Abstract
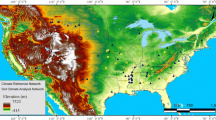
The spaceborne Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) has proven its worth in terrestrial remote sensing applications. Its application to detecting land surface soil moisture (SSM) is particularly intriguing, as it can provide fine-scale SSM products to supplement traditional satellite-based active and passive missions. Various retrieval algorithms have been developed to produce SSM products using spaceborne GNSS-R. However, detailed evaluations of product reliability and robustness are still absent. In this study, we used three data sources to evaluate the level-3 SSM products from the CYclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) mission: (1) satellite-based microwave radiometry product from Soil Moisture Active and Passive (SMAP) mission; (2) a model-based product of Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications; and (3) in situ measurements from over 1800 ground stations in the Chinese soil moisture monitoring network. The study uses typical relative skill metrics and triple collocation approach (TCA)-based metrics, along with corresponding confidence intervals, to analyze the performance of SSM products derived from CYGNSS observations. According to the pixel-by-pixel validation and overall statistical findings, the results reveal that the current CYGNSS-based SSM exhibits low performance in southern China when compared to the radiometry-based data. The coefficient of determination (R2) is low (median R2=0.088) and the unbiased root-mean-square-difference (ubRMSD) is 0.057 cm3cm−3, which is poorer than the results from SMAP against in situ measurements (median R2=0.25, ubRMSD=0.046 cm3cm−3). The TCA-based analysis also revealed that CYGNSS had a relatively poor performance, with the lowest median R2 value of 0.167 and the largest median error standard deviation (ESD) value of 0.055 cm3cm−3. To obtain improved results that can better support related operational applications in the future, enhanced retrieval algorithms and high-accuracy calibration referenced data must be utilized.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The CYGNSS data that support the findings of this study are freely available in the Physical Oceanography Distributed Active Archive Center (PODAAC, https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/datasetlist?values=CYGNSS&view=list&ids=Projects). The reference SMAP data are openly available in National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC, https://nsidc.org/data/spl3smp/versions/8). The MERRA-2 data at https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/reanalysis/MERRA-2/.
Code availability
The code related to the manuscript will be made available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Khaldi MM, Johnson JT, O’Brien AJ et al (2019) Time-series retrieval of soil moisture using CYGNSS. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57(7):4322–4331. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2890646
An R, Zhang L, Wang Z et al (2016) Validation of the ESA CCI soil moisture product in China. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 48:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2015.09.009
Ayres E, Colliander A, Cosh MH et al (2021) Validation of SMAP soil moisture at terrestrial National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON) sites show potential for soil moisture retrieval in forested areas. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 14:10903–10918. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3121206
Brocca L, Melone F, Moramarco T, Morbidelli R (2010) Spatial-temporal variability of soil moisture and its estimation across scales: SOIL MOISTURE SPATIOTEMPORAL VARIABILITY. Water Resour Res 46:2. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR008016
Brocca L, Hasenauer S, Lacava T et al (2011) Soil moisture estimation through ASCAT and AMSR-E sensors: an intercomparison and validation study across Europe. Remote Sens Environ 115:3390–3408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.08.003
Chen F, Crow WT, Bindlish R et al (2018) Global-scale evaluation of SMAP, SMOS and ASCAT soil moisture products using triple collocation. Remote Sens Environ 214:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.05.008
Chew CC, Small EE (2018) Soil moisture sensing using spaceborne GNSS reflections: comparison of CYGNSS reflectivity to SMAP soil moisture. Geophys Res Lett 45:4049–4057. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL077905
Chew C, Small E (2020) Description of the UCAR/CU soil moisture product. Remote sens 12:1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101558
Clarizia MP, Ruf CS (2016) Wind speed retrieval algorithm for the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) mission. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54:4419–4432. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2016.2541343
Clarizia MP, Pierdicca N, Costantini F, Floury N (2019) Analysis of CYGNSS data for soil moisture retrieval. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 12:2227–2235. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2895510
Colliander A, Reichle R, Crow W et al (2022) Validation of soil moisture data products from the NASA SMAP mission. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 15:364–392. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3124743
Cui C, Xu J, Zeng J et al (2017) Soil moisture mapping from satellites: an intercomparison of SMAP, SMOS, FY3B, AMSR2, and ESA CCI over two dense network regions at different spatial scales. Remote sens 10:33. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010033
D’Agostino RB (1971) An omnibus test of normality for moderate and large size samples. Biometrika 58:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/58.2.341
D’Agostino R, Pearson ES (1973) Tests for departure from normality. Empirical Results for the Distributions of b2 and Ob1. Biometrika 60:613. https://doi.org/10.2307/2335012
Dong Z, Jin S (2021) Evaluation of the land GNSS-reflected DDM coherence on soil moisture estimation from CYGNSS data. Remote sens 13:570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040570
Dorigo WA, Scipal K, Parinussa RM et al (2010) Error characterisation of global active and passive microwave soil moisture data sets. Global hydrology/Uncertainty analysis
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1986) Bootstrap methods for standard errors, confidence intervals, and other measures of statistical accuracy. Statist Sci 1:54–75. https://doi.org/10.1214/ss/1177013815
Entekhabi D, Njoku EG, O’Neill PE et al (2010) The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission. Proc IEEE 98:704–716. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2010.2043918
Eroglu O, Kurum M, Boyd D, Gurbuz AC (2019) High spatio-temporal resolution CYGNSS soil moisture estimates using artificial neural networks. Remote sens 11:2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192272
Gelaro R, McCarty W, Suárez MJ et al (2017) The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J Climate 30:5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1
Gleason S, Hodgart S, Sun Y et al (2005) Detection and processing of bistatically reflected GPS signals from low Earth orbit for the purpose of ocean remote sensing. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 43:1229–1241. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2005.845643
Gruber A, De Lannoy G, Crow W (2019) A Monte Carlo based adaptive Kalman filtering framework for soil moisture data assimilation. Remote Sens Environ 228:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.04.003
Gruber A, De Lannoy G, Albergel C et al (2020) Validation practices for satellite soil moisture retrievals: what are (the) errors? Remote Sens Environ 244:111806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111806
Hazra A (2017) Using the confidence interval confidently. J Thorac Dis 9:4124–4129. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2017.09.14
Jia Y, Jin S, Chen H et al (2021) Temporal-spatial soil moisture estimation from CYGNSS using machine learning regression with a preclassification approach. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 14:4879–4893. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3076470
Kerr YH, Waldteufel P, Wigneron J-P et al (2010) The SMOS mission: new tool for monitoring key elements of the global water cycle. Proc IEEE 98:666–687. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2010.2043032
Martin-Neira M, Caparrini M, Font-Rossello J et al (2001) The PARIS concept: an experimental demonstration of sea surface altimetry using GPS reflected signals. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.898676
Njoku EG, Entekhabi D (1996) Passive microwave remote sensing of soil moisture. J Hydrol 184:101–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02970-2
O'Neill PE, Chan S, Njoku EG, Jackson T, Bindlish R, Chaubell J (2021) L3 Radiometer Global Daily 36 km EASE-Grid Soil Moisture, Version 8. NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center, Boulder, Colorado USA. https://doi.org/10.5067/OMHVSRGFX38O
Peischl S, Walker JP, Rüdiger C et al (2012) The AACES field experiments: SMOS calibration and validation across the Murrumbidgee River catchment. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:1697–1708. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-1697-2012
Reichle RH, Draper CS, Liu Q et al (2017) Assessment of MERRA-2 land surface hydrology estimates. J Climate 30:2937–2960. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0720.1
Ruf CS, Gleason S, Jelenak Z et al (2012) The CYGNSS nanosatellite constellation hurricane mission. In: 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE, Munich, Germany, pp 214–216
Saeedi M, Sharafati A, Tavakol A (2021) Evaluation of gridded soil moisture products over varied land covers, climates, and soil textures using in situ measurements: a case study of Lake Urmia Basin. Theor Appl Climatol 145:1053–1074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03678-x
Stoffelen A (1998) Toward the true near-surface wind speed: error modeling and calibration using triple collocation. J Geophys Res 103:7755–7766. https://doi.org/10.1029/97JC03180
Vreugdenhil M, Greimeister-Pfeil I, Preimesberger W et al (2022) Microwave remote sensing for agricultural drought monitoring: recent developments and challenges. Front Water 4:1045451. https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2022.1045451
Wagner W, Dorigo W, de Jeu R et al (2012) Fusion of active and passive microwave observations to create an essential climate variable data record on soil moisture. ISPRS Ann Photogramm Remote Sens Spatial Inf Sci I–7:315–321. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsannals-I-7-315-2012
Wan W, Ji R, Liu B et al (2022) A two-step method to calibrate CYGNSS-derived land surface reflectivity for accurate soil moisture estimations. IEEE Geosci Remote Sensing Lett 19:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2020.3023650
Wang Y, Leng P, Peng J et al (2021) Global assessments of two blended microwave soil moisture products CCI and SMOPS with in-situ measurements and reanalysis data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 94:102234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2020.102234
Wu D, Gao T, Xue H (2016) The study of quality control for observing data of automatic soil moisture. Hans J Soil Sci 4:1–10 (in Chinese)
Yan Q, Huang W, Jin S, Jia Y (2020) Pan-tropical soil moisture mapping based on a three-layer model from CYGNSS GNSS-R data. Remote Sens Environ 247:111944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111944
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the CYGNSS team and other institutions for providing the data set used in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 42204014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, programming development, and analysis were performed by Zhounan Dong and Shuanggen Jin. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Zhounan Dong. Li Li and Peng Wang commented on and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z., Jin, S., Li, L. et al. Validation of CYGNSS soil moisture products using in situ measurements: a case study of Southern China. Theor Appl Climatol 153, 1085–1103 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04531-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04531-z