Abstract
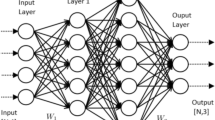
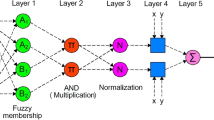
The use and importance of renewable energy sources (RES) have been increasing every passing year as fossil fuels will soon be depleted. Within this context, solar-photovoltaic (PV) is the most preferred energy type among RES. The PV has uncertain power output as its output depends on solar radiation, which is heavily influenced by environmental factors, so the prediction of solar radiation plays a crucial role in integrating these plants into the electricity grid. For the short-term 1-h-ahead solar radiation prediction, four time-series methods were implemented in this study: long short-term memory (LSTM) network, multilayer perceptron (MLP), and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) with grid partition (GP), and fuzzy c-means (FCM). Root mean square error (RMSE), correlation coefficient (R), and mean absolute error (MAE) were used as statistical error criteria. The obtained results by the LSTM, MLP, ANFIS-FCM and ANFIS-GP models were assessed by comparing with the actual data. Considering the testing procedure, the best MAE values were found to be 53.37 W/m2, 58.45 W/m2, 61.68 W/m2, and 78.17 W/m2 for the LSTM, ANFIS-FCM, MLP, and ANFIS-GP, respectively. Results showed that the LSTM model in 1-h-ahead solar radiation prediction yielded the best results among all four models with high accuracy.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdulkarim HT, Sansom CL, Patchigolla K, King P (2020) Statistical and economic analysis of solar radiation and climatic data for the development of solar PV system in Nigeria. Energy Rep 6:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2019.08.061
Abdulshahed AM, Longstaff AP, Fletcher S, Myers A (2015) Thermal error modelling of machine tools based on ANFIS with fuzzy c-means clustering using a thermal imaging camera. Appl Math Model 39:1837–1852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2014.10.016
Abonyi J, Andersen H, Nagy L, Szeifert F (1999) Inverse fuzzy-process-model based direct adaptive control. Math Comput Simul 51:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4754(99)00142-1
Adeleke O, Akinlabi S, Jen TC et al (2022) Evolutionary-based neuro-fuzzy modelling of combustion enthalpy of municipal solid waste. Neural Comput Appl 34:7419–7436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06870-2
Aguinaga A, Luo X, Hidalgo V et al (2017) A feed-forward backpropagation neural network method for remaining useful life prediction of Francis turbines. Proc World Congr Mech Chem Mater Eng. https://doi.org/10.11159/icmie17.126
Akhter MN, Mekhilef S, Mokhlis H, Shah NM (2019) Review on forecasting of photovoltaic power generation based on machine learning and metaheuristic techniques. IET Renew Power Gener 13:1009–1023. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2018.5649
Ali-Ou-Salah H, Oukarfi B, Bahani K, Moujabbir M (2021) A new hybrid model for hourly solar radiation forecasting using daily classification technique and machine learning algorithms. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6692626
Azizi A, Izadfar HR (2019) A novel ANFIS-based MPPT controller for two-switch flyback inverter in photovoltaic systems. J Renew Sustain Energy. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5082736
Bamisile O, Oluwasanmi A, Obiora S et al (2020) Application of deep learning for solar irradiance and solar photovoltaic multi-parameter forecast. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 00:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1801903
Benmouiza K, Cheknane A (2013) Forecasting hourly global solar radiation using hybrid k-means and nonlinear autoregressive neural network models. Energy Convers Manag 75:561–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.07.003
Benmouiza K, Cheknane A (2019) Clustered ANFIS network using fuzzy c-means, subtractive clustering, and grid partitioning for hourly solar radiation forecasting. Theor Appl Climatol 137:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2576-4
Benmouiza K, Tadj M, Cheknane A (2016) Classification of hourly solar radiation using fuzzy c-means algorithm for optimal stand-alone PV system sizing. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 82:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2016.03.019
Bezdek CJ (2003) Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms. PLENUM PRESS, NEW YORK
Bilgili M, Ozgoren M (2011) Daily total global solar radiation modeling from several meteorological data. Meteorol Atmos Phys 112:125–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-011-0137-9
Bilgili M, Yildirim A, Ozbek A et al (2021) Long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach in modeling renewable electricity generation forecasting. Int J Green Energy 18:578–594. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2020.1865375
Çakin E (2019) Analysis of the relationship between the personal characteristics and entrepreneurship potential with adaptive network based fuzzy inference system (anfis)
Chaudhuri S, Middey A (2011) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system to forecast peak gust speed during thunderstorms. Meteorol Atmos Phys 114:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-011-0158-4
Che Y, Chen L, Zheng J et al (2019) A novel hybrid model of WRF and clearness index-based kalman filter for day-ahead solar radiation forecasting. Appl Sci 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9193967
Chen JL, Li GS (2014) Evaluation of support vector machine for estimation of solar radiation from measured meteorological variables. Theor Appl Climatol 115:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-013-0924-y
Chen W, Li DH, Li S, Lam JC (2019) Estimating hourly global solar irradiance using artificial neural networks - A case study of Hong Kong. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/556/1/012043
Chen X, Huang J, Han Z et al (2020) The importance of short lag-time in the runoff forecasting model based on long short-term memory. J Hydrol 589:125359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125359
Dhakal S, Gautam Y, Bhattarai A (2020) Evaluation of temperature-based empirical models and machine learning techniques to estimate daily global solar radiation at biratnagar airport. Nepal Adv Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8895311
de Araujo JMS (2020) Performance comparison of solar radiation forecasting between WRF and LSTM in Gifu. Japan Environ Res Commun 2:045002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7620/ab7366
Dinçer F (2011) Türkiye’de Güneş Enerjisinden Elektrik Üretimi Potansiyeli - Ekonomik Analizi ve AB Ülkeleri ile Karşılaştırmalı Değerlendirme. Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam Univ J Eng Sci 14:8–17. https://doi.org/10.17780/KSUJES.10191
Dunn JC (1973) A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters. J Cybern 3:32–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/01969727308546046
Ghimire S, Deo RC, Raj N, Mi J (2019) Deep solar radiation forecasting with convolutional neural network and long short-term memory network algorithms. Appl Energy 253:113541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113541
Guermoui M, Melgani F, Gairaa K, Mekhalfi ML (2020) A comprehensive review of hybrid models for solar radiation forecasting. J Clean Prod 258:120357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120357
Huang J, Korolkiewicz M, Agrawal M, Boland J (2013) Forecasting solar radiation on an hourly time scale using a Coupled AutoRegressive and Dynamical System (CARDS) model. Sol Energy 87:136–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2012.10.012
Huynh ANL, Deo RC, An-Vo DA et al (2020) Near real-time global solar radiation forecasting at multiple time-step horizons using the long short-term memory network. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143517
IRENA (2021) Offshore renewables: An action agenda for deployment
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS: Adaptive-Network-Based Fuzzy Inference System. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23:665–685. https://doi.org/10.1109/21.256541
Jiménez-Pérez PF, Mora-López L (2016) Modeling and forecasting hourly global solar radiation using clustering and classification techniques. Sol Energy 135:682–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.06.039
Kim S, Seo Y, Rezaie-Balf M et al (2019) Evaluation of daily solar radiation flux using soft computing approaches based on different meteorological information: peninsula vs continent. Theor Appl Climatol 137:693–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2627-x
Kumari P, Toshniwal D (2021) Long short term memory–convolutional neural network based deep hybrid approach for solar irradiance forecasting. Appl Energy 295:117061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117061
Li X, Peng L, Yao X et al (2017) Long short-term memory neural network for air pollutant concentration predictions: Method development and evaluation. Environ Pollut 231:997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.114
Li C, Zhang Y, Zhao G, Ren Y (2021) Hourly solar irradiance prediction using deep BiLSTM network. Earth Sci Informatics 14:299–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00511-3
Linares-Rodriguez A, Ruiz-Arias JA, Pozo-Vazquez D, Tovar-Pescador J (2013) An artificial neural network ensemble model for estimating global solar radiation from Meteosat satellite images. Energy 61:636–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.09.008
Liu H, He B, Qin P et al (2021) Sea level anomaly intelligent inversion model based on LSTM-RBF network. Meteorol Atmos Phys 133:245–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-020-00745-2
Ma X, Tao Z, Wang Y et al (2015) Long short-term memory neural network for traffic speed prediction using remote microwave sensor data. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 54:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2015.03.014
Mirbolouki A, Heddam S, Singh Parmar K et al (2022) Comparison of the advanced machine learning methods for better prediction accuracy of solar radiation using only temperature data: A case study. Int J Energy Res 46:2709–2736. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7341
Moghaddamnia A, Remesan R, Kashani MH et al (2009) Comparison of LLR, MLP, Elman, NNARX and ANFIS Models-with a case study in solar radiation estimation. J Atmos Solar-Terrestrial Phys 71:975–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2009.04.009
Mohammadi K, Shamshirband S, Kamsin A et al (2016) Identifying the most significant input parameters for predicting global solar radiation using an ANFIS selection procedure. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 63:423–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.05.065
Naderloo L (2020) Prediction of solar radiation on the horizon using neural network methods, ANFIS and RSM (case study: Sarpol-e-Zahab Township, Iran). J Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-01414-z
Obiora CN, Ali A, Hasan AN (2020) Forecasting Hourly Solar Irradiance Using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Network. 11th Int Renew Energy Congr IREC 2020. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/IREC48820.2020.9310449
Ozgoren M, Bilgili M, Sahin B (2012) Estimation of global solar radiation using ANN over Turkey. Expert Syst Appl 39:5043–5051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.11.036
Pandey CK, Katiyar AK (2013) Solar Radiation: Models and Measurement Techniques. J Energy 2013:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/305207
Park I, Kim HS, Lee J et al (2019) Temperature prediction using the missing data refinement model based on a long short-term memory neural network. Atmosphere (basel) 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110718
Piri J, Kisi O (2015) Modelling solar radiation reached to the Earth using ANFIS, NN-ARX, and empirical models (Case studies: Zahedan and Bojnurd stations). J Atmos Solar-Terrestrial Phys 123:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2014.12.006
Qing X, Niu Y (2018) Hourly day-ahead solar irradiance prediction using weather forecasts by LSTM. Energy 148:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.177
Şenocak F (2018) Forecasting of weighted average electricity market clearing price using artificial neural networks and anfis. Karadeniz Teknik Üniversitesi
Shamim MA, Bray M, Remesan R, Han D (2015) A hybrid modelling approach for assessing solar radiation. Theor Appl Climatol 122:403–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-014-1301-1
Sharifi SS, Rezaverdinejad V, Nourani V, Behmanesh J (2022) Multi-time-step ahead daily global solar radiation forecasting: performance evaluation of wavelet-based artificial neural network model. Meteorol Atmos Phys 134:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00882-w
Sorkun MC, Durmaz Incel Ö, Paoli C (2020) Time series forecasting on multivariate solar radiation data using deep learning (LSTM). Turkish J Electr Eng Comput Sci 28:211–223. https://doi.org/10.3906/elk-1907-218
Sözen A, Arcaklioglu E, Özalp M (2004) Estimation of solar potential in Turkey by artificial neural networks using meteorological and geographical data. Energy Convers Manag 45:3033–3052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2003.12.020
Sthitapragyan M, Patra PK, Sahoo SS (2015) Comparison and prediction of monthly average solar radiation data using soft computing approach for eastern India. Comput Intell Data Min. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2202-6_28
Suyono H, Hasanah RN, Setyawan RA et al (2018) Comparison of solar radiation intensity forecasting using ANFIS and multiple linear regression methods. Bull Electr Eng Informatics 7:191–198. https://doi.org/10.11591/eei.v7i2.1178
Tao H, Ewees AA, Al-Sulttani AO et al (2021) Global solar radiation prediction over North Dakota using air temperature: Development of novel hybrid intelligence model. Energy Rep 7:136–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.11.033
Temur A (2019) Comparison of ARIMA, LSTM and Hybrid Models in Establishing Sales Budgets: A Case of Production Facility. Sakarya University
Turan E (2018) Calculation of Surface Leakage Current by ANFIS in High Voltage Insulator
Wang L, Kisi O, Zounemat-Kermani M et al (2017) Prediction of solar radiation in China using different adaptive neuro-fuzzy methods and M5 model tree. Int J Climatol 37:1141–1155. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4762
Wu Y, Wang J (2016) A novel hybrid model based on artificial neural networks for solar radiation prediction. Renew Energy 89:268–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.11.070
Xiao Y, Yin Y (2019) Hybrid LSTM neural network for short-term traffic flow prediction. Inf. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10030105
Yin J, Deng Z, Ines AVM et al (2020) Forecast of short-term daily reference evapotranspiration under limited meteorological variables using a hybrid bi-directional long short-term memory model (Bi-LSTM). Agric Water Manag 242:106386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106386
Zhang CJ, Wang HY, Zeng J et al (2020) Tiny-RainNet: a deep convolutional neural network with bi-directional long short-term memory model for short-term rainfall prediction. Meteorol Appl 27:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1956
Zhou Y, Liu Y, Wang D et al (2021) A review on global solar radiation prediction with machine learning models in a comprehensive perspective. Energy Convers Manag 235:113960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2021.113960
Acknowledgements
We had like to thank Pilye Energy Cons. Ind. and Trading Co., generously allowed us to use solar radiation data in our study.
Funding
No funds, grants or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interest to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Clemens Simmer, Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yildirim, A., Bilgili, M. & Ozbek, A. One-hour-ahead solar radiation forecasting by MLP, LSTM, and ANFIS approaches. Meteorol Atmos Phys 135, 10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00946-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00946-x