Summary
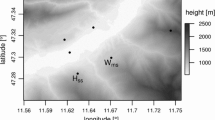
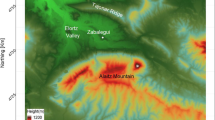
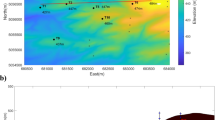
A method for the calculation of atmospheric turbulent diffusivity over complex terrain during day-time is presented, which may improve the predictions based on diagnostic meteorological models. The proposed procedure takes into account the geographic location of the area (latitude and longitude), the time of the day, the inclination and exposition of the surface, the soil type and the cloud cover. These data are used to compute the amount of solar heat flux contributing to the heating of the air mass above the ground level, and, consequently, the atmospheric turbulence. The model accounts for the effect of shadows generated by mountain profiles, which determine a differential heating at the valley floor and induce spatial and temporal variations of turbulent diffusivity. Model calibration has been performed through ground data collected during a field campaign in the Adige valley in the surrounding of the town of Trento.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonacci, G., Tubino, M. An estimate of day-time turbulent diffusivity over complex terrain from standard weather data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 80, 205–212 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-004-0100-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-004-0100-5