Abstract
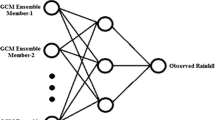
The ensemble method has long been used to reduce the errors that are caused by initial conditions and/or parameterizations of models in forecasting problems. In this study, neural network (NN) simulations are applied to ensemble weather forecasting. Temperature forecasts averaged over 2 weeks from four different forecasts are used to develop the NN model. Additionally, an ensemble mean of bias-corrected data is used as the control experiment. Overall, ensemble forecasts weighted by NN with feed forward backpropagation algorithm gave better root mean square error, mean absolute error, and same sign percent skills compared to those of the control experiment in most stations and produced more accurate weather forecasts.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buizza R, Miller M, Palmer TN (1999) Stochastic representation of model uncertainties in the ECMWF ensemble prediction system. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 125:2887–2908. doi:10.1002/qj.49712556006
Buizza R, Houtekamer PL, Toth Z, Pellerin G, Wei M, Zhu Y (2005) A comparison of the ECMWF, MSC and NCEP global ensemble prediction systems. Mon Weather Rev 133:1076–1097. doi:10.1175/MWR2905.1
Cybenko G (1989) Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Math Control Signals Syst 2(4):303–314. doi:10.1007/BF02551274
Drago GP, Ridella S (1992) Statistically controlled activation weight initialization (SCAWI). IEEE T Neural Netw 3:899–905. doi:10.1109/72.143378
Efe MÖ, Kaynak O (2000) Yapay sinir ağlari ve uygulamalari. Boğaziçi University Press, Istanbul
Guijaro-Berdiñas B, Fontenla-Romero O, Pérez-Sánchez B, Alonso-Betanzos, A (2006) A new initialization method for neural networks using sensitivity analysis. International Conference on Mathematical and Statistical Modeling, Spain, 28–30 June, 2006
Hagedorn R, Doblas-Reyes FJ, Palmer TN (2005) The rationale behind the success of multi-model ensembles in seasonal forecasting. Part I: basic concept. Tellus A 57(3):219–233. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2005.00103.x
Hastenrath S, Greischar L, Van Heerden J (1995) Prediction of the summer rainfall over South Africa. J Climate 8:1511–1518
Hornik KM, Stinchcombe M, White H (1989) Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw 2:359–366. doi:10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8
Kang IS, Shukla J (2006) Dynamical seasonal prediction and predictability of the monsoon. In: Wang B (ed) The Asian monsoon. Springer Praxis Books, Part 4, pp 585–612. doi:10.1007/3-540-37722-0_15
Kar SC, Hovsepyan A, Park CK (2006) Economic values of the APCN multi-model ensemble categorical seasonal predictions. Meteorol Appl 13:267–277. doi:10.1017/S1350482706002271
Krishnamurti TN, Kishtamal CM, LaRow TE, Bachiochi DR, Zhang Z, Williford CE, Gadgil S, Surendran S (1999) Improved weather and seasonal climate forecasts from multimodel Superensemble. Science 285:1548–1550. doi:10.1126/science.285.5433.1548
Krishnamurti TN, Kishtamal CM, Zhang Z, LaRow TE, Bachiochi DR, Williford CE (2000) Multimodel ensemble forecasts for weather and seasonal climate. J Climate 13:4196–4216. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2000) 013<4196:MEFFWA>2.0.CO; 2
Kulkarni MA, Patil S, Rama GV, Sen PN (2008) Wind speed prediction using statistical regression and neural network. J Earth Syst Sci 117(4):457–463
Lang S, Möhrlen C, Jørgensen J, Gallachóir BÓ, McKeogh E (2006) Application of a multi-scheme ensemble prediction system for wind power forecasting in Ireland and comparison with validation results from Denmark and Germany. European Wind Energy Conference EWEC, Athens, Greece, 27 February–2 March, 2006
Liu CM, Wu MC, Paul S, Chen YC, Lin SH, Lin WS, Lee YC, Hsu HH, Tseng RY, Chen CT (2011) Super-ensemble of three RCMs for climate projection over East Asia and Taiwan. Theor Appl Climatol 103:265–278. doi:10.1007/s00704-010-0275-x
Lorenz EN (1963) Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J Atmos Sci 20:130–141
Maqsood I, Abraham A (2006) Weather analysis using ensemble of connectionist learning paradigms. Appl Soft Comput 7:995–1004. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2006.06.005
Maqsood I, Khan MR, Abraham A (2004) An ensemble of neural networks for weather forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 13:112–122. doi:10.1007/s00521-004-0413-4
Möhrlen C, Jørgenseni JU, Pahlow M, Entekhabi D (2006) The probabilistic multi-trend filter: theoretical formulation and practical application. WEPROG (http://download.weprog.com/pmtfilter.pdf), Technical Document, June 2006
Molteni F, Buizza R, Palmer TN, Petroliagis T (1996) The ECMWF ensemble prediction system: methodology and validation. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 122:73–119. doi:10.1002/qj.49712252905
Navone HD, Ceccatto HA (1994) Predicting Indian monsoon rainfall—a neural network approach. Clim Dynam 10:305–312. doi:10.1007/BF00228029
Nguyen D, Widrow B (1990) Improving the learning speed of 2-layer neural networks by choosing initial values of the adaptive weights. Proc Int Joint Conf Neural Netw 3:21–26. doi:10.1109/IJCNN.1990.137819
Pei JS, Mai EC (2008) Constructing multilayer feedforward neural networks to approximate nonlinear functions in engineering mechanics applications. J Appl Mech 75(6):061002.1–061002.12. doi:10.1115/1.2957600
Pei JS, Mai E, Piyawat K (2006) Multilayer Feedforward Neural Network Initialization Methodology for Modeling Nonlinear Restoring Forces and Beyond. The 4th World Conference on Structural Control and Monitoring (4WCSCM), Paper No. 306. San Diego CA, July 11–13, 2006
Pellerin G, Lefaivre L, Houtekamer P, Girard C (2003) Increasing the horizontal resolution of ensemble forecasts at CMC. Nonlinear Proc Geoph 10:463–468. doi:10.5194/npg-10-463-2003
Peng K, Obradovic Z, Vucetic S (2004) Towards efficient learning of neural network ensembles from arbitrarily large datasets. 16th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), Valencia, Spain, pp 623–627
Reynolds CA, Ridout JA, McLay JG (2011) Examination of parameter variations in the U.S. Navy Global Ensemble. Tellus 63A:841–857
Sirdas S, Ross RS, Krishnamurti TN, Chakraborty A (2007) Evaluation of FSU synthetic superensemble performance for seasonal forecasts over the Euro-Mediterranean region. Tellus 59A:50–70
Srividya GP (1996) A novel neural network design for long range prediction of rainfall pattern. Curr Sci 70(6):447–457
Tangang FT, Hsieh WW, Tang B (1997) Forecasting the equatorial Pacific sea surface temperatures by neural network models. Clim Dynam 13:135–147. doi:10.1007/s003820050156
Tangang FT, Hsieh WW, Tang B (1998) Forecasting the regional sea surface temperature of the tropical Pacific by neural network models, with wind stress and sea level pressure as predictors. J Geophys Res 103:7511–7522. doi:10.1029/97JC03414
Toth Z, Kalnay E, Tracton SM, Wobus R, Irwin J (1997) A synoptic evaluation of the NCEP ensemble. Weather Forecast 12(1):140–153
Tracton MS, Kalnay E (1993) Operational ensemble forecasting prediction at the national meteorological center: practical aspects. Weather Forecast 8:379–398
Weigel AP, Liniger MA, Appenzeller C (2008) Can multi-model combination really enhance the prediction skill of probabilistic forecasts? Q J Roy Meteor Soc 134:241–260
Yun WT, Stefanova L, Krishnamurti TN (2003) Improvement of the multimodel Superensemble technique for seasonal forecasts. J Climate 22:3834–3840. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003) 016<3834:IOTMST>2.0.CO;2
Yun WT, Stefanova L, Mitra AK, Vijaya Kumar TSV, Dewar W, Krishnamurti TN (2005) A multi-model superensemble algorithm for seasonal climate prediction using DEMETER forecasts. Tellus A 57(3):280–289. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2005.00131.x
Yuval (2001) Enhancement and error estimation of neural network prediction of Nino -3.4 SST anomalies. J Climate 14:2150–2163
Zhang E, Trimble P (1996) Predicting effects of climate fluctuations for water management by applying neural network. World Resour Rev 8(3):1–18
Zhu Y (2005) Ensemble Forecast: a new approach to uncertainty and predictability. Adv Atmos Sci 22(6):781–788. doi:10.1007/BF02918678
Zurada JM (1992) Introduction to artificial neural systems. West Publishing, Saint Paul
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by The Science and Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK). The FSUGSM data and compiled NCEP Reanalysis were provided by Weather Predict Consulting Inc (www.weatherpredict.com). The authors would like to thank Zerefsan Kaymaz, Altug Aksoy, and Samuel Thomas Miller for their valuable review and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cakir, S., Kadioglu, M. & Cubukcu, N. Multischeme ensemble forecasting of surface temperature using neural network over Turkey. Theor Appl Climatol 111, 703–711 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0703-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0703-1