Summary
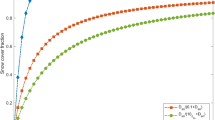
Melting snow is often patchy, and advection of heat from warm patches of snow-free ground can accelerate the melting. For large-scale atmospheric modelling applications, snowmelt rates and fluxes of heat and moisture over surfaces with snow cover distributed on scales too small to be resolved by the model grid have to be parametrized. In this paper, a boundary-layer model is used to model advection over surfaces with short vegetation and varying fractions of snow cover. Boundary-layer model results are used to assess the performance of a tile model, which calculates separate fluxes for snow-covered and snow-free fractions of the surface given area-average temperatures, humidities and windspeeds at a reference height in the atmosphere. It is found that the tile model can give good results, but its performance depends strongly on the choice of reference height.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received August 21, 1997 Revised February 23, 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Essery, R. Parametrization of Heterogeneous Snowmelt. Theor Appl Climatol 62, 25–30 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007040050071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007040050071