Summary
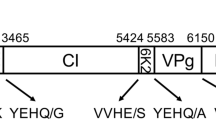
The genomic sequence of a Zimbabwe isolate of Cowpea aphid-borne mosaic virus (CABMV-Z) was determined by sequencing overlapping viral cDNA clones generated by RT-PCR using degenerate and/or specific primers. The sequence is 9465 nucleotides in length excluding the 3′ terminal poly (A) tail and contains a single open reading frame (ORF) of 9159 nucleotides encoding a large polyprotein of 3 053 amino acids and predicted Mr of 348. The size of the genome and the encoded polyprotein is in agreement with other potyviruses and contains nine putative proteolytic cleavage sites and motifs conserved in homologous proteins of other potyviruses. The P1 and P3 were the most variable proteins while CI, NIb and CP were the most conserved.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received August 2, 2001; accepted January 15, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mlotshwa, S., Verver, J., Sithole-Niang, I. et al. The genomic sequence of cowpea aphid-borne mosaic virus and its similarities with other potyviruses. Arch. Virol. 147, 1043–1052 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0800-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0800-z