Abstract
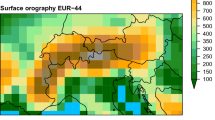
The 3-D complex topography effect on the surface solar radiative budget over the Tibetan Plateau is investigated by means of a parameterization approach on the basis of “exact” 3-D Monte Carlo photon tracing simulations, which use 90 m topography data as building blocks. Using a demonstrative grid size of 10 × 10 km2, we show that differences in downward surface solar fluxes for a clear sky without aerosols between the 3-D model and the conventional plane-parallel radiative transfer scheme are substantial, on the order of 200 W/m2 at shaded or sunward slopes. Deviations in the reflected fluxes of the direct solar beam amount to about +100 W/m2 over snow-covered areas, which would lead to an enhanced snowmelt if the 3-D topography effects had been accounted for in current climate models. We further demonstrate that the entire Tibetan Plateau would receive more solar flux by about 14 W/m2, if its 3-D mountain structure was included in the calculations, which would result in larger sensible and latent heat transfer from the surface to the atmosphere.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Hall A, Liou KN (2006) Application of 3D solar radiative transfer to mountains. J Geophys Res 111:D21111. doi:10.1029/2006JD007163
Dozier J, Frew J (1990) Rapid calculations of terrain parameters for radiation modeling from digital elevation data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 28:963–969. doi:10.1109/36.58986
Dubayah R, Rich P (1995) Topographic solar radiation models for GIS. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 9:405–419. doi:10.1080/02693799508902046
Dubayah R, Dozier J, Davis FW (1989) The distribution of clear-sky radiation over varying terrain. Proceedings IGARSS '89 vol. 2: 885–888, IEEE 89CH2768-0
Dubayah R, Dozier J, Davis FW (1990) Topographic distribution of clear-sky radiation over the Konza Prairie, Kansas. Water Resour Res 26:679–690. doi:10.1029/89WR03107
Essery R, Marks D (2007) Scaling and parameterization of clear-sky solar radiation over complex topography. J Geophys Res 112:D10122. doi:10.1029/2006JD007650
Fu Q, Liou KN (1992) On the correlated k-distribution method for radiative transfer in nonhomogeneous atmospheres. J Atmos Sci 49:2139–2156. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1992) 049<2139:OTCDMF>2.0.CO;2
Govaerts YM, Verstraete MM (1998) Raytran: a Monte Carlo ray tracing model to compute light scattering in three-dimensional heterogeneous media. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 36:493–505
Gu Y, Farrara J, Liou KN, Mechoso CR (2003) Parameterization of cloud-radiation processes in the UCLA general circulation model. J Climate 16:3357–3370. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003) 016<3357:POCPIT>2.0.CO;2
Gu Y, Liou KN, Xue Y, Mechoso CR, Li W, Luo Y (2006) Climatic effects of different aerosol types in China simulated by the UCLA atmospheric general circulation model. J Geophys Res 111:D15201. doi:10.1029/2005JD006312
Iwabuchi H, Kobayashi H (2008) Modeling of radiative transfer in cloudy atmospheres and plant canopies using Monte Carlo methods. FRCGC Technical Report 8: pp 199
Jarvis A, Reuter HI, Nelson A, Guevara E (2008) Hole-filled seamless SRTM data V4, International Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT), available from http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org
Lai Y-J, Chou M-D, Lin P-H (2010) Parameterization of topographic effect on surface solar radiation. J Geophys Res 115:D01104. doi:10.1029/2009JD012305
Lee W-L, Liou KN (2007) A coupled atmosphere–ocean radiative transfer system using the analytic four-stream approximation. J Atmos Sci 64:3681–3694
Lee W-L, Liou KN, Hall A (2011) Parameterization of solar fluxes over mountain surfaces for application to climate models. J Geophys Res 116:D01101. doi:10.1029/2010JD014722
Liou KN, Lee W-L, Hall A (2007) Radiative transfer in mountains: application to the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys Res Lett 34:L23809. doi:10.1029/2007GL031762
Mayer B, Hoch SW, Whiteman CD (2010) Validating the MYSTIC three-dimensional radiative transfer model with observations from the complex topography of Arizona’s Meteor Crater. Atmos Chem Phys 10:8685–8696
Molnar P, England P, Martinod J (1993) Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian monsoon. Rev Geophys 31:357–396
Preseindorfer RW, Mobley CD (1986) Albedos and glitter patterns of a wind-roughened sea surface. J Phys Oceanogr 16(7):1293–1316
Qiu J (2008) China: the third pole. Nature 454:393–396
Wang Q, Tenhunen J, Schmidt M, Otieno D, Kolcun O, Droesler M (2005) Diffuse PAR irradiance under clear skies in complex alpine terrain. Agric For Meteorol 128:1–15. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2004.09.004
Yang K, Pinker RT, Ma Y et al (2008) Evaluation of satellite estimates of downward shortwave radiation over the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res 113:D17204. doi:10.1029/2007JD009736
Acknowledgments
The research work presented in this paper was supported by the National Science Council, Taiwan under contracts NSC101-2111-M-001-001, NSC100-2119-M-001-029-MY5, and NSC98-2111-M-034-004-MY3, Academia Sinica, DOE Grant DE-SC0006742, and NSF Grant AGS-0946315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, WL., Liou, K.N. & Wang, Cc. Impact of 3-D topography on surface radiation budget over the Tibetan Plateau. Theor Appl Climatol 113, 95–103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0767-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0767-y