. 147, 1257–1262 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0805-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0805-7